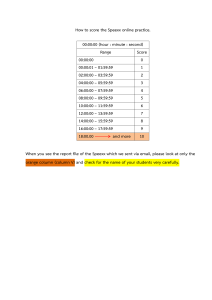
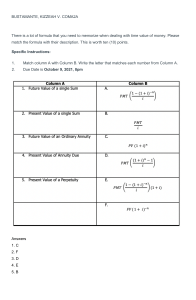
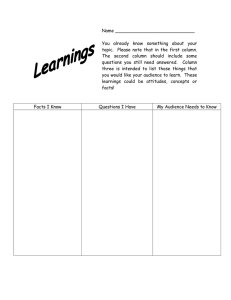
GRADE 12 ECONOMICS SECTION A REVISION 2022 This question paper consists of 30 pages. Activity 1 (SCE May/June 2017) SECTION A (COMPULSORY) 30 MARKS – 20 MINUTES QUESTION 1 1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Write down the question number (1.1.1–1.1.8), choose the answer and make a cross (X) over the letter (A–D) of your choice in the ANSWER BOOK. 1.1.1 The circular-flow model of an open economy shows the functioning of an economy that includes the … sector. A B C D 1.1.2 A diagram that shows expansion and contraction periods of economic activities is called a(n) … cycle. A B C D 1.1.3 by legislation is regulation. deregulation. centralisation. decentralisation. The term used to compare a country's export prices with its import prices by means of indices is called the … A B C D 1.1.5 business economic productivity inflationary The removal of unnecessary restrictions known as … A B C D 1.1.4 public business foreign domestic balance of payments. terms of trade. balance of trade. exchange rate. An example of a social indicator is … A B C D education. business confidence. employment. production. 1.1.6 An increase in the real value of production in a country is known as economic … A B C D 1.1.7 Which strategy failed in its objective to halve poverty and unemployment by 2014? A B C D 1.1.8 development. growth. integration. prosperity. New Growth Path (NGP) Reconstruction and Development Plan (RDP) Accelerated and Shared Growth Initiative for South Africa (AsgiSA) National Development Plan (NDP) A purpose-built industrial estate physically enclosed and linked to an international harbour or airport is known as a (n)… A B C D corridor. special economic zone (SEZ). industrial development zone (IDZ). integrated development plan (IDP) (8 x 2) (16) 1.2 1.3 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches the item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–I) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK. 1.2.1 COLUMN A Households 1.2.2 Nationalisation 1.2.3 Devaluation 1.2.4 Sanctions 1.2.5 Technology 1.2.6 Industry 1.2.7 Standard of living 1.2.8 Productivity A COLUMN B penalty or punishment imposed by one country on another for some wrongdoing B decrease in the value of the rand in terms of the pound due to market forces C transfer of ownership from the private sector to the public sector D consists of enterprises that produce the same kinds of products E ratio between output produced in the economy and input used to produce them F new scientific knowledge in the form of inventions and innovations G owners of the factors of production H expressed by the real GDP per capita, life expectancy and level of literacy I deliberate decrease in the value of the currency in terms of another currency (8 x 1) (8) Give ONE term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK. 1.3.1 A business owned wholly or partly by the state and run by a public authority 1.3.2 The strategy used by the Reserve Bank that focuses on the amount of money in the economy 1.3.3 The value of a country's currency exchanged for another currency 1.3.4 The process whereby people move from rural areas into towns and cities 1.3.5 Labour force from the age of 16 to 60 years 1.3.6 Worldwide interaction of economies with trade as an important element (6 x 1) (6) TOTAL SECTION A: 30 ACTIVITY 2 SECTION A (COMPULSORY) ( SCE MAY/JUNE 2018) 30 MARKS – 20 MINUTES QUESTION 1 1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.9 D. 1.1.1 The practice of selling goods in a foreign country at lower prices than in the country of origin is known as … A B C D 1.1.2 Savings flow back into the circular flow as … A B C D 1.1.3 public relations trade international demand-and-supply side When import duties are imposed as a percentage of the value of the imported goods, it is known as … duties. A B C D 1.1.5 investments. government spending. exports. imports. The new economic paradigm that relates to the smoothing of business cycles is rooted in … policies. A B C D 1.1.4 exportation. dumping. importation. import substitution. composite specific ad valorem average An increase in the productive capacity of the economy over a specific period of time is called … A B C D economic development. spatial development. economic growth. developmental economics. 