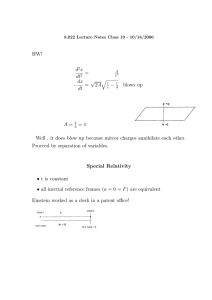
Systems Review Questions C-40 USAF 18 August 2022 Revision 1.0 First slide Log Out Flight compartment Home Return to previous slide Back one slide Forward one slide Return to Last Slide Filename.2 Show questions and answers Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click for Text Click an area for Systems Review Click a panel for questions Bleed Air Air Conditioning Choose a system to review 700 Bleed air use ** Slide 2 Which systems rely on bleed air for operation? • Air conditioning/ pressurization • Engine starting • Hydraulic reservoirs • Water tank pressure • Aspirated TAT Probe • Wing and engine thermal anti-icing • AUX fuel system • NGS system Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 Bleed elect The engine bleed air valve is ____ activated and _______ operated? • DC (electrically) • Pressure Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 Bleed elect Engine bleed air is obtained from which stages of the compressor section? • 5th and 9th. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 Bleed elect During takeoff, climb, and most cruise conditions, what is the position of the high stage valve? • Closed. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 Iso What is the purpose of the isolation valve? • To isolate the left and right sides of the bleed air duct during normal operations. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 AC power What is the power source for the isolation valve? • AC power. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 Iso position What is the normal position of the isolation valve in flight? • Closed. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 iso open Is the isolation valve in the OPEN or CLOSE position in this scenario? • OPEN. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 iso open What switches cause the isolation valve to open in the AUTO position? • Either engine bleed air switch or air conditioning pack switch is positioned OFF. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 Bleed Trip What causes this light to illuminate? • Engine bleed air temperature or bleed air pressure exceeds limits. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 Bleed trip 2 In the event of a bleed trip, would the isolation valve open? • No. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 Dual bld What caused the DUAL BLEED light to illuminate in this scenario? • The Number 1 ENGINE BLEED switch ON and APU BLEED valve OPEN. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 Dual bld 2 What caused the DUAL BLEED light to illuminate in this scenario? • The APU BLEED valve OPEN. • Number 2 ENGINE BLEED switch ON. • ISOLATION VALVE OPEN. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 Dual bld gnd air With ground air connected and the APU bleed valve open, will the DUAL BLEED light illuminate? • Even though there is a possibility of back pressuring the APU, the DUAL BLEED light will NOT illuminate. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 Dual bld 2 Just before taxi, you accomplish a recall and discover that the dual bleed light is still illuminated. What is the problem? • The APU Bleed Air Valve did not close. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 APU bleed Will the APU bleed valve open if the APU is not running? • No. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 APU power The APU bleed air valve is ____ activated and _______ operated? • DC (electrically). • Pressure. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 deflector door What is the purpose of the ram air deflector door? • Prevent slush ingestion prior to liftoff and after touchdown. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 deflector door When is the ram air deflector door open (extended)? • On the ground only. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 pack power The Pack valve is ____ activated and _______ operated? • DC (electrically). • Pressure. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 Bleed elect When should the RAM DOOR FULL OPEN lights extinguish? • In flight, flaps up. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 single pack True or False. A single pack is capable of maintaining pressurization and acceptable temperatures throughout the airplane up to the maximum certified ceiling. • True. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 single pack While the airplane is electrically powered, packs should be run or cooling air supplied when the OAT exceeds _____ (C/F). • 40C/103F. (L.10 and FCOM) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 high flow On the ground, what switch positions will activate the APU high air flow mode? • APU Bleed switch ON with APU running. • Pack switch HIGH. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 Pack Trip What causes this light to illuminate? • Pack temperature exceeds limit. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 high flow Both PACK switches in AUTO. What would cause the LEFT pack to automatically transition to the HIGH flow mode in flight, flaps up? • The RIGHT pack valve closes. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 Bleed Trip In flight, flaps up, in the event of a bleed trip, what will occur automatically? • The bleed valve closes. • The pack valve on the right pack will close. • The air mix valve on the right pack will drive full cold. • The left pack will go into the high flow mode. • For a left bleed trip, the NGS system shuts down also. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 high flow True or False. For a “no bleeds” situation (APU bleed valve open, Engine bleed switches OFF) the packs will transition to high air flow regardless of flap position, air/ground status, or number of packs operating. • True. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 high flow True or False. Packs should not be selected to the HIGH switch position during takeoff, approach or landing. • True. (L.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 high flow Is there a situation when a pack may be in HIGH during takeoff, approach or landing? • Yes. If the fire protection nonnormal procedures require the switch to be in the HIGH position. (L.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 Trip reset Do pilots receive air from the recirculation system under normal conditions? • No. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 Recirc fan What is the normal position of the Overboard Exhaust Valve in flight? • Closed. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 Recirc fan Where does the exhaust air go when the overboard exhaust valve is closed? • It warms the forward cargo compartment then is captured by the recirculation fan and put back into the mix manifold. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 Recirc fan What switch positions on the Air Conditioning Panel will cause the Overboard Exhaust Valve to open in flight? • Recirculation switch OFF and either pack switch in HIGH. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 Recirc fan Is there a situation when the Overboard Exhaust Valve will drive to open in flight without moving switches? • Yes. Upon activation of a Forward Cargo Fire Alarm. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 Recirc fan When the RECIRC FAN switch is in AUTO, the fan will operate except________ ? • When both packs are ON AND one or both pack switches are in the HIGH position, or • Forward Cargo Fire situation. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 Wing body ovht What causes this light to illuminate? • Bleed air duct leak. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 Wing body ovht 2 Can this light/system be reset with the TRIP RESET switch? • No. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 700 Trip reset Which lights can be reset with the trip reset switch once the condition that caused the trip is no longer present? • DUCT OVERHEAT. • PACK TRIP OFF. • BLEED TRIP OFF. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Duct ovht ** Slide 1 What causes this light to illuminate? • Bleed air temperature in related duct exceeds limit. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Duct ovht2 What happens to the air mix valve in this condition? • It drives full cold. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Duct ovht2 How may the pilot bypass the automatic temperature controller in the event of a controller malfunction? • Place the temperature selector to the MANUAL mode. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Duct ovht reset How is the system reset when the temperature drops below the exceedance temperature? • By pressing the TRIP RESET switch. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Intro Window Heat ** Slide 1 What does the green ON light indicate? • Window heat is being applied to the selected window. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide How is icing defined? • Icing conditions exist when OAT (on the ground) or TAT (in-flight) is 10˚C or below and: – Visible moisture (clouds, fog with vis < 1 sm, rain, snow, sleet, ice crystals) is present, or – Standing water, ice or snow is present on the ramps, taxiways, or runways (FOM, SP.17.2). Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Intro Window Heat ** Slide 1 If one or more windows are not being heated, what switch actuation can give you confidence that the system is working correctly? • Place the Test switch in the PWR TEST position. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide WH Ovrht test sw What occurs when this switch is placed in the OVHT position? • The system simulated a window overheat condition for those windows with the power switch in the ON position. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Window ovht What causes this light to illuminate? • Overheat is detected, or • Electrical power is interrupted to window. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Window ovht What occurs as a result of this indication? • Power is removed from window Left number 1. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Side pwr Which switches control power to windows 3 (4, and 5 if installed)? • The SIDE switches. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Side pwr What device delivers heat to windows 3 (4, and 5 if installed)? • Thermal switches. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Window glass The conductive coating is on the outer glass pane of which windows? • 1 and 2. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Window glass Which window can be opened from the exterior of the airplane? • 2R. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Probe heat What might cause erroneous or unreliable airspeed indications? • Blocked or frozen pitot-static system(s). • Severely damaged or missing radome. (QRH Ch 10-Note) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Probe heat What causes this light to illuminate? • The related probe is not heated. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Static ports Are the static ports heated? • No. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Ignition req’d? What is the purpose of engine anti-icing? • Prevent the formation of ice on the engine cowl lip. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Cowl bright blue What is the position of the right cowl anti-ice valve? • CLOSED or in transit to OPEN. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Ignition req’d? Is ignition required during icing conditions? • Yes. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Ignition req’d? At what temperature (below 10° Celcius) is anti-ice no longer required during climb or cruise? • -40° SAT. (L10.3) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Cowl stik shkr Discuss stick shaker logic in reference to cowl anti-ice? • When valve is open, stick shaker logic is set for icing conditions. When the valve closes, stick shaker logic returns to normal if wing anti-ice has not been used in flight. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Cowl AI lite What causes this light to illuminate? • An overpressure condition downstream of the engine cowl anti-ice valve. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide WAI purpose What is the purpose of the wing anti-ice system? • Provides protection for the three inboard leading edge slats by using bleed air. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide WAI le flaps not heated Are the leading edge flaps protected by the wing anti-ice system? • No. Neither are the outboard leading edge slats. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide WAI AC valves The wing anti-ice control valves are ____ motor operated? • AC. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide WAI bright blue What is the position of the right wing anti-ice valve? • CLOSED or in transit to OPEN. