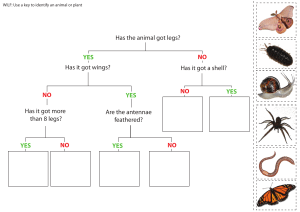
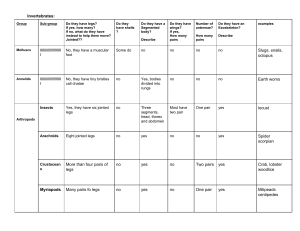
Chapter 1: Characteristics and classification of living organisms Hi! I am MRS GREN M ovement Respiration S ensitivity Growth Reproduction E xcretion Nutrition 7 characteristics of living things MCQ #01 MCQ #01 answer Movement Respiration Sensitivity Growth Reproduction an action by an organism or part of an organism causing a change of position or place the chemical reactions in cells that break down nutrient molecules and release energy for metabolism the ability to detect and respond to changes in the internal or external environment a permanent increase in size and dry mass the processes that make more of the same kind of organism Excretion the removal of the waste products of metabolism and substances in excess of requirements Nutrition the taking in of materials for energy, growth and development Classification Describe: - species: a group of organisms that can reproduce to produce fertile offspring - binomial system: an internationally agreed system in which the scientific name of an organism is made up of two parts showing the genus and species Homo sapiens Dichotomous key: Classification Methods Nitrogenous base to reflect evolutionary relationships 1. Morphology -- the overall form and shape of the bodies 2. Anatomy -- the detailed body structure by dissection 3. Sequences of bases in DNA -- groups of organisms which share a more recent ancestor (are more closely related) have base sequences in DNA that are more similar than those that share only a distant ancestor A -- T C -- G MCQ #02 MCQ #02 MCQ #03 Common features in living organisms Cell membrane DNA Cytoplasm Ribosome Enzymes Seven Levels of Classification Kingdom Phylum Class Increase in similarity Order Decrease in numbers Family Genus Species Kingdom #01 -- Protoctists multicellular/ unicellular have nucleus may/may not have cellular cell wall or chloroplasts feed by photosynthesis/ on organic substances Amoeba Paramecium Kingdom #02 -- Prokaryotes unicellular no nucleus/ nuclear membrane have a cell wall, not made of cellulose (murein/ peptidoglycan cell wall) may/may not photosynthesise naked loop of DNA (plasmids) no membrane-bound organelles e.g. mitochondria reproduce by binary fission Kingdom #03 -- Fungi multicellular do not have chlorophyll and do not photosynthesise have a nucleus and cell wall (not made of cellulose) feed by saprophytically, or parasitically, on organic material like faeces, human foods and dead plants or animal Kingdom #04 -- Plantae multicellular organisms cell wall made of cellulose feed by photosynthesis may have roots, stems and leaves Kingdom #05 -- Animals Multicellular Have a nucleus Feed on substances made by other living things Phylums -- Vertebrates (5 classes) Fish Amphibians Birds Reptiles Mammals Scales Fins Lateral line Moist skin Four limbs Feathers Beak Two wings Two scaly legs Scaly,dry skin Four limbs Fur/hair Four limbs Pinna/extern al ears Nose/snout Nipples Fish Amphibians Birds Reptiles Mammals Eggs Jelly-covered Jelly-covered Hard-shelled Soft-shelled live young Fertilisation External External Internal Internal Internal Body temperature regulation Ectothermic Ectothermic Endothermic Ectothermic Endothermic Gas exchange Gills Skin/Lungs Lungs Lungs Lungs Additional info - - -4 chambers in the heart - -mammary glands -placenta -4 chambers in the heart -diaphragm -4 types of teeth -sweat glands Phylums -- Arthropods -invertebrates -waterproof exoskeletons -segmented body -jointed legs Insects Crustaceans 3 pairs of jointed legs head, thorax, abdomen 1 or 2 pairs of wings 1 pair of antennae 1 pair of compound eyes breathe through trachea chelipeds/claws 2 pairs of antennae 5 pairs of jointed legs exoskeleton + calcium salts breathe through gills Phylums -- Arthropods -invertebrates -waterproof exoskeletons -segmented body -jointed legs Myriapods long, thin, segmented body each segment has jointed legs 1 pair of antennae no obvious thorax and abdomen many legs (more than 10) Arachnids 4 pairs of jointed legs 2 pairs of antennae cephalothorax, abdomen no wings breathe through book lungs MCQ #04 Phylums -- Invertebrates Nematodes s d i l e n An t) n e m e v o m ( s le t bris ucus m h it w d e r e v o body c r) (conserve wate mouth + anus sex) r e t in ( e it d o r h p herma dy o b d e t n e m g e s , long no segments, smooth long, cylindrical body body painted on both ends Molluscs soft, unsegmented body muscular foot (burrowing + movement) mantle visceral mass slimy body Phylums (Plants) Flowering plants e.g. corn, pea Have xylem and phloem Reproduce by producing seeds Seeds produced inside ovary, inside flower Non flowering plants Have roots,stems and leaves e.g. ferns, mosses Have leaves called fronds Do not produce flowers Reproduce by spores Dicots vs Monocots Dicots Monocots Cotyledons 2 1 Floral parts 4x or 5x 3x Veins branched parallel Leaves broad narrow tap root branching root Root system Viruses - not true living things but complicated assemblies of molecules - no show 7 characteristics of living things protein coat, capsid genetic material (DNA or RNA strand) no typical cell structure