1.1.6 The interaction of economies with trade as an important element is known as … A B C D 1.1.7 The number of employed persons as a percentage of the economically active population (EAP) is called the … A B C D 1.1.8 employment rate. economic growth. productivity rate. labour productivity. value-added products in all Economic activities which create sectors is known as … development. A B C D 1.2 privatisation. globalisation. entrepreneurship. export promotion. social employment mining industrial (8 x 2) (16) Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches the item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–I) next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK. 1.2.1 1.2.2 COLUMN A Monetary policy A Marginal propensity to consume B refers to personal income after tax has been deducted C removal of trade barriers D buying and selling of government securities to influence the money supply E approach taken by a country's central bank to influence spending in the economy F measures headline inflation G strategies used to encourage production H trade policy that promotes the manufacturing of local products for foreign markets I proportion of their disposable incomes that households spend 1.2.3 Terms of trade 1.2.4 Export promotion 1.2.5 Open-market transactions 1.2.6 Incentives 1.2.7 Trade liberalisation 1.2.8 Consumer price index (CPI) COLUMN B compares export prices with import prices by means of indexes (8 x 1) (8) 1.3 Give the ONE term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK. Abbreviations, acronyms and examples will NOT be accepted. 1.3.1 A market for short-term savings and loans 1.3.2 A negative economic growth rate for at least two consecutive quarters 1.3.3 A trade policy that discourages imports to guard domestic industries from harmful foreign competition 1.3.4 The Act that promotes redress and transformation in the workplace in terms of race, gender and disabilities 1.3.5 A policy that targets taxes and government expenditure to influence economic activity 1.3.6 The migration of people from rural areas to cities and towns (6 x 1) (6) TOTAL SECTION A: 30 ACTIVITY 3 (SCE MAY/JUNE 2019) SECTION A (COMPULSORY) 30 MARKS – 20 MINUTES QUESTION 1 1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.9 D. 1.1.1 Labour can be bought and sold in the … market. A B C D 1.1.2 Comparative cost advantage shows that world output can increase if countries … in what they do best. A B C D 1.1.3 goods factor financial consumer impose tariffs limit the use of technology specialise protect workers The medium-term expenditure framework (MTEF) is a …-year government expenditure and revenue projection. A B C D three one two four 1.1.4 The peak of a business cycle is characterised by a … A B C D 1.1.5 An increase in the productive capacity of the economy over a specific period of time is called … A B C D 1.1.6 Expanded Public Works Critical Infrastructure Small Business Support Skills Development An example of an economic indicator is … A B C D 1.1.8 contraction. economic development. economic growth. globalisation. Cost-sharing grants by government to improve roads is called the … Programme. A B C D 1.1.7 high demand for credit. stable inflation rate. high unemployment rate. low output. sanitation. population growth. life expectancy. production price index. Social grants to the citizens of South Africa forms part of the … policy. A B C D monetary trade growth fiscal (8 x 2) (16) 1.2 1.3 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches the item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–I) next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK. 1.2.1 COLUMN A Multiplier 1.2.2 Privatisation 1.2.3 Diverting trade 1.2.4 Free-floating exchange rate 1.2.5 World Bank 1.2.6 Industrial development zones (IDZ) 1.2.7 Employment equity 1.2.8 Consumer price index (CPI) A COLUMN B when a state-owned business is sold to a private sector enterprise B bring disadvantaged groups to an equal level in terms of hiring, promotion and other aspects of employment C responsible for infrastructure and business investments in neglected and underdeveloped areas D international institution established to promote recovery and development E high quality standards are imposed to make the importing of goods more difficult F the value of a currency in terms of another, that is determined by market forces G measures price changes of an average basket of goods and services purchased by a consumer H a small initial increase in spending produces leads to a proportionally larger increase in aggregate income I industrial estates that are physically enclosed and near to a harbour or airport (8 x 1) Give ONE term for EACH of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK. Abbreviations, acronyms and examples will NOT be accepted. 1.3.1 The total value of final goods and services produced within the borders of a country in a given period 1.3.2 Predicting the future economic activities using facts or information that is known 1.3.3 Record of all trade and financial transactions between a country and the rest of the world (8) 1.3.4 The increase in the standard of living of the people over a period of time 1.3.5 Efforts by governments to move manufacturing and other businesses from metropolitan areas to rural areas 1.3.6 It measures the distance between the peak and the trough of a business cycle (6 x 1) (6) TOTAL SECTION A: 30 ACTIVITY 4 (SCE MAY/JUNE 2021) SECTION A (COMPULSORY) 30 MARKS – 20 MINUTES QUESTION 1 1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.9 D. 1.1.1 Cycles that last 3–5 years and are caused by businesses adapting their inventory levels: A B C D 1.1.2 A decrease in the value of the currency due to market forces is known as … A B C D 1.1.3 revaluation. devaluation. appreciation. depreciation. Newly established firms that still need protection are called … industries. A B C D 1.1.4 Jugler Kitchin Kuznets Kondratieff competitive strategic declining infant The continuous movement of factors of production, goods and services among the participants in the economy is called … A B C D leakages. injections. real flows. money flows. 