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide WAI auto close What two conditions will cause the wing anti-ice valves to close automatically on the ground with the switch in the ON position? • Thrust set above the takeoff warning setting, or • If either temperature sensor detects a duct over-temperature. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide WAI auto switch off What happens to the wing anti-ice valve switch if it is ON at lift off? • It trips OFF. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide WAI stick shakr Discuss stick shaker logic in reference to wing anti-ice? • When valves are open in flight, stick shaker logic is set for icing conditions regardless of subsequent switch position. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide WAI stick shakr Above FL____ use of wing antiice may cause bleed trip off and possible loss of cabin pressure • 350. (L.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Holding in icing conditions with flaps extended is ______. (L.10) A. B. C. D. fun exciting recommended prohibited Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Holding in icing conditions with flaps extended is ______. (L.10) A. B. C. D. fun exciting recommended prohibited Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide APU Start cycle How long could the APU start cycle be? • 120 seconds. (7.30) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide APU maint lite ** Slide 1 What causes this light to illuminate? • APU Maintenance problem exists. APU may be operated. Light is disarmed when APU switch is OFF. (7.15) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide APU Low press What causes this light to illuminate? • During start until APU oil pressure is normal. • Oil pressure is low causing an automatic shutdown (after start cycle is complete). • If light is illuminated when APU switch is placed to OFF, light extinguishes after 5 minutes. Light disarmed when APU switch is OFF. (7.15) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide APU fault What causes this light to illuminate? • A malfunction exists causing APU to initiate automatic shutdown. • If light is illuminated when APU switch is placed to OFF, light extinguishes after 5 minutes. Light disarmed when APU switch is OFF. (7.15) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide APU ovrspd What causes this light to illuminate? • RPM limit exceeded causing APU to initiate automatic shutdown. • Failed a self-test during normal shutdown. • If light is illuminated when APU switch is placed to OFF, light extinguishes after 5 minutes. Light disarmed when APU switch is OFF. (7.15) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide APU Load shed C40 Discuss APU automatic load shedding? • If APU is the only source, all galley busses are shed. • If more shedding is required, both main AC busses, mission busses, mission AC busses, selected 60 Hz AC and selected mission busses are shed. • On the ground, full load is attempted. Then sheds as in flight. (7.30) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide APU Max alt bleed air What is the maximum altitude to use APU bleed air? • 17,000 feet. (L10.3) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide APU Max alt elec What is the maximum altitude to use APU electrical load? • 41,000 feet. (L10.3) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide APU Max alt bleed air + elec What is the maximum altitude to use APU bleed air and electrical load? • 10,000 feet. (L10.3) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide APU Max alt bleed air + elec APU start attempts are not recommended above ________ feet? • 25,000 feet. (QRH Ch 6-Note) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide APU batt sw What happens to the APU if the battery switch is turned OFF? • APU shuts down. (7.30) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide APU ECU functions What are some of the functions of the APU Electronic Control Unit (ECU)? • Automatic shutdown. • Controls APU speed through electronic fuel control. • Load shed function. • Regulates bleed air through inlet guide vane control. (7.30) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide APU fire If an APU fire is detected, will the ECU shut down the APU if airborne? • Yes. It will do so on the ground or in the air. (8.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide APU fire Is there a situation in which the APU fire bottle will automatically discharge? • Yes. If on the ground and both engines are shutdown, the fire bottle will discharge 10 seconds after the fire is detected. (01-0015, 01-0041, 01-0042, 02-0203-05-4613) (8.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide APU fire What are the conditions that will cause the APU to shutdown? • Overspeed • Low oil pressure • High oil temperature • EGT exceedence • Fuel control unit failure • APU fire. (8.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Overwing Door ** Slide 1 What causes this light to illuminate? • The related overwing exit is not closed and locked, or • With takeoff thrust set, the related door flight lock failed to engage when commanded locked. (1.30) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Equip Door What causes this light to illuminate? • Either the Forward Equipment Compartment Door or the E&E Doors are not closed and locked. (1.30) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Bat Disch lite ** Slide 1 What causes this light to illuminate? • An excessive battery discharge is detected. (6.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Batt chrgr What DC bus is primarily powered by TR3 under normal circumstances? • Battery bus. (6.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide HBB What switch activates the hot battery bus? The hot battery bus is always connected to the main battery. There is no switch in this circuit. (6.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide HBB When AC power is available to charge the main battery, and the battery is fully charged, what powers the loads connected to the hot battery bus? The battery charger in constant voltage TR mode. It also powers the switched hot battery bus. (6.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide TR lite What causes this light to illuminate? • On the ground: any TR has failed. • In the air: TR1 failed or TR2 AND TR3 failed. (6.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide TR lite Is autoland available if a TR UNIT light illuminates while airborne? • No. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide TR lite What are the flight deck indications of a failure of TR 4 or 5 (if installed)? • There are no indications in the flight deck. (6.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Elec lite What causes this light to illuminate? • A fault exists in DC power system or standby power system. • Illuminates on the ground only. (6.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Drive lite What causes this light to illuminate? • IDG low oil pressure caused by one of the following: – IDG failure. – Engine shutdown. – IDG automatic shutdown. due to high oil temperature. – IDG disconnected through generator drive disconnect switch. (6.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Drive lite What conditions are necessary in order to disconnect the IDG with the generator drive disconnect switch? • The engine start lever is in IDLE and • Electrical power (switched hot battery bus ─ not in FCOM) is available. (6.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Disc sw Can the IDG be reconnected in the air? • No. (6.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Stby Pwr lite What causes this light to illuminate? • One or more of the following busses are unpowered: – AC standby bus. – DC standby bus. – Battery bus. (6.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Stby power Two fully charged batteries have sufficient capacity to provide standby power for a minimum of _____ minutes. • 60. (6.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide STBY PWR SW OFF What occurs when the STANDBY POWER switch is placed to OFF? • STANDBY POWER OFF light illuminates. AC standby bus, static inverter, and DC standby bus are not powered. (6.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide STBY PWR BATT What occurs when the STANDBY POWER switch is placed to BAT? • AC standby bus is powered by battery through the static inverter. • DC standby bus, and • Battery bus are powered directly by battery. (6.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide GND AC Pwr Avail lite What causes this light to illuminate? • Ground Power is connected and meets airplane power quality standards. (6.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide GND AC Pwr Avail lite With ground power on the airplane, must the ground power switch be placed in the ON position in order to operate the lights and utility outlets in the passenger compartment? • No. The flight attendant may use the ground service switch on the forward flight attendant panel. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide GND AC Pwr Avail lite When is the ground service switch overridden? • When both AC transfer busses are powered. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide GEN OFF BUS lite What causes this light to illuminate? • IDG is not supplying power to the related transfer bus. (6.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide APU AC Pwr lite What causes this light to illuminate? • APU is running and not powering a bus. (6.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide TXFR BUS lite amber What causes this light to illuminate? • Illuminates when the related bus is not powered. In this case, the automatic bus tie breaker operation was manually overridden by placing the BUS TRANS switch in the OFF position. (6.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide SOURCE OFF BUS lite amber What causes this light to illuminate? • No source has been manually selected to power the related transfer bus, or • The manually selected source has been disconnected. (6.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Test In this scenario, what is supplying AC power to the transfer busses? • Ground Power. (6.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide APU & GND PWR Could you supply power to transfer bus 1 from the APU Generator and power to transfer bus 2 from GND POWER simultaneously? • No. (6.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Cross bus tie In flight, the Master Caution light illuminates with an ELEC annunciation. You look up at the AC power panel and see this indication. What has happened? • Generator number two has tripped off and generator number one is supplying electrical power to both transfer busses. (6.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Cross bus tie If the APU were running, would it automatically switch to the APU generator? • No. There is no automatic source switching. (6.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Cross bus tie In this scenario, what is powering transfer bus two? • Generator number one. (6.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Test In this scenario, assuming the APU is running, what is supplying AC power to the transfer busses? • Transfer bus #1 – Generator #1. • Transfer bus #2 – APU. (6.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto connect If the airplane is in the air in this condition (APU running), what will cause the engine generators to automatically connect to their related transfer busses? • If the APU either shuts down or fails. (6.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Cross bus tie When does the cross bus tie open automatically to isolate DC bus 1 from DC bus 2? • At glide slope capture during a flight director or autopilot ILS approach. • Bus Transfer switch positioned to OFF. (6.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto connect Discuss APU automatic load shedding? • If APU is the only source, all galley busses are shed. If more shedding is required, both main AC busses are shed. (01-0015 02-0042 : mission busses, mission AC busses, selected 60 Hz AC and selected mission busses are shed.) On the ground, full load is attempted. Then sheds as in flight. (7.30) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Cross bus tie Discuss engine generator load shedding. • Engine generator sheds galleys on transfer bus 2, then on transfer bus 1; if an overload still exists main bus 1 and main bus 2 are shed. (01-0015-020042: Main bus shed logic also sheds the mission AC bus, and portions of the 60 Hz AC and mission DC busses). (6.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto connect What conditions require the pilots to “Plan to land at the nearest suitable airport” ? • One main AC power source remains (such as engine or APU generator). • One hydraulic system remains (the standby system is considered a hydraulic system). • Cabin smoke or fire persists. • Any other situation determined by the crew to have a significant adverse effect on safety if the flight is continued. Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click for Text Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide NOT ARMED lite ** Slide 1 What causes this light to illuminate? • The Emergency Exit Lights Switch is out of the ARMED position. (1.40) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Emerg exit lite auto With the Emergency Exit Lights ARMED, when will the emergency exit lights illuminate automatically? • If electrical power to DC bus 1 fails or if AC power has been turned off. (1.40) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Emerg lite, flt attend Can the Emergency Exit Light switch on the Attendant's panel override this switch? • Yes. (1.40) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Eng St Gnd ** Slide 1 What occurs when the Engine Start switch is placed to GND? • Start Valve Opens. Engine Bleed Valve Closes. • On ground: selected igniter provides ignition when start lever raised to IDLE. • Releases to OFF at start valve cutout. • Inflight: both igniters provide the ignition. (7.15) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Eng St Gnd ** Slide 1 What power source is used to accomplish these functions? • 28 volt DC battery power. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Eng St Off The left igniter plug receives power from the associated _______. The right igniter plug receives power from the _______. • Left – AC transfer bus. • Right – AC standby bus. (7.20 ) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Eng St Cont What occurs when the Engine Start switch is placed to CONT? • Provides ignition to selected igniters when engine is operating and engine start lever is in IDLE. • In flight: provides ignition to both igniters when N2 is below idle and engine start lever is in IDLE. (7.15) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Eng St Flt What occurs when the Engine Start switch is placed to FLT? • Provides ignition to both igniters when engine start lever raised to IDLE. (7.15) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Eng St Off Is there a situation when igniters will activate with the engine start switch in the OFF position? • Yes. When engine start lever is in IDLE and: An uncommanded rapid decrease in N2 occurs or, N2 is between 57% and 50% or, Inflight- N2 is between idle and 5%. (7.15) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Eng St Inflight starts Discuss the two methods of inflight restarts? • Crossbleed and Windmill. If a crossbleed start is required, the X-BLD indication (XB for compact display) is displayed above the N2 dial. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Eng St Inflight starts For inflight starts, at low N2 values, is it permissible to see a low oil quantity indication? Why or why not? • Yes, the oil scavenge pump may not provide enough pressure to return oil to the tank. Normal oil quantity should be indicated after start, however. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Low oil steady What causes this light to illuminate steady? • Oil pressure at or below red line. (7.15) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Oil filter bypass steady What causes this light to illuminate steady? • Indicates an impending bypass of the scavenge oil filter. (7.15) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Exhaust off lite ** Slide 1 What causes this light to illuminate? • No airflow from Exhaust Fan (Normal fan in this situation). • May also be an indication of a pressurization problem. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Exh fan off lite Selecting the alternate fan should cause the light to extinguish in ___ seconds? • Five (5). Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Exhaust off lite ** Slide 1 What will cause the exhaust fan to shut off automatically? • A forward cargo fire warning. The light is inhibited. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide EQUIP Supply off lite What causes this light to illuminate? • No airflow from Supply Fan (Normal fan in this situation). • May also be an indication of a pressurization problem. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide EQUIP Supply off lite What occurs on the ground if this light illuminates and either IRS switch is out of the OFF position? • The crew call horn in the nose wheel well will activate. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide FC Panel No A hydraulics ** Slide 1 What causes this light to illuminate? • Low pressure in the A hydraulic system. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide No A, with Stby Rud STBY RUD ON What happens to the light when you place the FLT CONTROL A switch to STBY RUD position? • The light extinguishes because it is deactivated and no longer responds to hydraulic pressure sensors. (13.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide No A, Stby Rud On, Light On STBY RUD ON If the light remained illuminated, what component has failed to operate correctly? • The Standby Rudder Shutoff Valve did not open. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide No A, with Stby Rud STBY RUD ON What causes this light to illuminate? The standby hydraulic system is commanded on to pressurize the standby rudder power control unit. (13.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Stby Rud Pump ON STBY RUD ON What pump activates when you place the switch to STBY RUD position ? • The Standby Hydraulic Pump. (13.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Stby Rud Low Press lite STBY RUD ON What light illuminates momentarily and then extinguishes to indicate that the standby hydraulic system has sufficient pressure? Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Stby Rud Low Press lite 2 STBY RUD ON What light illuminates momentarily and then extinguishes to indicate that the standby hydraulic system has sufficient pressure? • The STANDBY HYD low pressure light. (13.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Stby Rud Low Press lite Armed STBY STBY RUD RUD ON ON When is the STANDBY HYD low pressure light armed? • Only when standby pump operation has been selected or automatic standby function is activated. (13.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Stby Rud Low quant lite Armed STBY RUD ON When does this light illuminate? • When there is low quantity in the standby hydraulic reservoir. (13.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto ops STBY RUD ON When would the standby hydraulic system initiate automatic operation? • When all of the following conditions exist: 1. Loss of system A or B 2. Flaps extended 3. Airborne, or wheel speed greater than 60 knots, or 1. The main PCU Force Fight Monitor (FFM) trips. (13.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide FFM STBY RUD ON What is the purpose of the Force Fight Monitor (FFM) on the main rudder PCU? • Detects opposing pressure (force fight) between A and B actuators. This may occur if either system A or B input is jammed or disconnected. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide FFM output STBY RUD ON How would you know that the FFM has sensed a jammed rudder? • The FFM output automatically turns on the standby hydraulic pump and opens the standby rudder shutoff valve to pressurize the standby rudder PCU. This illuminates the STBY RUD ON light and the Master Caution light and FLT CONT annunciator. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Alt Fl Mstr Sw Arm What happens when you place the ALTERNATE FLAPS master switch to ARM? • The standby hydraulic pump activates • Trailing edge flap bypass valve closes, and • The ALTERNATE FLAPS position switch arms. (9.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Alt Fl DOWN What happens if you place the ALTERNATE FLAPS position switch to the DOWN position? • Fully extends the LE devices using standby hydraulic pressure AND if held to DOWN position, electrically extends the TE flaps until released. (9.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Alt Fl DOWN Can the LE devices be retracted by the standby hydraulic system? • No. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Alt Fl DOWN With a loss of Hydraulic System B, a flaps 15 approach and landing is required. Are autoland operations authorized for a flaps 15 landing? • No. (QRH Ch 7 – Note) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Alt Fl DOWN Alternate flap extension time from flaps up to flaps 15 is approximately ____ minutes? • 2. (QRH Ch 9 – Note) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto ops STBY RUD ON What is Manual Reversion? • Operation of the primary flight control inputs (pitch and roll) through cables attached to the control wheel. It occurs after a loss of both A and B hydraulic systems. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto ops STBY RUD ON Which computer simulates aerodynamic forces using airspeed from the elevator pitot system? • Elevator Feel Computer. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Feel Diff Press Lite What causes this light to illuminate? • When either hydraulic system fails or the elevator feel pitot system fails. This indicates excessive differential pressure in the elevator feel computer. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide EFS Module What is the purpose of the Elevator Feel Shift (EFS) module? • Increases A system pressure to the elevator feel and centering unit during a stall. This increases forward control column force to approximately four times normal feel pressure. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide EFS Module2 When is the Elevator Feel Shift (EFS) module inhibited? • On the ground • Radio Altitude less than 100 feet and autopilot engaged. However, if the EFS is active when descending through 100 feet RA, it remains active until the angle of attack is reduced below stickshaker threshold. (9.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide EFS Module2 What are the flight deck indications that the Elevator Feel Shift (EFS) module is properly armed or activated? • There are no flight deck indications. (9.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Rudder Authority At speeds above approximately ____knots, both hydraulic system A and B pressure are each reduced within the main rudder PCU by approximately 25% each. This function limits full rudder authority in flight after takeoff and before landing. • 135. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Speed Trim Fail What causes this light to illuminate? • A failure in the speed trim system or failure of a single FCC channel when recall is activated and light extinguishes when the Master Caution System is reset. (9.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Speed Trim Fail Purpose What does speed trim accomplish? • It improves flight characteristics during operations with low gross weight, aft center of gravity, and high thrust when the autopilot is not engaged. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Speed Trim Fail conditions What are the conditions for speed trim operation? • N1 above 60%. • Autopilot not on. • Airspeed between 100 KIAS and Mach .5. • 10 seconds after takeoff. • 5 seconds following release of trim switches. • Sensing of trim requirement. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto ops STBY RUD ON What 3 systems work together to help the pilot identify and prevent further movement into a stall condition? • Elevator Feel Shift (EFS). • Yaw damper. • Speed Trim. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Mach Trim Fail lite What causes this light to illuminate? • A failure in the mach trim system or failure of a single FCC channel when recall is activated and light extinguishes when the Master Caution System is reset. (9.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Mach Trim Fail purpose What does mach trim accomplish? • It provides speed stability above Mach .615 by adjusting the elevators through the mach trim actuator. The actuator simultaneously repositions the elevator feel and centering unit which adjusts the control column neutral position. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto Slat Fail lite What causes this light to illuminate? • A failure in the auto slat system or failure of a single Stall Management Yaw Damper computer when recall is activated and light extinguishes when the Master Caution System is reset. (9.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto Slat Fail purpose What does the autoslat operation accomplish? • With the TE flaps 1 through 5 selected and the LE slats in the extend position. As the airplane approaches the stall angle, the slats automatically drive to the full extend position, prior to stick shaker activation. It enhances stall characteristics at high angle of attack during takeoff or approach to landing. