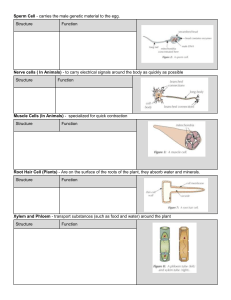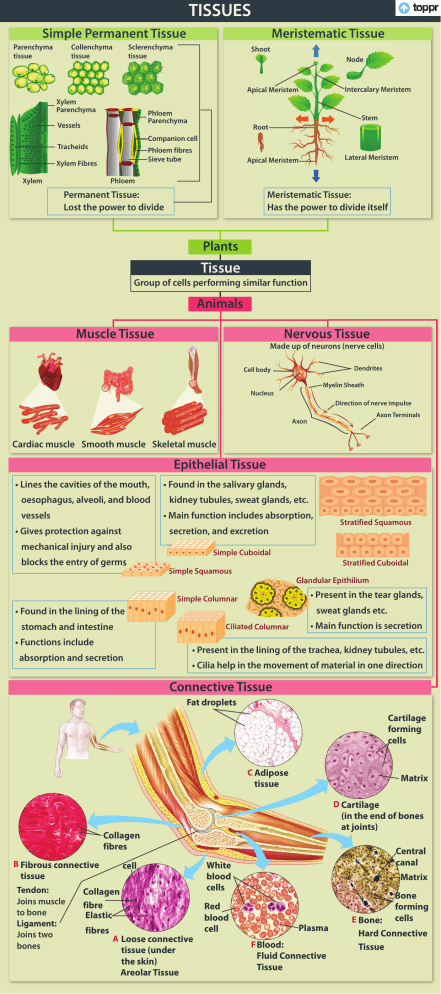
TISSUES Materials- Metals &Non-metals Simple Permanent Tissue Parenchyma tissue Collenchyma tissue Meristematic Tissue Sclerenchyma tissue Shoot Node Intercalary Meristem Apical Meristem Xylem Parenchyma Phloem Parenchyma Vessels Stem Root Companion cell Tracheids Phloem fibres Sieve tube Xylem Fibres Xylem Lateral Meristem Apical Meristem Phloem Permanent Tissue: Lost the power to divide Meristematic Tissue: Has the power to divide itself Plants Tissue Group of cells performing similar function Animals Nervous Tissue Muscle Tissue Made up of neurons (nerve cells) Dendrites Cell body Myelin Sheath Nucleus Direction of nerve impulse Axon Terminals Axon Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle Skeletal muscle Epithelial Tissue • Lines the cavities of the mouth, oesophagus, alveoli, and blood • Found in the salivary glands, kidney tubules, sweat glands, etc. • Main function includes absorption, vessels Stratified Squamous secretion, and excretion • Gives protection against mechanical injury and also blocks the entry of germs Simple Cuboidal Stratified Cuboidal Simple Squamous Glandular Epithilium • Present in the tear glands, Simple Columnar sweat glands etc. • Found in the lining of the stomach and intestine Ciliated Columnar • Functions include • Main function is secretion • Present in the lining of the trachea, kidney tubules, etc. absorption and secretion • Cilia help in the movement of material in one direction Connective Tissue Fat droplets Cartilage forming cells C Adipose Matrix tissue D Cartilage (in the end of bones at joints) Collagen fibres B Fibrous connective cell tissue Tendon: Joins muscle to bone Ligament: Joins two bones Collagen fibre Elastic fibres A Loose connective tissue (under the skin) Areolar Tissue Central canal White blood cells Matrix Red blood cell Plasma F Blood: Fluid Connective Tissue E Bone: Bone forming cells Hard Connective Tissue