1.1.5 Service delivery to ensure the daily management of cities and towns is the responsibility of the ... government. A B C D 1.1.6 A nationwide government intervention to create employment using labour-intensive methods is known as the … A B C D 1.1.7 Black Economic Empowerment Programme. National Skills Development Strategy. Expanded Public Works Programme. Joint Initiative on Priority Skills Acquisition. Issues related to human well-being over a period of time are monitored by using … indicators. A B C D 1.1.8 local national provincial central growth social economic communication A track of land that forms a passageway allowing access from one area to another is called a/an … A B C D corridor. special economic zone. spatial development initiative. industrial development zone. (8 x 2) (16) 1.2 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches the item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–I) next to the question number (1.2.1 to 1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK. 1.2.1 COLUMN A Embargo 1.2.2 Length of the business cycle 1.2.3 Comparative advantage 1.2.4 A COLUMN B when a country engages in foreign trade and produces a given good at a lower input cost than other countries B a complete ban imposed on the importing of goods from a particular country Marginal propensity to save C measured from peak to peak or trough to trough 1.2.5 Non-rivalry D the proportion of income that households do not consume 1.2.6 Wealth tax E consumption by one person does not reduce consumption by another person F economic goods which do not take a tangible and storable form G measured in terms of per capita real gross domestic product H levied on properties according to their market value I extensive increase in organised economic activity to manufacture, mine, farm and deliver services (8 x 1) 1.2.7 1.2.8 Industrial development Services (8) 1.3 Give ONE term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK. Abbreviations, acronyms and examples will NOT be accepted. 1.3.1 The curve that indicates the relationship between the unemployment rate and inflation rate 1.3.2 An economy that excludes the foreign sector 1.3.3 A strategy to strengthen the institutional capacity to deliver services that facilitate economic and social development 1.3.4 A regional development initiative that attracts infrastructure and business investments to neglected areas 1.3.5 A tariff based on a fixed amount per unit, weight or size that is levied on imported goods 1.3.6 A business cycle approach based on forces inside the market system (6 x 1) (6) TOTAL SECTION A: 30 ACTIVITY 5 (NOV 2017) SECTION A (COMPULSORY) 30 MARKS – 20 MINUTES QUESTION 1 1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.9 D. 1.1.1 In an economy where injections exceed leakages, the … A B C D 1.1.2 Long-term funds are borrowed or saved on the ... market. A B C D 1.1.3 production of goods and services will decrease. national income will increase. national income will decrease. gross value added in production will decline. capital money foreign exchange goods Goods and services that benefit the society are called ... goods. A B C D 1.1.4 Economic integration where member countries agree on a common economic policy is called a ... A B C D 1.1.5 monetary growth fiscal economic The number of years that a new-born baby is expected to live is referred to as … A B C D 1.1.8 New Growth Path National Development Plan Expanded Public Works Programme Reconstruction and Development Programme Cash grants paid out to the poor form part of the … policy. A B C D 1.1.7 free-trade area. custom union. economic union. common market. Which government policy seeks to eliminate poverty and reduce inequality by 2030? A B C D 1.1.6 demerit harmful common merit the mortality rate. malnutrition. obesity. life expectancy. The North-South divide can also be referred to as the … gap. A B C D development inflation monetary supply (8 x 2) (16) 1.2 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches the item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–I) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK. 1.2.1 COLUMN A Exogenous explanation 1.2.2 Leading indicators 1.2.3 Special drawing rights 1.2.4 Free-floating 1.2.5 Public goods 1.2.6 Nationalisation 1.2.7 World Bank 1.2.8 Repo rate A COLUMN B liquid assets made available by the IMF to finance deficits on the balance