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto ops STBY RUD ON The Captain’s control wheel (column) is connected by cables to the _____ PCUs, the First Officer’s control wheel is connected by cables to the _____ PCUs. • Aileron. • Spoiler. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto ops STBY RUD ON Why shouldn’t we use aileron trim when the autopilot is engaged? • If the aileron trim is used with the autopilot engaged, the trim is not reflected in the control wheel position. Any aileron trim applied when the autopilot is engaged can result in an out of trim condition and an abrupt rolling movement when the autopilot is disconnected. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto ops STBY RUD ON When the control wheel is displaced more than approximately ___ degrees, spoiler deflection is initiated? • 10 (ten). ( 9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto ops STBY RUD ON When is the autopilot stabilizer trim active in the high speed mode? • When flaps are extended. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto ops STBY RUD ON If the autopilot is engaged and you activate the control wheel stabilizer trim switches, what will occur? • The autopilot will disengage and the trim will reposition the stabilizer. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto ops STBY RUD ON When would control column stabilizer trim cutout switches automatically stop operation of the main electric and autopilot trim? • When the control column movement opposes trim direction. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto ops STBY RUD ON True or False. Manual rotation of the trim wheels can be used to override autopilot or main electric trim. • True. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto ops STBY RUD ON Can you put more units of stabilizer trim in with electric trim or manual trim? • Manual trim. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto ops STBY RUD ON If two pilots are applying maximum manual effort to control a runaway stab trim wheel, may it cause a cable or system failure? • No. (QRH Ch 9 – Note) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto ops STBY RUD ON Will elevator control be sufficient to safely land the airplane regardless of stabilizer position? • Yes. (QRH Ch 9 – Note) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto ops STBY RUD ON What will occur if you attempt to takeoff with the stabilizer trim out of the green band? • An intermittent horn sounds (Takeoff warning horn). • The TAKEOFF CONFIG light illuminates. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto ops STBY RUD ON What is the purpose of the yaw damper? • Prevents dutch roll • Gust damping • Turn coordination Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto ops STBY RUD ON After a loss of hydraulic system B, what event will allow the YAW DAMPER switch to be reset to ON? Why? • Loss of Hydraulic System A. • Gives rudder assist to help turn the airplane when control of the ailerons is through manual reversion. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto ops STBY RUD ON Operation of the speed brake lever is different when on the ground and in the air. Explain. • On the ground flight spoilers and ground spoilers actuate. • In the air, only flight spoilers actuate. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto ops SPEEDBRAKE EXTENDED When does the SPEEDBRAKES EXTENDED light illuminate in the air? • When speed brakes are extended while in the landing configuration or below 800 feet AGL. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide SPEEDBRAKE EXTENDED If you see the SPEEDBRAKES EXTENDED light illuminate on the ground, what has happened? • There is hydraulic pressure sensed in the ground spoiler shutoff valve with the speed brake lever in the DOWN position. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto ops STBY RUD ON Why is moving the speed brake lever beyond the flight detent prohibited in flight? • It causes buffeting. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto ops STBY RUD ON During landing, the auto speed brake system operates when these conditions occur: • Speed brake lever is in the ARMED position. • SPEED BRAKE ARMED light is illuminated. • Radio altitude is less than 10 feet. • Landing gear strut compresses on touchdown. • Both thrust levers are in IDLE. • Main landing gear wheels spin up more than 60 knots. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto ops STBY RUD ON Compression of any landing gear strut enables the flight spoilers to deploy. However compression of the ____ main landing gear strut enables the GROUND spoilers to deploy. • Right. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide SB STBY RUD ON If the SPEED BRAKE lever is in the DOWN position during landing or rejected takeoff, the auto speed brake system operates under these conditions: • Main landing gear spin up > 60 Kt. • Both thrust levers in IDLE. • Reverse thrust levers positioned for reverse thrust. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Flaps STBY RUD ON When do the leading edge flaps extend fully? • Flaps 1 or greater. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Flaps STBY RUD ON At what flap setting are the slats fully extended? • Greater than Flaps 5. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Skew vs Asym Flaps STBY RUD ON What is the difference between asymmetry and skew flaps? • Asymmetry – a flap on one wing does not align with the symmetrical flap on the other wing. • Skew – a TE flap or LE slat panel does not operate at the same rate causing the panel to twist during extension or retraction. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Flaps What causes this light to illuminate? LE FLAPS TRANSIT • Any LE device in transit. • Any LE device not in programmed position with respect to the TE flaps. • A LE slat skew condition exists (slats 2 through 7 only). • During alternate flap extension until LE devices are fully extended and TE flaps reach flaps 10. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Flaps Is this light inhibited during autoslat operation? • Yes. (9.20) LE FLAPS TRANSIT Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Flaps What is the purpose of the flap load relief function? • Protect the flaps from excessive air loads. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Flaps What flap settings does this function operate? • Flaps 30 and 40 only. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Flaps At flaps 30, what happens if the flap load relief function is activated? • Retracts the TE flaps to 25. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Flaps At flaps 40, what happens if the flap load relief function is activated? • Retracts the TE flaps to 30. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Skew vs Asym Flaps STBY RUD ON What is the purpose of the Flap/Slat Electronic Unit (FSEU)? • Monitors the TE flaps for asymmetry and skew conditions and LE devices for improper position and skew conditions on slats 2 through 7. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Skew vs Asym Flaps STBY RUD ON What does the FSEU do if it detects a trailing edge asymmetry or skew condition? • Closes the TE flap bypass valve. • Displays a split needle on the flap position indicator. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Skew vs Asym Flaps STBY RUD ON Is slat skew detection inhibited during autoslat operation? • Yes. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Skew vs Asym Flaps STBY RUD ON Uncommanded motion is detected when no TE flap position or autoslat command is present and 2 LE flaps move on one wing or 2 or more slats move on one wing. What occurs in this case? • The FSEU shuts down the LE control and illuminates the amber LE FLAPS TRANSIT light. • The FSEU maintains pressure on the retract lines and depressurizes the extend and full extend lines. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Skew vs Asym Flaps STBY RUD ON In the event of uncommanded motion of the TE flaps, what occurs? • The FSEU shuts down the TE drive unit by closing the TE flap bypass valve. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Skew vs Asym Flaps STBY RUD ON How will the crew recognize this failure? • The flap position indicator disagreeing with the FLAP lever position (there is no flap needle split). (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Skew vs Asym Flaps STBY RUD ON In the event of uncommanded motion of the TE flaps, after the FSEU shuts down the TE drive unit, can the crew reset the system? • No. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Skew vs Asym Flaps STBY RUD ON How will the crew operate the TE flaps for landing? • They must use the alternate flap system to control the TE flaps. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Alt Fl DOWN STBY RUD ON What normal flap and slat protections are no longer operational in the alternate flap mode? • No skew protection • No asymmetry protection • No load relief • No uncommanded movement protection. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Engine Fuel Valve ** Slide 1 What causes the ENG VALVE CLOSED lights to illuminate bright blue? • When the valve is in transit or valve position and engine start lever or engine fire warning switch disagree. This valve is powered from the battery bus. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Spar Fuel Valve Power Source What is the power source for opening and closing the SPAR FUEL SHUTOFF VALVES? • DC power from the Hot Battery Bus. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Fuel Temp Where is the fuel temperature sensor located? • In the main tank number one. (12.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Fuel Temp What is the maximum fuel temperature? • 49°C. (L10.4) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Fuel Temp What is the minimum inflight fuel temperature? • 3°C above the fuel freezing point or –43°C, whichever is higher. (L10.4) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Spar fuel flow measured Fuel flow is measured after passing through the ________________ valve? • Engine fuel shutoff (fuel flow information is also provided to the FMS). (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide HMU To meet thrust requirements, the EEC meters fuel through the _______ ______ unit? • Hydro Mechanical Unit (HMU). (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide exchangers What component heats the fuel prior to reaching the second stage fuel pump? • Fuel/oil heat exchangers. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide CROSSFEED Fuel Valve lite What causes the CROSSFEED VALVE OPEN light to illuminate bright blue? • When the valve is in transit or valve position and crossfeed SELECTOR disagree. (12.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide CROSSFEED power source What is the power source for opening and closing the CROSSFEED VALVE? • DC from the battery bus. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Boost pump power AC What is the power source for the fuel boost pumps? • AC power. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Loss of AC power for fuel pumps If AC power was lost in flight, which fuel tanks have trapped fuel that cannot be suction fed to the engines? • Center Wing and Aux Tanks. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide APU Fuel When AC fuel pumps are operating, fuel for the APU is supplied from the _______ side of the fuel manifold. • Left Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Filter Bypass lite What causes this light to illuminate? • Impending fuel filter bypass due to a contaminated filter. (12.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Filter Bypass lite What may occur as a result of fuel contamination? • Erratic engine operation and flameout. (QRH Ch 12-Note) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide CW Vs Main Pumps What is the difference between the center tank LOW PRESSURE lights and main tank lights in operation? • The center tank lights extinguish when switches are placed in the OFF position. • One center tank low pressure light will result in a Master Caution alert. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide CW Vs Main Pumps What is the difference between the center and main tank pump operation? • When a center tank low pressure light illuminates, the pump shuts off after 10 seconds. • Center tank pumps put out more pressure than main tank pumps. (12.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide One Main Pump Fail and MC Would the Master Caution light illuminate in this scenario? • No. (12.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide One Main Pump Fail and MC What might cause a LOW PRESSURE light to flicker? • When tank quantity is low in turbulent air or in a climb or descent. (QRH Ch 12-Note) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Fuel Quant Indic power source What power source is necessary to illuminate the Fuel Quantity Indicators? • Standby AC power. