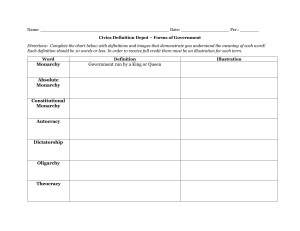
GOVERNMENT Types of Governments Page #: 50 Date: 11/20 EQ: What is government? What does it do? Why do we need it? GOVERNMENT 1. What is government? 2. What does a government do? 3. Why do people need government? 4. Who has authority or power in a government? What is power? 5. What types of government are there? GOVERNMENT 1.What is government? GOVERNMENT 1. What is government? • • • Government is an organization people set up to protect the community and make rules There is a leader or leaders in charge There are rules or laws to follow GOVERNMENT 2. What does a government do? GOVERNMENT 2. What does a government do? Protects the community Makes laws Keeps or maintains order/peace Collects taxes to take care of things (roads, public buildings, postal service, military, schools) GOVERNMENT 3. Why do people need government? GOVERNMENT 3. Why do people need government? For protection of people and property Making rules- to maintain order Enforcing laws- to ensure safety To have someone in charge of schools, roads, military, etc. Without it= chaos, disorder, unsafe GOVERNMENT 4. Who has authority or power in a government? What is power? GOVERNMENT 4. Who has authority or power in a government? What is power? The leader (king, president, emperor) The leader’s “people” (assistants, noblemen, aristocrats…) The citizens (by voting) Power is….. GOVERNMENT 5. What types of government are there? GOVERNMENT 5. What types of government are there? Common types are: Monarchy Oligarchy Tyranny/Dictatorship Democracy/Republic Theocracy Monarchy Power is in the hands of a king, queen, emperor or empress. Royal Family The ruling position can be passed on to the ruler’s children. In some traditional monarchies, the monarch has absolute power (judges, leading army, making laws) But a constitutional monarchy, like the UK, also has a democratic government that limits the monarch's control. Aristocrats or noblemen (the king’s “people”) can help make decisions if he wants them to. Oligarchy Oligarchy means “rule by a few” A government in which a few people have power (political group, one social class, or one race – Often times they are wealthy $$$) The Oligarchs care only about themselves. The make decisions to benefit their group and many times are described as “making the rich richer and the poor poorer”. Tyranny/Dictatorship A country ruled by a single leader known as a Tyrant or Dictator. The leader has NOT been elected and may use force to take and keep control. The tyrant or dictator has all the power over citizens’ lives and citizens have no choices. Some tyrants made their supporters happy and helped the poor. They did this so they were not overthrown. Others were not so kind. Theocracy A form of government in which God (or the gods) is the supreme ruler The leader is thought to serve through his “divine right” and represent God on Earth The laws often come from the Holy Books/texts that the religion of the culture follows Examples: The Pope in the Vatican City/Roman Catholic Church Saudi Arabia is an Islamic Theocracy Democracy In a democracy, the government is elected by the people. Everyone who is eligible to vote has a chance to have their say over who runs the country. It is different from governments controlled by a particular social class or group A democracy is determined either directly or through elected representatives. Direct Democracy People vote directly on every issue Only practical in a small community This was the type of Democracy Athens started Representative Democracy People are represented by elected officials They vote for the person they think has similar opinions or views as themselves. Used in large countries (Like the USA) Citizens have power and choices VERY similar to a Republic government Republic A republic is a country with elected representatives and an elected head of state who is not a monarch. The head of the country is usually an elected president. Citizens can vote and have power. This is very similar to a Representative Democracy Rome’s Republic Roman citizens were divided into 3 classes: Patricians, Plebeians, and Slaves The plebeians were the lower class & the patricians were the wealthy upper class. The Plebeians (poor) started a war to demand their rights! We will talk more about this when we study Rome. Other Governments There are many other types of governments that we will not study this year. Some common ones we will not cover are: Theocracy- priests rule in the name of God who is the ultimate authority, religious law Anarchy- NO government, disorder, usually after a government fails before another one begins Communism- the state or country owns and operates everything on behalf of the people. People have no control. 1. NAME THAT GOVERNMENT: The pharaoh was an absolute ruler. He commanded the army and controlled irrigation and grain supplies. People in this society considered the pharaoh to be a god. 1. NAME THAT GOVERNMENT: The pharaoh was an absolute ruler. He commanded the army and controlled irrigation and grain supplies. People in this society considered the pharaoh to be a god. Monarchy 2. NAME THAT GOVERNMENT In the first century AD, the Greeks recognized three types of government: monarchy, aristocracy, and anarchy. The Jews at the time did not fit into any of these categories as they believed only God and his laws were sovereign. 2. NAME THAT GOVERNMENT In the first century AD, the Greeks recognized three types of government: monarchy, aristocracy, and anarchy. The Jews at the time did not fit into any of these categories as they believed only God and his laws were sovereign. Theocracy 3. NAME THAT GOVERNMENT: In 450 B.C. this civilization assembled and all citizens voted on laws. A council of 500 prepared business for the assembly. 3. NAME THAT GOVERNMENT: In 450 B.C. this civilization assembled and all citizens voted on laws. A council of 500 prepared business for the assembly. Direct Democracy 4. NAME THAT GOVERNMENT: The Nazi Party took over every aspect of this country’s social, economic & political life. Hitler quickly secured his power by burning down a legislative building and used the incident to obtain emergency powers, becoming an absolute ruler. 4. NAME THAT GOVERNMENT: The Nazi Party took over every aspect of this country’s social, economic & political life. Hitler quickly secured his power by burning down a legislative building and used the incident to obtain emergency powers, becoming an absolute ruler. Dictatorship 5. NAME THAT GOVERNMENT: In this country some people are elected to make laws and some people are appointed officials. 5. NAME THAT GOVERNMENT: In this country some people are elected to make laws and some people are appointed officials. Representative Democracy