of payments (BOP) B supplies financial development assistance mostly to developing countries C charged by the Reserve Bank to other financial institutions for loanable funds D markets are inherently stable and need no government intervention E shows the direction in which the economy might be heading F believes markets are inherently unstable and government intervention is necessary G the state takes ownership of privatelyowned enterprises and assets H exchange rate system where the value of the currency is determined by market forces only I provided by the government for use by all members of society, for example public libraries (8 x 1) (8) 1.3 Give ONE term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK. Acronyms and abbreviations will NOT be accepted. 1.3.1 Value of all final goods and services produced within the borders of a country for a specific period 1.3.2 A curve that shows the relationship between tax rates and tax revenue 1.3.3 A trade policy which promotes the replacement of imported goods with locally produced goods 1.3.4 A spatial area for regional development that forms a passageway 1.3.5 Removal of unnecessary laws and regulations to improve the functioning of the economy 1.3.6 Return of land to those who have lost it due to discriminatory laws of the past (6 x 1) TOTAL SECTION A: ACTIVITY 6 (NOV 2018) SECTION A (COMPULSORY) 30 MARKS – 20 MINUTES QUESTION 1 1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.9 D. 1.1.1 An open economy is best described as a … sector economy. A B C D 1.1.2 Investment is an example of a/an ... in the circular flow model. A B C D 1.1.3 one two three four leakage injection withdrawal loss Fiscal policy is an action taken by government in respect of taxation and ... to influence economic activity. A B C D exchange control money supply expenditure credit control (6) 30 1.1.4 Economies of scale are associated with … A B C D 1.1.5 Production by the citizens of a country, locally and abroad, is called the … product. A B C D 1.1.6 spatial development initiatives. industrial development zone. special economic zone. foreign investment grant. The comparison of a country's export prices with import prices by means of indexes is referred to as the … A B C D 1.1.8 gross national gross domestic net national net domestic A physically enclosed area next to a harbour or airport where production for exports is encouraged through incentives, is known as the … A B C D 1.1.7 mass production. limited output. long-term average cost increases. increased wastage. exchange rate. conditions of trade. terms of trade. inflation rate. Economic development is measured in terms of the … A B C D per capita gross domestic product. increase in the productive capacity. nominal gross domestic product. money supply. (8 x 2) (16) 1.2 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches the item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–I) next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK. 1.2.1 COLUMN A Nationalisation 1.2.2 Medium-term expenditure framework 1.2.3 System of national accounts 1.2.4 A COLUMN B number of years a person will live after birth B persuasion of banks by the South African Reserve Bank (SARB) C indicator used to measure the change in the price of goods produced locally when it leaves the factory floor Money flows D measures income inequality and wealth 1.2.5 Protectionism E movement of income and expenditure between participants in the economy 1.2.6 Gini coefficient F shows income and expenditure estimates for a three-year period G prescribed by the United Nations to compile gross domestic product figures H trade policy that tries to keep the domestic economy safe by restricting the import of goods and services I transfer of functions and ownership of entities from the private to the public sector (8 x 1) 1.2.7 Life expectancy 1.2.8 Production price index (8) 1.3 Give ONE term for EACH of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK. Abbreviations, acronyms and examples will NOT be accepted. 1.3.1 A systematic record of all trade and financial transactions between one country and other countries for a particular period of time 1.3.2 Money paid by the government to a person/institution without any counterperformance 1.3.3 When a product is sold on a foreign market at a price that is lower than the cost of production in the country of origin 1.3.4 Increase in the productive capacity of a country 1.3.5 The rate at which commercial banks borrow money from the South African Reserve Bank 1.3.6 The policy inflation that aims to stabilise prices by combating (6 x 1) (6) TOTAL SECTION A: 30 ACTIVITY 8 (NOV 2019) SECTION A (COMPULSORY) 30 MARKS – 20 MINUTES QUESTION 1 1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.9 D. 1.1.1 A period when there is a general increase in economic activities is known as a(n) … A B C D 1.1.2 downswing. upswing. depression. recession. National income will increase when … A B C D G + I + X > S + T + M. G + I + X < S + T + M. G + I + X = S + T + M. S + T + M > G + I + X. 1.1.3 Indicators that change at the same time and in the same direction as the economy changes are known as … indicators. A B C D 1.1.4 Where one country can produce goods or services cheaper than another country within a given time period it is called … A B C D 1.1.5 foreign trade. inflation. money supply. real GDP. The Department of Trade and Industry initiative that focuses on improving competitiveness in production is called the … A B C D 1.1.8 tax revenue and tax rate. income and expenditure. nominal and real figures. tax revenue and wages. Production, as an economic indicator, relates to … A B C D 1.1.7 comparative advantage. absolute advantage. terms of trade. free trade. The Laffer curve shows the relationship between … A B C D 1.1.6 leading lagging composite co-incident National Industrial Policy Framework. National Research and Development Strategy. Integrated Manufacturing Strategy. Small Business Support Programme. The demand-side policy relates to … A B C D a reduction in costs. improving the efficiency of inputs. the influence on inflation and unemployment. improving the efficiency of markets. (8 x 2) (16) 1.2 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches the item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–I) next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK. 1.2.1 COLUMN A Leakages 1.2.2 Exogenous approach 1.2.3 Human Development Index 1.2.4 Extrapolation 1.2.5 Portfolio investment 1.2.6 Terms of trade 1.2.7 Gross domestic product 1.2.8 Deregulation A COLUMN B estimate figures or trends in future from facts that are known B a country's export prices are compared to its import prices C the removal of laws, regulations and bylaws by government D independent factors that influence business cycles and originate outside the economy E a trade policy where the state discourages the import of certain goods and services to protect local industries F outflow of money from the economy G total value of final goods and services produced within the boundaries of a country for a specific period H buying of financial assets such as shares in companies on the stock exchange of another country I the well-being of people determined by health, education and income (8 x 1) (8) 1.3 Give ONE term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK. Abbreviations, acronyms and examples will NOT be accepted. 1.3.1 The initial change in spending produces a proportionately larger increase in national income 1.3.2 The point where the economic contraction is at its lowest 1.3.3 A transfer of functions and ownership from the public sector to the private sector 1.3.4 An increase in the price of a currency in terms of another currency due to market forces 1.3.5 The movement of imports and exports between countries without any restrictions 1.3.6 The social indicator that relates to the size of the country's population (6 x 1) (6) TOTAL SECTION A: 30 ACTIVITY 9 (NOV 2020) SECTION A (COMPULSORY) 30 MARKS – 20 MINUTES QUESTION 1 1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.9 D. 1.1.1 The difference in the value of the output at the peak and the value of the output at the trough of a business cycle is known as the … A B C D 1.1.2 One of the member countries of the BRICS Protocol is … A B C D 1.1.3 length. trend line. amplitude. real output. Japan. China. England. Italy. If the marginal propensity to consume (mpc) is 0,6 in a 2-sector model, the marginal propensity to save (mps) will be … A B C D 4. 6. 9,4. 0,4. 1.1.4 Which ONE of the following is presented in October to inform parliament of changes in the budget since February? A B C D 1.1.5 Long-term deposits of the domestic sector at monetary institutions are part of the … money supply. A B C D 1.1.6 income levels. preferences and tastes. the size of the population. labour resources. An interest rate that commercial banks offer to their most valued clients is called the … rate. A B C D 1.1.8 M1 M2 M3 M4 A supply reason for international trade is/are … A B C D 1.1.7 Main budget Medium-term Budget Policy Statement Medium-term Expenditure Framework National budget prime repo fixed preference Which ONE of the following is classified as excise duties? A B C D Tax on alcohol Gun licence Value-added tax Personal income tax (8 x 2) (16) 1.2 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches an item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–I) next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK. COLUMN A Autonomous consumption A 1.2.2 New economic paradigm B coordinates government actions to increase the competitiveness of South African businesses 1.2.3 Bureaucracy C focus on the acquisition of skills 1.2.4 Mass production D 1.2.5 JIPSA spending that takes place irrespective of the level of income 1.2.6 Dumping E the smoothing of business cycles using monetary and fiscal policy 1.2.7 Economic growth F ensures the supply of standardised articles through an automated mechanical process G increase in a country's production capacity H official rules and regulations that can hinder service delivery I selling goods in another country at very low prices with which the local industry cannot compete (8 x 1) 1.2.1 1.2.8 Integrated manufacturing strategy COLUMN B the owners of the factors of production in the economy . (8) 1.3 Give ONE term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK. Abbreviations, acronyms and examples will NOT be accepted. 