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Fuel Quant Indic power source For ground operations, center tank fuel pump switches must not be positioned ON unless the center tank fuel quantity exceeds _____ (lb/kg) except when defueling or transferring fuel. • 1000 /453. (L.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Fuel Quant Indic power source Which fuel tank does the scavenge jet pump take fuel from? • The center wing fuel tank. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Fuel Quant Indic power source The fuel scavenge jet pump uses what kind of electrical power? • The pump does not use electricity. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Fuel Quant Indic power source The fuel scavenge jet pump works automatically as long as the following conditions are met. • Main tank fuel pump number 1 FWD switch is on and • Main tank number 1 is about one-half full. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Fuel Quant Indic power source A DC operated APU fuel boost pump is installed to ensure positive fuel pressure to the APU fuel control unit. During APU operation the pump operates automatically. When does the pump shut off? • When an AC fuel pump pressurizes the fuel manifold. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Fuel Low Indication When does the fuel LOW indication illuminate? • When the fuel quantity is less than 2000 pounds/907 kilograms in the related main tank. (12.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Fuel Config Indication When does the fuel CONFIG indication illuminate? • When the center tank quantity is greater than 1600 pounds/726 kilograms, both center tank pumps are positioned off, and either engine is running. (12.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Fuel config if CW>1000 Main tanks must be full if the center tank contains more than ______ pounds/kilograms? • 1000 /453. (L10.4) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Fuel Imbal Indication When does the fuel IMBAL indication illuminate? • When main tank quantity differ by more than 1000 pounds/453 kilograms. Remains until imbalance is reduced to 200 pounds/ 91 kilograms. (12.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Fuel Imbal Indication scheduled Allowable scheduled lateral imbalance between main tanks 1 and 2? • Zero. (L10.4) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Fuel Imbal allowed Allowable random lateral imbalance between main tanks 1 and 2 must not exceed ______ pounds/kilograms? • 1000/453. (L10.4) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Fuel imbal inhibit When is the fuel IMBAL indication inhibited? • When the airplane is on the ground or when the LOW indication exists at the same time. (12.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Aux fuel feed Which tank is fed by auxiliary fuel? • Center tank. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Aux fuel feed What is the purpose of the two vent valves in each auxiliary fuel tank? • They close to allow pressurization of the aux tanks so fuel will flow to the Center Wing Tank. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Aux fuel feed The vent valves automatically open upon landing. True or False. • True. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Aux fuel in FMC Is auxiliary fuel quantity included in the airplane total fuel quantity sent to the FMC for fuel computations? • Yes. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Maint messages in flight Are MAINT messages automatically displayed in flight? • No. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Maint messages in flight Can the MAINT messages be displayed in flight? • Yes. By pushing the MAINT switch. However, this is not proper procedure. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide FWD Alert messages displayed LOW PRESSURE What causes this light to illuminate? • An ALERT message is present. (12.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide FWD Alert messages displayed LOW PRESSURE How can multiple ALERT messages be displayed? • Repeated pushing of the ALERT switch will cycle through all active messages. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Aux Fuel Bleed Air Normal The transfer of fuel from aux tanks to the Center Wing tank is accomplished using pressurized air from ___________? • The cabin. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Aux Fuel Bleed Air What is the purpose of the AUX FUEL BLEED AIR switches? • Bleed air can be selected to pressurize the aux fuel tanks if cabin pressure is not adequate. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Aux Fuel Transfer What is the purpose of the AUX FUEL TRANSFER switches? • OFF closes respective auxiliary fuel transfer valves. AUTO arms respective auxiliary fuel transfer valves to begin fuel transfer. (12.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Aux Fuel Transfer After these switches are in the AUTO position, how long after takeoff will the auxiliary fuel system begin operation? • No sooner than 10 minutes after takeoff. • Center tank below 14,020 pounds (01-0015 thru 02-0042). • Center tank below 24,000 pounds (02-201 thru 05-4613). Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Aux Fuel Transfer The main fuel tanks must be full and center tank must be scheduled ______ if the auxiliary fuel system is to be loaded or contain fuel. • To contain a minimum of 17,320 lbs /7856 Kgs of fuel (01-0015 thru 02-0042). • To be full (02-201 thru 05-4613). (L.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide NGS What is the purpose of the Nitrogen Generation System (NGS)? • Converts bleed air to nitrogen-enriched air and delivers it to the center fuel tank to reduce flammability of the tank. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide NGS What are the flight deck indications for the proper functioning of the system? • The NGS operation is transparent and there are no flight deck indications. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide NGS When does the NGS system automatically start? • After takeoff and runs continuously through climb, cruise, descent, landing, and during taxi for a short period of time. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide NGS When does the NGS system automatically shut down? • After a specified period of lack of bleed air pressure. • Aircraft on the ground and not in test mode. • Either engine not running in flight. • Fire or smoke detection in the cargo or main deck areas. • Left air conditioning pack overheat. • Center tank refueling valve is open. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide NGS Note: During the external preflight, observe the Nitrogen Generation System indication in the Right Main Wheel Well adjacent to the APU fire control panel. • Look for a green, OPERATIONAL, light. Any other indication requires you to consult the MMEL or DDPG. • Generally dispatch is acceptable. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide PUMP VOLUME How many hydraulic systems are there? • Three (3). • A, B, and Standby. (13.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide PUMP VOLUME The hydraulic systems power which airplane systems? • Flight Controls • LE / TE flaps and slats • Landing Gear • Wheel brakes * Nosewheel steering * Thrust reversers * Autopilot Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide PUMP VOLUME Which system components are common to both A and B? • Flight Spoilers • Elevator • Ailerons • Rudder Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide PUMP VOLUME What electrical power source drives the electric motor driven pumps? • AC power Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide PUMP VOLUME Which transfer bus energizes the A electric motor driven pump? • Number two (2). Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide PUMP VOLUME An engine driven pump supplies approximately ___ times the fluid volume of the related electrical motor driven pump? • Four (4). Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Eng Pump low pres lite What causes this light to illuminate? • Low output pressure of associated pump. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Eng Pump low pres lite One pump can supply sufficient pressure for normal system operation. True or False? • True. (QRH Ch 13-Note) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Eng Pump low pres lite In the event of a loss of the engine driven pump and a high demand on the system, what might one expect to happen to the remaining electrical driven pump system? • An intermittent illumination of the electrical driven pump LOW PRESSURE light. (QRH Ch 13-Note) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide LG TU OPS Hydraulic fluid used for cooling and lubrication of the pumps passes through a heat exchanger before returning to the reservoir. Where is the heat exchanger for system A located? • Main fuel tank number 1. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide LG TU OPS What is the minimum fuel for ground operations of electric motor-driven pumps? • 1675 pounds/760 kgs in the related main tank. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Pump ovht A Elec What causes this light to illuminate? • Electrical pump has overheated OR Hydraulic fluid used to cool and lubricate electrical pump has overheated. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide PUMP Turning on the engine hydraulic pump de-energizes a blocking valve in the pump to allow pump pressure to enter the system. Why is the switch left on? • To prolong solenoid life. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Hydr with FIRE SW pulled How does pulling the engine fire warning switch affect the hydraulic system? • Shuts off fluid flow to the engine driven pump. • Deactivates the related LOW PRESSURE light. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Pump operation Will the engine driven hydraulic pump continue to rotate even when the fire switch is pulled? • Yes, however fluid flow is isolated from system components. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Syst press Why are the hydraulic reservoirs pressurized by bleed air? • To ensure positive fluid flow to all hydraulic pumps. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide foaming fluid What can occur at higher altitudes within the hydraulic reservoirs if they are not properly pressurized? • Foaming may occur. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide foaming fluid What are some indications that foaming has occurred? • Pressure fluctuations. • Blinking of related LOW PRESSURE light. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide LEAK in A system System A – If a leak develops in the engine driven pump or related lines, will all fluid be eventually lost? • No. A standpipe in the reservoir prevents a total system fluid loss. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide LEAK in A system System A – With fluid level at the top of the standpipe, the reservoir quantity displayed indicates approximately ____ % full. • 20% Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide LEAK in A system System A – If a leak develops in the electric motor-driven pump, will the quantity decrease to zero? • Yes. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide LEAK in A system System B – If a leak develops in the engine driven pump, will the quantity decrease to zero? • Yes. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide LEAK in A system System B – If a leak develops in the electric motor-driven pump, will the quantity decrease to zero? • Yes. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide LEAK in A system System B – What is the purpose of the standpipe then? • It supplies fluid to both engine driven pump and electric motordriven pump and is sufficient for power transfer unit operation. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide B & STBY share fluid The B system and the standby system share fluid. Will a leak in system B affect operation of the standby hydraulic system? • No. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide B & STBY share fluid If a leak occurs in the standby hydraulic system, the B system will continue to operate normally. What will the fluid level eventually stabilize at? • 72% full. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide PTU purpose What is the purpose of the Power Transfer Unit (PTU)? • Supply the additional volume needed to operate the autoslats and leading edge flaps and slats at the normal rate when system B engine-driven hydraulic pump volume is lost. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide PTU Operates What conditions cause the PTU to operate? • System B engine driven pressure below limits. • Airborne. • Flaps less than 15 but not up. