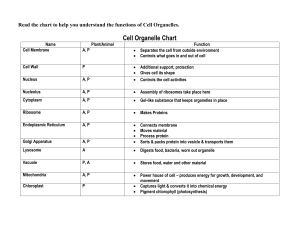
Labels to use: Cell wall Centrioles Chloroplast Chromatids (chromosomes) Cytoplasm Endoplasmic reticulum (rough) Endoplasmic reticulum (smooth) Golgi body Lysosome Mitochondrion Nuclear envelope/membrane Nucleolus Nucleus Peroxisome Plasma membrane Ribosomes Tonoplast membrane Vacuole A double membrane composed of lipids and proteins. Present both in plant and animal cells. Provides shape, protects the inner organelles of the cell and acts as a selectively permeable membrane. Present only in plant cells and contains a greencoloured pigment known as chlorophyll. Surrounded by a double membrane, contains grana and stroma. It is the site of photosynthesis. It plays a major role in spindle formation in cell division. Structures are present in pairs. Found only in animal cells A small spherical region within the nucleoplasm. It manufactures rRNA and assembles the ribosomes. A network of membranous 3D tubules, present within the cytoplasm of a cell and continuous with the nuclear membrane. Forms the skeletal framework of the cell, involved in the synthesising, storing and transporting of lipids and carbohydrates. A network of membranous 3D tubules, present within the cytoplasm of a cell and continuous with the nuclear membrane. Contains ribosomes on the surface. Provide a large surface area for the synthesis of proteins and glycoproteins. Membrane-bound, sac-like organelles made of flattened sacs called cisternae, present within the cytoplasm of the eukaryotic cells. It is mainly involved in the modification and secretion of proteins and lipids. Forms lysosomes. An oval-shaped, double membrane-bound organelle, also called as the “Powerhouse of The Cell”. The inner membrane folds into cristae and the space in between is the matrix. It is the main site of cellular aerobic respiration and also involved in storing energy in the form of ATP molecules. Non-membrane organelles, found floating freely in the cell’s cytoplasm or embedded within the endoplasmic reticulum. Contains two subunits and are either 80S or 70S. Involved in the synthesis of proteins. A jelly-like substance, which consists of water, dissolved nutrients and waste products of the cell. Responsible for the cell’s metabolic activities. Rigid, tough structure found only in plants. Made of cellulose forming a matrix. The middle lamella joins cells and allows cell communication. It provides mechanical strength to individual cells and the plant itself, and allows water movement. The largest, double membrane-bound organelles, which contains all the cell’s genetic information. Surrounded by the nuclear membrane containing nuclear pores. Controls the activity of the cell, helps in cell division and controls the hereditary characters. A membrane-bound (tonoplast membrane), fluidfilled organelle found within the cytoplasm. Provides shape and rigidity to the plant cell and may act as a temporary food store. A membrane-bound cellular organelle present in the cytoplasm, which contains a reducing enzyme. Involved in the catabolism of long-chain fatty acids and hydrogen peroxide. A tiny, circular-shaped, single membrane-bound organelles, filled with digestive enzymes known as lysozymes. Helps in the removal of wastes and digests dead and damaged organelles and cells (autolysis).