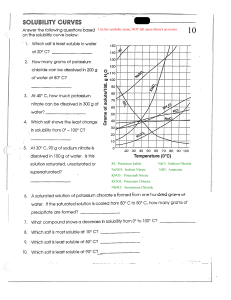
LET’S RECAP Carbon + nitrogen Pure element Diamonds Made up from element carbon Carbon + boron Made up of water and various salt Seawater Carbon + nickel Every one of its atom is exactly the same Memory game: Purity 8-carat 14-carat SCIENCE FRESHMEN TOPIC 5 MATERIALS AND CYCLES ON EARTH 5.2 PURITY @auntydhia OBJECTIVES 1. Students are able to explain what is meant by purity. 2. Students are able to calculate percentage of purity. 3. Students are able to describe how it is difficult to get a pure product. NOTES PURE ELEMENTS Pure element - 8 carat Its an alloy Slightly coppery 8 out of 24 parts are gold - The rest made up of other metals such as silver or copper - All the atoms inside is exactly the same 14 carat Its an alloy Rose gold 14 out of 24 parts are gold - The rest made up of other metals such as silver or copper - 18 carat Its an alloy Bright yellow gold 18 out of 24 parts are gold - The rest made up of other metals such as silver or copper - 24 carat Pure gold bar Yellow gold 24 out of 24 parts are gold - 999 stands for 99.9% gold PURITY CALCULATION Calculate the purity of gold in 18-carat gold jewellery. Calculate the purity of 925 silver. 𝟏𝟖 x 100 = 75% 𝟐𝟒 𝟗𝟐𝟓 x 100 = 92.5% 𝟏𝟎𝟎𝟎 Thus, 18-carat gold has a purity of 75% pure gold Thus, 925 silver is 92.5% pure silver DIAMONDS - Made from the element carbon - Carbon atoms arranged in a particular way - Colourless and translucent (lets the light pass through) Carbon atoms + Nitrogen Carbon atoms + Boron - Very rare - One atom per 1000 carbon atoms is replaced by nitrogen, nickel or hydrogen. SEAWATER Mass of sodium chloride in 1000g of seawater 𝟔𝟖 = x 35 𝟏𝟎𝟎 = 23.8g Made up of water and various salt such as sodium chloride Obtain sodium chloride from water by evaporate off the water Letting sea water fill flat and shallow areas called bed. Allowing the water to evaporate in the heat form the sun 1000g seawater = 35g salt (3.5%) - 68% sodium chloride - The rest made up of magnesium chloride, sodium sulfate, calcium chloride and others salt. PURE PRODUCTS Important to obtain a pure product In the medical field, impurities in the product could stop the medicine from working or could harm the patient. Magnesium + oxygen Silver nitrate + sodium chloride Barium chloride + sodium sulfate Copper carbonate + hydrochloric acid magnesium oxide sodium nitrate + silver chloride barium sulfate + sodium chloride copper chloride + water + carbon dioxide When more than one product, they are mixed up together They may also be mixed with some of the unused reactants Need to be separated and purified to gain pure product ACTIVITY Think like a scientist Procedure: 1. Half fill a test tube with silver nitrate solution. 2. Slowly add some sodium chloride solution. 3. When sodium chloride is added to silver nitrate, a white precipitate, silver chloride forms. Safety: 1. Silver nitrate is an irritant. Take care when you use it. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xR_VZXOz64A Think like a scientist https://www. youtube.com/ watch?v=2h0 1ovEzBTw Think like a scientist https://www. youtube.com/ watch?v=uaB HB5GSgHU Think like a scientist https://w ww.youtu be.com/w atch?v=di W7q7RFJ BM Think like a scientist https://www.yo utube.com/watc h?v=pCDAXJyr ABw EXERCISES All the atoms inside are exactly the same and made of just one type of atom. carbon atoms elements boron yellow rarest nickel The advice that the assistant gave to the customer is based on science because of the fact that an alloy that is made by mixing different metals together will be increasing the hardness of the alloy. But the assistant also needs to mention that if the percentage of gold is too small, the gold alloy is brittle. When the percentage of gold decreases by adding up other metals to make an alloy, the hardness of the gold is increasing. But when the percentage of gold is below 75%, the hardness of the gold alloy decreases. 9-carat gold is both less ductile and less malleable than 18-carat, it is more likely to become brittle and crack over years of wear and tear. 18-carat gold is more resistant to tarnish and corrosion.