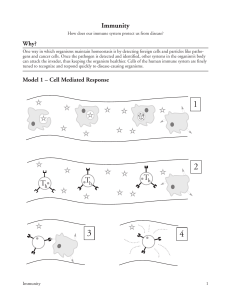
Diseases and Immunity Part 2 Background • Focusing on transmissible diseases (can be passed on from one host to another) • This type of diseases are caused by pathogens • Pathogen: disease-causing organism (bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa/protist) • Transmissible disease: disease in which the pathogen can be passed on from one host to another Transmission DIRECT Involve transfer through blood and other body fluids i.e. HIV and Malaria INDIRECT Involve infection from pathogen on contaminated surfaces i.e Salmonella food poisoning, contaminated water, waste disposal, contamination by houseflies, Tinea (‘ringworm’) a fungal parasite, Amoebic dysentery, Airborne, ‘droplet’ or aerosol infection. Defences against diseases MECHANICAL BARRIERS *skin *hairs in the nose *ciliated cells in the trachea First line of defence Non-specific CHEMICAL BARRIERS *Acid in stomach *Moist lining of nasal passages & mucus produced by the lining of the trachea & bronchi Defences against diseases IMMUNE CELLS When pathogen passes the first defence *Phagocytes – phagocytosis *Lymphocytes – antibody and anti-toxin production Second line of defence Specific VACCINATION To enhance the body’s defences *Involves harmless form of the pathogen being introduced into the body by injection or swallowing Lymphocytes B-CELLS Different functions but inter dependent T-CELLS ‘Helper’ T-cells ‘Killer’ T-cells From bone marrow From the Thymus gland *become short-lived plasma cells & produce antibodies that are released into blood *some B cells remain in the lymph nodes as memory cells *have receptor molecules on their surface, which attach them to antibodies *T cells kill the infected cells/pathogen *Helper T-cells stimulate B-cells to divide and produce antibodies Antibodies & Immunity • Lock on to antigens leading to direct destruction of pathogen or marking of pathogens for destruction by phagocytes • Each pathogen has its own antigens, which have specific shapes.