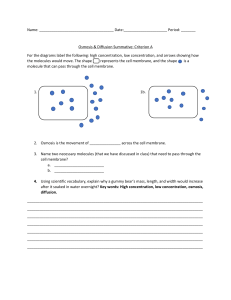
Osmoregulation: Guided Notes Directions: Fill in the blanks below. -Let’s take it back a step Osmosis is an example of __________________________________. Passive transport is the movement of molecules across a cell membrane with ________ ___________________________________. Ie. Osmosis, Diffusion, Facilitated Diffusion -Check for understanding Why is osmosis considered to be an unique example of passive transport? Molecules in Passive Transport ● Molecules that are able to freely pass the cell membrane ○ _______________________ ○ _______________________ ○ _______________________ -Components of the Cell Membrane ● HYDROPHILIC ○ Having a tendency to ___________________________ by water. ● HYDROPHOBIC ○ Having the tendency to ___________________________ water. -Facilitated Diffusion Facilitated diffusion is the movement of substances across a cell membrane by ______ _______________________ that use no energy. -Protein Involvement ● _____________________ ○ A transport protein that is specific for a molecule, or group of substances. ■ Ie. ATPase, ABC Transporters etc. ● ______________________ ○ A type of transport protein, acts like a pore in the membrane that lets water molecules or small ions through quickly ● ________________________ ○ A transport protein that opens a "gate," allowing a molecule to pass through the membrane. Gated channels have a binding site that is specific for a given molecule or ion. ■ Ie. Sodium-potassium pump -Facilitated Diffusion Cont’d ● Concentration Gradient ○ The gradient creates potential energy which increases as the concentration difference increases, which results in faster diffusion. ● Temperature ○ Carrier transport rates increase more rapidly with temperature. ● Saturation ○ Since the number of carrier proteins in the membrane is limited, once all the proteins are bound, they can no longer bind more molecules. ● Selectivity ○ There is a reciprocal relationship between the transport rate and the selectivity of the transport process. -What is ATP? ● Adenosine triphosphate, abbreviated usually ATP ○ Is an important “______________________” found in all life forms ● ATP is the energy form for cells. ○ It is one of the byproducts of Cellular Respiration and the breakdown of __________. -Sodium-Potassium Pump Sodium-Potassium pump is a transport system in a biological membrane where ________ Na+ ions are taken out while _________ K+ ions are taken into the cell against their respective concentration gradients. -What Does It Do? ● In the Kidneys specifically, it helps maintain osmoregularity. ○ It does this by automatically having salt leave a cell when a cell begins to swell. ○ Function is to pump ____________ sodium ions out of the cells and ________________ potassium ions within the cells -Let’s Figure It Out 1. What is going on here? 2. On a cellular level, what process/es are preventing homeostasis in the muscle cells here?