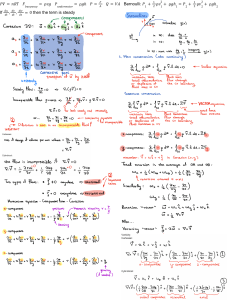
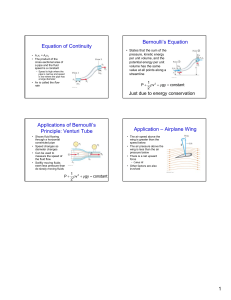
FLUID DYNAMICS Engr. Hassan Arshad Today’s Content • • • • Different types of heads (or energies) of a liquid in motion Bernoulli’s equation Euler’s equation for motion Bernoulli’s equation for real fluids INTRODUCTION The science which deals with the action of the forces in producing or changing motion of fluids is known as “hydrokinetics”. The dynamic equation of fluid motion is obtained by applying Newton’s second law of motion. The fluid is assumed to be incompressible and nonviscous. DIFFERENT TYPES OF HEADS (OR ENERGIES) OF A LIQUID IN FLOW Potential head or potential energy: This is due to configuration or position above some suitable datum line. It is denoted by z. Velocity head or kinetic energy: This is due to velocity of flowing liquid and is measured as V2/2g. Pressure head or pressure energy: This P/w. is due to the pressure of liquid and reckoned as Total head Total Head In a pipe of 90 mm diameter water is flowing with a mean velocity of 2 m/s and at a gauge pressure of 350 kN/m2. Determine the total head, if the pipe is 8 meters above the datum line. Neglect friction. EULER’S EQUATION OF MOTION FOR FLOW ALONG A STREAMLINE This is equation of motion in which the forces due to gravity and pressure are taken into consideration. This is derived by considering the motion of a fluid element along a stream-line. EULER’S EQUATION BERNOULLI’S EQUATION BERNOULLI’S EQUATION FOR REAL FLUIDS Some Comments on B.EQ’s In 1738 Daniel Bernoulli published his Hydrodynamics in which an equivalent of this famous equation first appeared. To use it correctly we must constantly remember the basic assumptions used in its derivation: viscous effects are assumed negligible, the flow is assumed to be steady, the flow is assumed to be incompressible, and the equation is applicable along a streamline. Finding Pressure using B.EQ The water is flowing through a pipe having diameters 20 cm and 10 cm at sections 1 and 2 respectively. The rate of flow through pipe is 35 liters/s. The section 1 is 6 m above datum and section 2 is 4 m above datum. If the pressure at section 1 is 39.24 N/cm2, find the intensity of pressure at section 2. Any Questions?