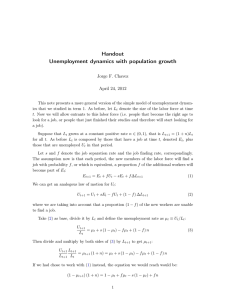
MONTHLY TEST ­ SEPTEMBER 2020 ECONOMICS 10 (Cambridge) ......... Duration : 2 periods Instructions to Candidates : Candidate's name : Answer all the questions. ............................................................... Admission no : ................... 1 Part ­ I Mark the correct answer on the separate answer sheet. (1) A government spreads its officers throughout the country even though it is expensive. Which type of unemployment is this policy most likely to reduce? A cyclical B frictional C regional D seasonal (2) Which policy would be most likely to reduce unemployement in the short run? A a programme of privatisation. B a reduction in the standard rate of income tax. C grants to firms to research new technology. D removal of all restrictions on imports into the country. (3) What could discourage women from seeking employment? A More education and training are provided. B More flexible and part­time jobs are available. C There are fewer promotion opportunities for women. D There is a shift in employment to the services sector. (4) What is an example of someone who lost their job because of structural unemployment? A Aneesha lost her job as an engineer when her firm had to make redundancies in a recession. B Jamie lost his job as an ice cream seller during the winter months when little ice cream was sold. C Sunjeev decided to stop working and claim benefits when the government increased unemployment benefits. D Sunjit lost his job as a bank worker when the bank replaced his job with a new computer system. contd.....to page 2 2 Grade 10 Economics contd.....from page 1 (5) The diagram shows the rate of unemployment and the periods of recession in a country between 1978 and 2012. unemployment rate % 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 key 1980 1990 2000 recession years 2010 What can be concluded from the diagram? A Each recession lasted for more than two years. B Recessions occurred at regular intervals. C The unemployment rate peaked in a recession period. D The unemployment rate rose during recession periods. (6) What could affect the size of the labour force in an economy? A the existence of a trade union. B the government's immigration policy. C the quality of university graduates. D the ration of male to female employees. (7) A government aims to reduce unemployment through a supply­side policy measure. Which measure would it use? A It would increase government spending. B It would increase tariffs on imported goods and services. C It would introduce retraining schemes. D It would reduce the rate of interest. (8) What is most likely to decreases when employment increases? A economic growth. B government welfare payments. C the price level. D the standard of living. contd.....to page 3 3 Grade 10 Economics contd.....from page 2 (9) Information about job vacancies on government website has led to a decrease in short­term unemployment. What is the term for this type of unemployment? A cyclical unemployment B frictional unemployment C Structural unemployment D technological unemployment (10) As a result of a decrease in the demand for coal, several coal mines were closed. What type of unemployment would this cause? A cyclical B frictional C seasonal D structural (11) The table provides information about a country's labour market. population size labour force size number of employed number of full­time students 2 000 000 1 200 000 900 000 100 000 What is the unemployment rate of this country? A 15% B 25% C 50% D 75% (12) Which type of unemployment is likely to lead to the most serious regional problems in a country? A cyclical B frictional C residual D structural (13) What is likely to lead to a decrease in structural unemployment? A reducing the interest rate B increasing the rate of unemployment C reducing the rate of income tax D increasing labour mobility (14) What is the most likely reason for a company to employ more workers? A increased demand for its product B increased taxes on the product C investment in labour­saving machinery D wage rises in the company contd.....to page 4 4 Grade 10 Economics contd.....from page 3 (15) Which type of unemployment is directly caused by a general lack of demand? A cyclical B frictional C seasonal D structural (16) Which combination of government policies is most likely to reduce unemployment? A B C D income tax rate government spending decrease decrease decrease increase increase decrease increase increase rate of interest increase decrease decrease increase (17) As a result of two months of bad weather, the demand for hotel rooms decreases and staff are not required. What type of unemployment is this A cyclical B frictional C seasonal D structural (18) Official statistics in 2010 showed South Africa had a very high unemployment rate at around 25%, although wages were double those in Brazil. What might be a reason for South Africa's high wages in a time of high unemployment compared with Brazil? A a skilled workforce in Brazil. B high levels of savings in South Africa. C more labour­intensive production in Brazil. D strong trade union in South Africa. (19) What is most likely to happen as unemployment falls? A Economic growth falls B C Spending on welfare benefits rises. D Inflation falls. Tax revenue rises. (20) The following extract appeared in an international newspaper. China's unemployed peasants flock to cities Hundreds of thousands of peasants, fleeing rural poverty and drudgery, have flocked into China's cities seeking work. What would be the most likely result for the Chinese economy? A a reduction in productivity. B a rise in unemployment in the city areas. C a rise in the amount of unemployment in rural areas. D a rise in the proportion of skilled labour in cities. [Total = 20 marks] contd.....to page 5 5 Grade 10 Economics contd.....from page 4 PART – II Answer all the questions. (1) (a) Define the term ‘full employment’. (b) Analyse why the pattern of employment in a country may change over time. (c) Discuss whether unemployment always harms an economy. (2) (a) Explain what is meant by an unemployment rate of 24%. (b) Explain two consequences to firms of unemployment. (2 marks) (6 marks) (8 marks) [Total = 16 marks] (2 marks) (4 marks) (c) Discuss whether or not an increase in government spending will reduce unemployment. (8 marks) [Total = 14 marks] END Ref : CT