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide LG TU purpose What is the purpose of the Landing Gear Transfer Unit? • Supply the additional volume needed to raise the landing gear at a normal rate when system A engine-driven hydraulic pump volume is lost. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide LG TU OPS What conditions cause the Landing Gear Transfer Unit to operate? • Airborne. • No. 1 Engine RPM drops below a limit value. • Landing gear lever UP. • Either main landing gear is not up and locked. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Auto connect What conditions require the pilots to “Plan to land at the nearest suitable airport” ? • One hydraulic system remains (the standby system is considered a hydraulic system). • Cabin smoke or fire persists. • One main AC power source remains (such as engine or APU generator). • Any other situation determined by the crew to have a significant adverse effect on safety if the flight is continued. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Press Sys Auto-fail ** Slide 1 What do these lights indicate? • A single controller failure in the pressurization system that has automatically transferred to the ALTN mode. (2.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Press Sys Auto-fail ** Slide 1 What causes the AUTO FAIL light to illuminate? • Loss of DC power • Controller fault • Outflow valve control fault • Differential pressure (>8.75) • Excessive rate of cabin pressure change (+/- 2000 feet per minute) • Cabin altitude >15,800 feet (2.40) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Press Sys ALTN MODE What does this panel indicate? • The pressurization system is in the ALTN mode. (2.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Press Sys Dual fail What does this panel indicate? • A dual controller failure in the pressurization system. (2.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Press Sys Manual What causes this light to illuminate? • Placing the pressurization system in the manual mode. (2.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Press Sys Manual The outflow valve can take up to ___ seconds to open. • 20. (QRH Ch 8 – Note) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Press Sys Off sched des What does this light indicate? • Airplane descended before reaching the planned cruise altitude set in the FLT ALT indicator. (2.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Press Sys Off sched des If no further inputs are given, what landing elevation will the controller program into the system? • Takeoff field elevation. (2.40) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Press Sys Off sched des If the FLT ALT indicator is changed to extinguish the light will the system continue to use the takeoff field elevation for landing? • No, the automatic abort capability to the original takeoff field elevation is lost. (2.40) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Press Sys type power What type of electrical power does the pressurization system require? • 28v DC from DC Bus 1 and DC Bus 2. (2.40) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Press outflow vlv What is the normal position of the outflow valve on the ground? • Full open. (2.40) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide OEV normal position What is the normal position of the Overboard Exhaust Valve in flight and pressurized? • Closed. Exhaust air from the E&E bay is diffused to the lining of the forward cargo compartment. (2.40) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide OEV drive full open What causes the Overboard Exhaust Valve to drive full open in flight? • If either pack switch is in HIGH and the recirculation fan is OFF. This discharges air from the E&E bay overboard for smoke removal. • Forward Cargo Fire. (2.40) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Max cabin pres dif 9.1 What is the maximum cabin pressure differential (relief valves)? • 9.1 psi. (L10.2) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 10,000 cabin alt warn horn What cabin altitude activates the Altitude Warning Horn and Light? • 10,000 feet. (2.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 10,000 cabin alt warn horn (05-730, 05-0932) What cabin altitude activates the Altitude Warning Horn and Light if the High Altitude Landing Switch is energized? • 14,000 feet. (2.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 10,000 cabin alt warn horn (05-730, 05-0932) When the High Altitude Landing system is engaged and the actual landing altitude is set, the controller brings the cabin altitude to the ______ _____ elevation when the descent mode is activated. • Landing airport. (2.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide 10,000 cabin alt warn horn (05-730, 05-0932) Upon departure from a high altitude airport, the system returns to normal operation as the cabin descends through ___ feet. • 8000. (2.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Aft Overhead **** Click a panel for questions Voice recorder ** Slide 1 The cockpit voice recorder uses 4 independent channels to record flight deck audio for _____ minutes? • 120. (5.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Reverser lite ** Slide 1 What causes this light to illuminate? • One or more of the following has occurred: • Auto-restow circuit has been activated. • Thrust reverser sleeve(s) not in commanded state. • Isolation valve or thrust reverser control valve not in commanded position. • Synchronization shaft lock circuitry failure. (7.15) Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Reverser lite ** hyd source What hydraulic source is used for pressure for the operation of engine No. 1 thrust reverser? • A system. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Reverser lite ** stby source What hydraulic source is used as a backup system for pressure for the operation of engine No. 1 thrust reverser in the event of an “A” system failure? • Standby hydraulic system. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Reverser lite ** 12 sec Any time the REVERSER light illuminates for more than ____ seconds, the MASTER CAUTION and ENG lights illuminate. • 12. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Reverser lite ** 10 feet The thrust reverser can be deployed when either radio altimeter senses less than ____ feet altitude? • 10. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Reverser lite ** detent 2 Under normal conditions the thrust reverser can be raised to detent No. 2 while the amber REVERSER light is illuminated. True or False? • False. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Reverser lite ** 16 sec While positioning the thrust levers past the detent No. 1 towards the stowed position, but not in the stowed position, a pause of approximately ____ seconds engages the electro-mechanical lock and prevents the thrust reverser sleeves from further movement? • 18. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Reverser lite ** 16 sec How may the pilot clear the fault and restore normal operations in the condition previously described? • Cycle the thrust reverser levers. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Eng control lite Is it permissible to back up with reverse thrust? • No. (L.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Eng control lite What causes this light to illuminate? Faults in the Engine Control System. Not dispatchable. Light operates when: • Engine is operating. • Airplane is on the ground and: – Below 80 knots prior to takeoff, or – Approximately 30 seconds after touchdown. (7.15) Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Eng control lite What is the purpose of the EEC? • Regulates the engine • Monitors autothrottle and flight crew inputs to automatically set engine thrust. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide EEC ** 2 channels The digital EEC has ___ independent control channels? • 2. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide EEC ** 2 channels Does the EEC automatically control reverse thrust output? • Yes. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide EEC ** lever full The full rated takeoff thrust for the installed engine is available at a thrust lever position less than the forward stop. True or False? • True. Fixed or assumed temperature derated takeoff thrust ratings are set at thrust lever positions less than full rated takeoff. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide EEC ** full thrust lever True or False. If the thrust lever is advanced to the forward stop, the EEC limits the maximum thrust according to the airplane model. • True. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide EEC ** HMU The EEC provides N1 and N2 red line overspeed protection in both the normal and alternate modes. True or False. • True. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide EEC ** HMU During ground starts, the EEC monitors engine parameters to detect___________. • Impending hot starts, • EGT start limit exceedences, and • Wet starts. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide EEC ** HMU If a wet start is detected, the EEC turns off the ignition and shuts off fuel to the engine ____ seconds after the start lever is moved to IDLE. • 15. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide EEC ** HMU During ground starts, the EEC monitors engine parameters to detect impending hot starts, EGT start limit exceedances, and wet starts. Are these protection features functional during inflight starts? • No. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide EEC ** HMU At high altitudes or in heavy precipitation, engines may accelerate to idle very slowly. True or False? • True. • Can you continue the start if the N2 is steadily increasing and EGT stays within limits? • Yes. (QRH Ch 7 – Note) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide EEC ** HMU Does the EEC provides red line EGT exceedence protection other than on the ground during engine start? • No. The EGT limit must be observed by the crew. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide EEC ** fuel flow The EEC compares actual N1 to commanded N1 and adjusts _________ to achieve commanded N1. • Fuel flow. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide EEC ** idle What are the three possible “idle” settings available through the EEC? • Ground Minimum Idle. • Flight Minimum Idle. • Approach Idle. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide EEC ** app idle When does the EEC automatically select Approach Idle? • In flight and flaps in landing configuration OR engine anti-ice is ON for EITHER engine. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide EEC ** app idle What is the purpose of Approach Idle? • Improves engine acceleration time in the event of a go-around. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide EEC ** app idle If a fault prevents the EEC from receiving flap or anti-ice signals, below what altitude will the EEC begin the Approach Idle schedule? • 15,000 feet. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Eng control ALTN lite What mode is the EEC in? • EEC has automatically switched to the SOFT alternate mode. It could also be in the HARD alternate mode if this occurred in flight and the thrust lever were moved to the IDLE position. In either case, required signals are not available for normal operation. (7.15, 7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide SOFT alt What does the EEC use to define engine parameters in the soft alternate mode? • The last valid flight conditions. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Hard alt 1 What mode is the EEC in, now? • EEC has been manually switched to the HARD alternate mode. (7.15) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Hard alt 2 What does the EEC use to define engine parameters in this mode? • The alternate mode thrust schedule. Hard alternate mode thrust is always equal to or greater than normal mode thrust for same thrust lever position. Maximum certified thrust rating can be exceeded. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide DEU Loss of either DEU will result in a loss of signal to both EECs. True or False? • True. Each EEC reverts to the alternate mode to prevent the engines from operating on a single source of data. (7.