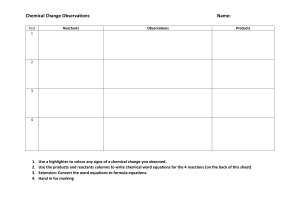
SNC2D Conservation of Mass Page 1 of 1 Conservation of Mass • • atomic theory states that matter is neither created, nor destroyed significant contributions were made by Antoine Lavoisier who, together with his wife Marie-Anne, conducted hundreds of experiments on chemical reactions • their work is summarized in the Law of Conservation of Mass which states that In a chemical reaction, the total mass of the products is always the same as the total mass of the reactants • • • therefore, in a chemical reaction, the atoms are simply rearranged chemical reactions are shown using chemical equations the general form is shown below REACTANTS PRODUCTS Left Side Starting Substances • Right Side Ending Substances there are 3 types of chemical equations: 1. Word Equations e.g., hydrogen + describe the chemical reaction in words oxygen water “hydrogen reacts with oxygen to produce water” 2. Skeletal Equations e.g., 3. e.g., H2 + words are replaced with chemical formulas O2 H2 O Balanced Chemical Equation follows the Law of Conservation of Mass – type and number of atoms on reactant side equals that on the product side 2 H2 + O2 2 H2 O Coefficients are used to show how many molecules are reacting NOTE: you must never change the subscripts – this changes the chemical formula for a substance Additional Information • often the letters s, l, g are added to the compounds to show the state of matter (i.e., (s) is a solid; (l) is a liquid; and (g) is a gas) • (aq) refers to aqueous solution – something dissolved in water