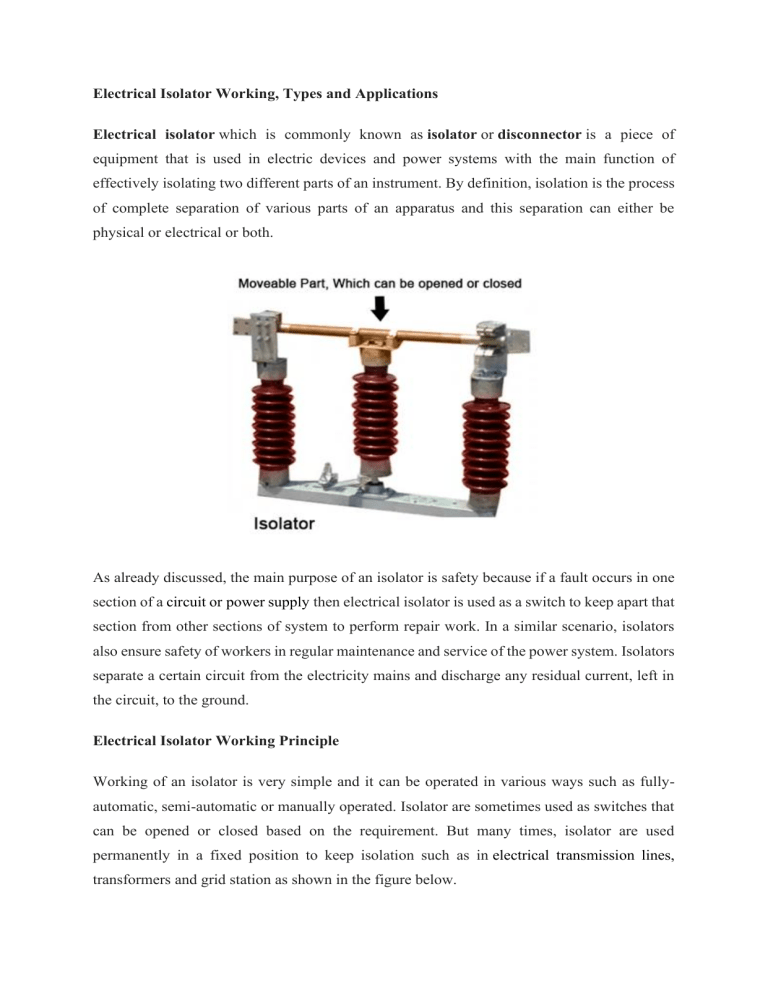
Electrical Isolator Working, Types and Applications Electrical isolator which is commonly known as isolator or disconnector is a piece of equipment that is used in electric devices and power systems with the main function of effectively isolating two different parts of an instrument. By definition, isolation is the process of complete separation of various parts of an apparatus and this separation can either be physical or electrical or both. As already discussed, the main purpose of an isolator is safety because if a fault occurs in one section of a circuit or power supply then electrical isolator is used as a switch to keep apart that section from other sections of system to perform repair work. In a similar scenario, isolators also ensure safety of workers in regular maintenance and service of the power system. Isolators separate a certain circuit from the electricity mains and discharge any residual current, left in the circuit, to the ground. Electrical Isolator Working Principle Working of an isolator is very simple and it can be operated in various ways such as fullyautomatic, semi-automatic or manually operated. Isolator are sometimes used as switches that can be opened or closed based on the requirement. But many times, isolator are used permanently in a fixed position to keep isolation such as in electrical transmission lines, transformers and grid station as shown in the figure below. This figure shows isolators being used as insulators in transmission lines to isolate transmission tower from the conductor. And here isolators are particularly useful in eliminating grounding loops, such as lowering the risk of accidental paths for electric current to flow towards the ground. Isolator switches, in particular, are used in power grids and substations to efficiently isolate very high voltage apparatuses such as transformers and circuit-breakers when they are due for maintenance. Commonly used isolators are not intended to stop current during a fault or eliminate high voltage arcs, which occur due to disturbance in electric conductors. In highvoltage power systems, isolators are used in conjunction with circuit breakers to provide an extra layer of safety. First circuit breaker is opened which disconnects the circuit then isolator is also opened. And for the reverse process, first isolator is closed then circuit breaker is closed and circuit is reconnected. Picture below shows the isolators in a disconnected state within a power substation. It can be seen that it is a physical and mechanical system. And It can be operated manually or it can be actuated automatically. Applications of Isolators have found in providing safety during the service and maintenance of power system, power grid and transmission lines. They are also used in homes to provide essential safety and protection against any electrical problem. Types of Isolators There are various kinds of isolators available in the market. Choice of electrical isolators depend upon the requirement and application and based on the placement in the system. Isolators based on Application can be classified into four types 1. Single Break Isolator 2. Double Break Isolator 3. Pantograph Isolator 4. MCB Isolator Depending upon the position in power system, the Isolators can further be categorized into following three types according to their placement in the power system. 1. Bus side isolator: It directly connects to the main bus 2. Transfer bus side isolator: It directly connects to the transfer bus. 3. Line side isolator: It is generally located at line side of the feeder In single break isolator only one terminal connects and disconnects whereas in double break isolator both terminals at each side connect and disconnect because central terminal is moveable. In pantograph type isolator both terminals at each side connect and disconnect only because of the forces of stress or tension, and usually is no locking mechanism. This type of pantograph isolator is widely used in electric trains to obtain electricity from overhead transmission lines. Miniature circuit breaker (MCB) as apparent from the name is designed for low power requirements such as homes and offices. It is designed in small compact cases so that it can be used in domestic scale wiring systems. Horizontal double break isolator in substations use is abundant. Isolators are generally used on both side of the circuit breaker, this measure is taken just to ensure extra safety and protection because in power system incoming and outgoing lines can have multiple sources of power and disconnecting one side is sometimes not enough. So, isolator on both sides of circuit breaker allow essential replacement and services requirements to be performed safely. Difference between Isolator and Circuit Breaker A major question arises in mind that why isolator is used on both sides of circuit breaker? Isolator is designed to work when there is no load connected which makes it an off-load device. Whereas circuit-breaker is considered an on-load device. Both of these devices have the common purpose of disconnecting a certain section of the circuit from rest of the system. Circuit breaker is an electronic device made up of solid-state components like MOSFETs and BJTs whereas an isolator is a mechanical equipment and it works as a switch. A question arises that what is the point of using isolator when it cannot even be used under load whereas circuitbreaker trips automatically under fault? Answer to this question is quite straight forward. When circuit breaker trips due to a certain fault then we cannot make sure whether or not a faulty area is completely isolated because circuit-breakers are mostly installed remotely. To make sure that a system is completely isolated, a physical and mechanical on-site isolation system is used. Isolators have overall lower capacity of withstanding current and voltage relative to circuit breaker. Applications of Isolator The applications of isolator include the following. • High Voltage Devices: Isolators are used in High Voltage devices. • Isolator in Substation: When a fault occurs in a substation, then isolator cuts out a portion of a substation. • Signal Isolation: Isolators can be used for isolation of signal.