1.3.1 The labour force between the ages of 15 and 65 that are willing and able to work 1.3.2 It illustrates (shows) the relationship between unemployment and inflation 1.3.3 A form of credit from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) which can be used when balance of payments difficulties are experienced 1.3.4 A penalty imposed by one or more countries on another country by restricting trade 1.3.5 Consultation between the South African Reserve Bank and banks to persuade them to act in a manner that is desirable 1.3.6 An increase in the number of people moving from rural areas to cities (6 x 1) (6) TOTAL SECTION A: 30 ACTIVITY 10 (NOV 2021) SECTION A (COMPULSORY) 30 MARKS – 20 MINUTES QUESTION 1 1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.9 D. 1.1.1 Long-term financial instruments, such as shares, are traded in the … market. A B C D 1.1.2 money capital foreign exchange labour Business cycles that are caused by changes in the construction industry that last for 15 to 20 years are called … cycles. A B C D Kuznets Kitchin Jugler Kondratieff 1.1.3 Transfer of ownership of entities from the private sector to the public sector is called … A B C D 1.1.4 Investment contracts that base their value on the underlying assets, such as currencies and commodities, are known as … A B C D 1.1.5 National Development Plan. Reconstruction and Development Programme. Growth, Employment and Redistribution Programme. Accelerated and Shared Growth Initiative for South Africa. A cash incentive that aims to provide investment in the training of the South African labour force to gain new expertise, is called the … A B C D 1.1.8 World Bank. International Monetary Fund. World Trade Organisation. World Health Organisation. The growth and development policy that aims to eliminate poverty and reduce inequality by 2030, is known as the … A B C D 1.1.7 other investments. direct investments. financial derivatives. portfolio investments. The international organisation that reduces tariffs and other trade barriers to liberalise trade is called the … A B C D 1.1.6 privatisation. commercialisation. deregulation. nationalisation. Critical Infrastructure Programme. Skills Support Programme. Custom Free Incentives. Small Business Support Programme. The percentage of the population living in poverty in a country is indicated by … A B C D the Gini coefficient. life expectancy. per capita gross domestic product. the headcount index. (8 x 2) (16) 1.2 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches the item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–I) next to the question numbers (1.2.1–1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.2.9 J. 1.2.1 COLUMN A Transfer payment 1.2.2 Investment 1.2.3 Cash reserve requirements B monitors identifiable and definable issues related to human well-being 1.2.4 Price discrimination C 1.2.5 Social indicator nationwide government intervention to create employment using labour intensive methods 1.2.6 Desirable mix D money received without any productive service rendered 1.2.7 Industrial development zones E charging different customers, different prices for the same product Expanded Public Works Programme F spending by businesses on capital goods G used to control money supply through buying and selling of government securities H purpose-built industrial estates that are physically enclosed and link to international ports I the minimum amount of money that the South African Reserve Bank requires banks to maintain in order to manipulate money creation activities (8 x 1) 1.2.8 A COLUMN B combination of international trade policies suitable for the prevailing conditions in an economy (8) 1.3 Give ONE term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK. Abbreviations, acronyms and examples will NOT be accepted. 1.3.1 When a country involved in international trade, produces more output than other countries given the same input 1.3.2 A document that details expected revenue and projected expenditure for the next fiscal year 1.3.3 Tax systems where low-income earners pay higher tax rates while high-income earners pay lower tax rates 1.3.4 The provision of incentives to encourage local businesses to produce goods to sell to other countries 1.3.5 The process that focuses on the improvement of people's standard of living 1.3.6 The industrial development strategy that focuses on improving the competitiveness in manufacturing by considering input prices and technology. (6 x 1) (6) TOTAL SECTION A: 30