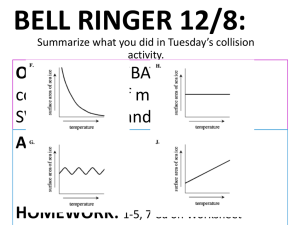
Name : …………………………… Date : …………………….. Conservation of Linear Momentum A) Objectives: 1) Make a conclusion about the kinetic energy (KE) and momentum of a system in elastic and inelastic collisions. 2) Calculate the KE and momentum before and after collision. B) Procedure: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Go to https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/collision-lab/latest/collision-lab_en.html Select Explore 1D To make the collision elastic, drag the slider all the way to the right until it says 100% elastic. Click the box, more data to get information on position, velocity, and momentum. Complete Table C to G. C) Elastic Collision Same Mass Objects m1 m2 v1 v2 1 1 2 -3 2 2 1 -2 3 3 0 -3 pi = m1v1+m2v2 𝟏 𝟏 KEi = 𝟐 m1v12 + 𝟐 m2v22 v1’ v2’ pf = m1v1’+m2v2’ 𝟏 𝟏 KEf = 𝟐 m1 v1’2 + 𝟐 m2 v2’2 D) Elastic Collision Different Mass Objects m1 m2 v1 v2 1 2 3 -1 2 3 2 -3 3 1 0 -3 pi = m1v1+m2v2 𝟏 𝟏 KEi = 𝟐 m1v12 + 𝟐 m1v22 v1’ v2’ pf = m1v1’+m2v2’ E) Elastic Collisions Questions: 1) What do you notice about the value of the kinetic energy before and after collision? 2) Compare the momentum of the system before and after the collision. 𝟏 𝟏 KEf = 𝟐 m1 v1’2 + 𝟐 m1 v2’2 Note: For F and G, make sure that you move the elasticity slider all the way to the left to simulate inelastic collision. F) Inelastic Collision Different Mass Objects m1 m2 v1 v2 1 2 3 -1 2 3 2 -3 3 1 0 -3 pi = m1v1+m2v2 𝟏 𝟏 v1’ v2’ pf = m1v1’+m2v2’ KEf = 𝟐 m1 v1’2 + 𝟐 m1 v2’2 𝟏 𝟏 v1’ v2’ pf = m1v1’+m2v2’ KEf = 𝟐 m1 v1’2 + 𝟐 m1 v2’2 KEi = 𝟐 m1v12 + 𝟐 m1v22 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 G) Inelastic Collision Same Mass Objects m1 m2 v1 v2 1 1 2 -3 2 2 1 -2 3 3 0 -3 pi = m1v1+m2v2 KEi = 𝟐 m1v12 + 𝟐 m1v22 H) Inelastic Collisions Questions : 1) What do you observe about the momentum before and after collision for both table F and G? 2) What do you observe about the kinetic energy before and after collision for both table F and G? I) Conclusion 1) Describe elastic collisions in terms of KE and momentum before and after collisions. 2) Describe inelastic collisions in terms of KE and momentum before and after collisions.