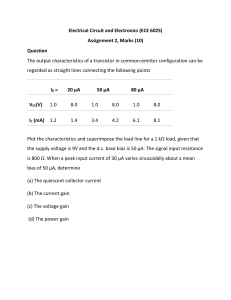
Module 1 DC Biasing of BJT Circuits Dr SATHYA P Associate Professor SENSE Introduction • A transistor must be dc biased in order to operate as an amplifier. • The term biasing refers to the application of dc voltages to establish a fixed level of current and voltages in a circuit. • The resulting dc voltage and current establish an operating point on the characteristic curve that defines the region employed for amplification of input signal. • Q point is also called as quiescent point. Operating point Types of Biasing • Fixed bias method • Collector to base bias method • Emitter stabilized bias • Voltage divider bias • Constant current bias Fixed bias/ Base bias method Emitter Stabilized Bias Collector to Base Bias Voltage Divider Bias Self bias/VDB IE = I B + I C Collector–Emitter Loop: Load Line points • The output load line equation is given by • Put IC = 0, VCE (max) = VCC • Put VCE = 0, IC (max) = VCC / (RC + RE) • X axis points: (VCE(max), 0) • Y axis points: (0, IC(max)) • Numerical 1: Determine the collector-emitter voltage in the voltage divider bias circuit shown and plot the Q point. Assume β = 100.