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Flight Rec ** Slide 1 Normal in flight When does the flight recorder operate? • When In flight: it operates anytime AC electrical power is available. • On the ground: after either engine is started. (10.16) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Flight Recorder OFF lite What causes this light to illuminate? • Indicates the recorder is not operating or the test is invalid. May indicate power failure, loss of input data, or electronic malfunction. (10.16) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Flight Recorder OFF lite 2 The light is illuminated on the ground with battery power applied. When does it extinguish? • When either engine is operating (on the ground). (10.16) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Flight Recorder TEST Why does the OFF light extinguish in the TEST position? • Because the flight recorder receives power. If it is recording, then the OFF light will extinguish. (10.16) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide GPS Lite ** Slide 1 What causes this light to illuminate? • Indicates a failure of both GPS sensor units. If it illuminates only after recall is pushed, indicates a single GPS sensor unit failure. (11.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide GPS Lite ** Slide 1 What effect will this have on look-ahead terrain alerting and displays? • They will be unavailable due to position uncertainty. (QRH Ch 11 – Note) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide IRS On DC light ** Slide 1 What causes these lights to illuminate? • The related IRS is operating on DC power from the switched hot battery bus (AC power not normal). If on the ground, the crew call horn in the nose wheel well sounds. (11.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide IRS left irs power source Which bus normally powers the left IRS? • AC Standby Bus. (11.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide IRS right irs power source Which bus normally powers the right IRS? • AC Transfer Bus 2. (11.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto switch to SW hot batt bus If AC power is not normal, either or both systems automatically switch to DC power from which bus. • Switched Hot Battery Bus. (11.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide IRS backup dc power to right IRS Backup DC power to the right IRS is automatically terminated if AC power is not restored within ___ minutes. • 5. (11.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide IRS Fault light What causes this light to illuminate? • A system fault affecting the related IRS ATT or NAV modes has been detected. (11.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide IRS Fault light In this situation, the IRS transfer switch will be moved to the BOTH ON R position. Will autopilot operation be affected? • Yes. Autopilot A is not available. Autopilot B may be used except during approach. (QRH Ch 11 – Note) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide IRS DC fail What causes this light to illuminate? • DC power is not normal for the related IRS. If the other lights are extinguished, the IRS is operating normally on AC power. (11.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide IRS DC fail With both DC FAIL lights illuminated, the ___________ battery bus is not powered or the battery is nearly discharged? • Switched Hot. (QRH Ch 11 – Note) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide IRS Align ON What causes these lights to illuminate? • Steady - IRS is operating in the ALIGN mode, the initial ATT mode, or the shutdown cycle. • Flashing - alignment cannot be accomplished due to: No present position entry OR significant difference between previous and entered positions. (11.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide IRS Align off What causes the align lights to extinguish? • IRS not in align mode. With mode selector in NAV, alignment is complete. • With mode selector in ATT, attitude information is available. Heading information is available following entry of initial magnetic heading. (11.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide IRS ATT What is the left IRS providing in this scenario? • Only attitude and heading information. The selector must be cycled to OFF before reselecting ALIGN or NAV. (11.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Mach a/s test ** Slide 1 On the ground, what will happen if you push the Mach and Airspeed Warning test button? • It tests the respective Mach warning system. (15.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Mach a/s inhibit Is this function inhibited when airborne? • Yes. (15.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Stall warn pwr source AC Is AC power required for the Stall Warning Test? • Yes. (15.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Stall warn computer (SMYD) Which computer is checked through this system? • The Stall Management Yaw Damper Computer. (15.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Stall warn computer (SMYD) Is this function inhibited when airborne? • Yes. (15.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Normal crew Oxygen press ** Slide 1 What does this gage indicate? • Crew Oxygen Cylinder pressure. (1.30) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto Oxygen What causes this light to illuminate with the switch in the NORMAL position? • Passenger oxygen activates automatically if cabin altitude climbs to 14,650. Passenger masks drop. (1.30) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Manual Oxygen What happens if the pilot places the switch in the ON position? • Passenger oxygen activates. Passenger masks drop. (1.30) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto Oxygen How long will passenger oxygen flow once initiated? • Approximately 12 minutes. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto Oxygen Once initiated, can passenger oxygen be shut off? • No. (1.30) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Pseu lite ** Slide 1 What causes this light to illuminate on the ground? • A fault in the PSEU or an overwing exit flight lock fails to disengage when commanded. (15.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Pseu in flight - not What causes this light to illuminate in flight? • It does not. It is inhibited from thrust lever advance for takeoff until 30 seconds after landing. (15.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Click a panel for questions Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide GPWS 1 What causes this light to illuminate? • GPWS computer malfunction or power loss. (15.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide GPWS Slide 1 The GPWS monitors terrain proximity using a discrete function of the weather radar system. True or False? • False, it uses an internal world wide data base. (15.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide GPWS Slide 1 What type of events will the GPWS alert for? • Excessive descent rate. • Excessive terrain closure rate. • Altitude loss after takeoff or go around. • Unsafe terrain clearance when not in the landing configuration. • Excessive deviation below an ILS glide slope. • Excessive deviation below glide path. Click (15.20) for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide GPWS Slide 1 Can terrain and weather displays appear on a display unit simultaneously? • No. (15.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide GPWS Slide 1 Can terrain and TCAS displays appear on a display unit simultaneously? • Yes. (15.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide GPWS Slide 1 If pilot reaction is immediate, a ground proximity alert guarantees terrain clearance. True or False? • False. (15.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Auto brake disarm lite ** Slide 1 What causes this light to illuminate? • RTO selected on the ground. • Malfunction in system. • Manual brakes applied during RTO or Landing. • Landing with RTO selected. • Speed Brake lever moved down during RTO or Landing. • Thrust levers advanced during RTO or Landing. (14.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto brake RTO In the RTO position, above what speed will the system apply maximum brake pressure when thrust levers are retarded to idle? • 90 knots. (14.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto brake RTO conditions What conditions must exist in order to arm the RTO mode prior to takeoff? • Switch in the RTO position. • On the ground. • Antiskid and autobrake systems operational. • Wheel speed <60 Knots. • Thrust levers in IDLE. (14.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto brake RTO in air In the air, with the switch in RTO, the RTO mode is automatically disarmed. Will the AUTO BRAKE DISARM light illuminate? • No. (14.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto brake RTO landing If a landing is made with RTO selected will any automatic braking occur? • No. (14.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto brake set at 80K If the pilot selects a landing autobrake setting during landing roll at 80 knots, will the system begin braking? • Yes. If selected prior to 30 knots of ground speed, braking will begin immediately. (14.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto brake set at 80K With autobrakes set to 2, will the landing distance be extended if the thrust reversers are not used? • No. The autobrakes detect the deceleration and will apply more braking to stop the airplane. (14.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto brake three ways disarm After auto braking has initiated, name three ways the pilot may disarm the system? • Apply manual brakes. • Speed brake to down detent position. • Advancing forward thrust levers (except during first 3 seconds after touchdown). (14.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Auto brake three ways disarm What causes this light to illuminate? • An anti-skid system fault has occurred. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Antiskid 2 When setting the parking brake, if the ANTI SKID INOP light illuminates, what has occurred? • The parking brake valve is not in the commanded position. (14.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto brake three ways disarm Is locked wheel protection available in this condition? • No. (QRH Ch 14 – Note) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Antiskid 1 Will antiskid protection be available with the alternate brake system? • Yes. (14.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Antiskid 2 How does antiskid braking differ between normal and alternate braking? • With the alternate braking system, antiskid protection is applied to main gear wheel pairs instead of individual wheels. (14.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Antiskid 2 Is locked wheel and hydroplane protection available with Alternate brakes? • Yes. (14.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Antiskid 2 Is anti skid protection available if both “A” and “B” systems are lost? • Yes. (14.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide LG lever off ** Slide 1 Hydraulic power for retraction, extension, and nose wheel steering is normally supplied by hydraulic system _____? • A. (14.20) Click for Text BOEING is a trademark of Boeing Management Company. Copyright © 2010 Boeing. All rights reserved. Log Out Home Return to Last Slide LG lever off ** Slide 1 What nose wheel deflection is achieved with full rudder deflection? • 7 degrees. (14.20) Click for Text BOEING is a trademark of Boeing Management Company. Copyright © 2010 Boeing. All rights reserved. Log Out Home Return to Last Slide LG lever off ** Slide 1 What nose wheel deflection is achieved with full turn of the Nose Wheel Steering? • 78 degrees. (14.20) Click for Text BOEING is a trademark of Boeing Management Company. Copyright © 2010 Boeing. All rights reserved. Log Out Home Return to Last Slide LG lever off ** Slide 1 On the ground, what prevents the landing gear lever from moving to the retract position? • A landing gear lever lock. (14.20) Click for Text BOEING is a trademark of Boeing Management Company. Copyright © 2010 Boeing. All rights reserved. Log Out Home Return to Last Slide NWS If you turn the nose wheel steering wheel and conduct rudder pedal steering simultaneously, which one has priority? • Nose wheel steering wheel. (14.10) Click for Text BOEING is a trademark of Boeing Management Company. Copyright © 2010 Boeing. All rights reserved. Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Red gear light During retraction, the ALTERNATE brakes automatically stop rotation of the main gear wheels. True or False? • True. (14.20) Click for Text BOEING is a trademark of Boeing Management Company. Copyright © 2010 Boeing. All rights reserved. Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Red gear light During retraction, what stops the nose gear tires? • Nosewheel snubbers. (14.20) Click for Text BOEING is a trademark of Boeing Management Company. Copyright © 2010 Boeing. All rights reserved. Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Red gear light What does a red GEAR light indicate? • Landing gear does not agree with the Landing Gear position lever OR landing gear is not DOWN and LOCKED with either or both thrust levers retarded to idle and below 800 feet AGL. (14.20) Click for Text BOEING is a trademark of Boeing Management Company. Copyright © 2010 Boeing. All rights reserved. Log Out Home Return to Last Slide LG lever off ** Slide 1 What happens when the landing gear lever is placed to OFF? • Hydraulic pressure is removed from the landing gear system. (14.20) Click for Text BOEING is a trademark of Boeing Management Company. Copyright © 2010 Boeing. All rights reserved. Log Out Home Return to Last Slide LG lever off ** Slide 1 What is the landing gear retract speed limit? • 235 Knots (See the placard). (14.20) Click for Text BOEING is a trademark of Boeing Management Company. Copyright © 2010 Boeing. All rights reserved. Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Gear down – lever up After takeoff you place the gear handle in the UP position and you see this indication several minutes afterwards. What could be the problem? • The manual landing gear extension door might be OPEN. (14.20) Click for Text BOEING is a trademark of Boeing Management Company. Copyright © 2010 Boeing. All rights reserved. Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Gear down – lever up With the manual landing gear extension door open, could you extend the landing gear with the lever in the UP position? • Yes, however this is not proper procedure. (14.20) Click for Text BOEING is a trademark of Boeing Management Company. Copyright © 2010 Boeing. All rights reserved. Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Nosegear doors Once lowered manually, can the gear be retracted? • No. (QRH Ch 14 – Note) Click for Text BOEING is a trademark of Boeing Management Company. Copyright © 2010 Boeing. All rights reserved. Log Out Home Return to Last Slide NWS Are the brakes for the nose wheels on the B hydraulic system? • There are no brakes for the nose wheels. (14.10) Click for Text BOEING is a trademark of Boeing Management Company. Copyright © 2010 Boeing. All rights reserved. Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Fitting2 What will stop a spinning tire with loose tread from entering the main wheel well? • A fitting in the wheel well ring opening will break and that gear stops retracting and free falls back to the down position. (14.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Gear down – lever up After takeoff, you raise the gear and see this indication. What may have happened? • The right main gear did not retract. • May be caused if the blown tire impact fitting had broken off. (14.20) Click for Text BOEING is a trademark of Boeing Management Company. Copyright © 2010 Boeing. All rights reserved. Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Accumulator If system B hydraulic pressure is lost, will the accumulator continue to be pressurized by the A system? • No. However, trapped hydraulic pressure can still provide several braking applications or parking brake application. (14.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Takeoff config1 When is the Takeoff Configuration warning horn armed? • On the ground and either or both thrust levers are advanced for takeoff. (15.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Takeoff config2 What causes the Takeoff Configuration light to illuminate and warning horn to sound when the thrust levers are advanced up for takeoff? • TE flaps not in the 1 to 25 takeoff range. • LE devices are not configured for takeoff. • Speedbrake lever not down. • Spoilers not down. • Parking brake set. • Stabilizer trim not in the takeoff range. (15.20) Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click for Text Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Lights A landing gear is down and locked as long as one associated green indicator light (center or overhead panel) is illuminated. True or False? • True. (QRH Ch 14-Note) Click for Text BOEING is a trademark of Boeing Management Company. Copyright © 2010 Boeing. All rights reserved. Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Fitting1 Why would this light illuminate? • With the autopilot engaged, it means that the autopilot is not trimming the stabilizer properly. (4.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Fitting1 Is a momentary illumination of this light normal during large changes in trim requirements? • Yes. (QRH Ch 9 – Note) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide TO config lite What causes this light to illuminate? • Activates on the ground as throttles are advanced if the airplane is not properly configured correctly for takeoff. • Activation is simultaneous with aural warning intermittent horn for TAKEOFF CONFIGURATION alert. (15.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Cabin Alt lite What causes this light to illuminate? • Illuminates at 10,000 feet if the cabin has not been pressurized. • During flight with loss of cabin pressure. • Activation is simultaneous with aural warning intermittent horn for CABIN ALTITUDE alert. (15.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Click a panel for questions Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Cargo Fire Test ** Slide 1 Is this a satisfactory test of the cargo fire panel? • Yes. AC power is required. (8.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Cargo Fire det fault What causes this light to illuminate? • After AC power is applied, both loops in one or both cargo compartments have failed. During the TEST, one loop in either or both cargo compartments has failed. (8.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Cargo Fire FWD lite What causes this light to illuminate? • At least one detector in each loop (in the forward cargo compartment, in this scenario) detects smoke. If power failed in one loop, at least one detector in the remaining loop detects smoke. (8.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Cargo Fire FWD lite What else automatically occurs in the event of a forward cargo fire? • The RECIRC FAN shuts down • The exhaust fan shuts down • The overboard exhaust valve opens • The NGS system shuts down (for any cargo compartment fire) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Cargo Fire Armed What does activating the ARMED switch accomplish? • Arms the extinguisher for the forward cargo compartment. (8.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Cargo Fire Disch lite What does the DISCH light signify? • Any extinguisher bottle has discharged. (8.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Cargo Fire Disch lite After pushing the CARGO FIRE DISCH switch, the light may need up to _____ seconds to illuminate. • 30. (QRH Ch 8 – Note) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Cargo Fire 2nd bottle When does the last bottle discharge? • After 60 minutes. • Airborne. • The switch remains armed. (8.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Cargo Fire elect pwr What electrical power source is required to discharge the cargo fire bottle(s)? • Hot Battery Bus. (8.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto connect What conditions require the pilots to “Plan to land at the nearest suitable airport” ? • Cabin smoke or fire persists. • One hydraulic system remains. (the standby system is considered a hydraulic system) • One main AC power source remains. (such as engine or APU generator) • Any other situation determined by the crew to have a significant adverse effect on safety if the flight is continued. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Auto connect WARNING Inform ground personnel NOT to open any cargo door after landing until all passengers and crew have exited the airplane and fire fighting equipment is nearby. Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Stab trim override What is the purpose of the STAB TRIM override switch? • Control column actuated stabilizer trim cutout switches stop operation of the main electric and autopilot trim when the control column movement opposes trim direction. When the STAB TRIM override switch is positioned to OVERRIDE, electric trim can be used regardless of control column position. (9.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Cabin Smoke Detector 01-0015 - 02-0042 What is the purpose of the Cabin Smoke Detector? • Detect smoke in the passenger cabin (8.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Cabin Smoke Detector 01-0015 - 02-0042 What happens when you select the TEST position? • Does a lamp test of the LAV indicators • Initiates a test for the DV compartment smoke detectors (4) • Initiates a test for the AVIO RACK 3/4 smoke detectors (2). (8.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Cabin Smoke Detector 01-0015 - 02-0042 How do you silence the alarm buzzer? • Select the MUTE position of the selector switch (8.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Cabin Smoke Detector 01-0015 - 02-0042 Do crew members in the passenger compartment receive a local warning if there is smoke in the AVIO RACK? • No. Pilot must inform them of the alarm. (8.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Engine Fire Ovht Is this a satisfactory test of the fire detection system? • Yes. Is AC power available? – Yes. (8.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Engine Fire Ovht What causes this light to illuminate? • Indicates overheat in related engine. (8.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Engine Fire Ovht Is the Fire Switch for engine number one unlocked now? • Yes. The switch unlocks upon activation of the overheat indication. (8.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Engine Fire Ovht What happens when you pull the engine fire switch up? • Engine Fuel Valve closes/Spar Fuel Valve closes. • Hydraulic fluid shutoff valve closes/Engine driven pump light is deactivated. • Generator trips. • Bleed air valve closes. • Disables thrust reverser. Click • Arms discharge squib. for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Apu det inop What causes this light to illuminate? • Indicates the APU detector loop has failed. (8.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Engine Fire Fault lite What causes this light to illuminate? • With OVHT DET switch in Normal it indicates both detector loops for one engine have failed. With the OVHT DET switch in A or B, it indicates that the selected loop has failed. (8.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Engine Fire fault and MC Does the Master Caution light and OVHT/DET annunciator illuminate with this light? • No. (8.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Apu bottle disch What caused this light to illuminate? • APU fire switch was pulled and rotated. (8.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Apu bottle disch If an APU fire occurs on the ground, while engines are shut down, what occurs? • The ECU causes the APU to shut down (inflight also) • The extinguisher automatically discharges after 10 seconds regardless of the fire switch position. (01-0015, 01-0041, 02-0042, 02-0203-05-0932) (8.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Apu bottle disch What happens when you pull the APU fire switch? • APU fuel shutoff valve closes. • APU bleed air valve closes. • APU inlet door closes. • APU generator trips. • Arms the squib. (8.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Engine Fire L bottle disch What power source electrically discharges the APU and Engine fire bottles? Hot Battery Bus. (8.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide Warning System What causes the FIRE WARN light to illuminate? • Engine Fire. • APU Fire. • Cargo Fire. • Wheel Well Fire. (15.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Warning System What else occurs when this warning light illuminates? • The fire warning bell sounds. • If on the ground and the APU is running, the remote APU fire warning horn sounds. (15.10) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Warning System Will pushing the FIRE WARN light also silence the remote APU fire warning horn? • Yes. (15.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Warning System When does the MASTER CAUTION light illuminate? • When any caution occurs outside the normal field of vision of the flight crew. (15.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Warning System After resetting the system by pressing the MASTER CAUTION light, how can you determine which faults are still stored in the Master Caution System? • Push the system annunciator to recall the fault(s) on the system annunciator panel. (15.20) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Warning System If the recall switch were to fail, is there an alternate method of finding the stored faults and causing them to annunciate? • Place the Master Lights Test and Dim Switch in the TEST position. A master caution recall and stored faults will cause the associated light to remain illuminated when the switch is released. (1.30) Click for Text Log Out Home Return to Last Slide Click on the HOME button to return to the flight deck. Log Out Home Click for Text Return to Last Slide