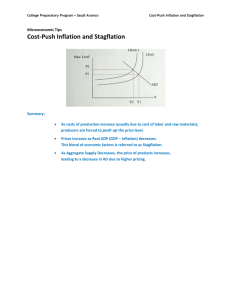
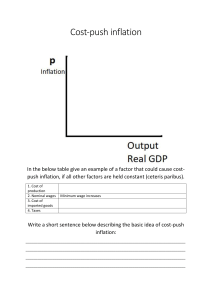
Four Market Structures Exercises Market structure Number of firms Control over price Type of goods Ease of market Answers entry Many, few, one None, little, Some/a lot, total Different, identical, Easy/difficult unique Many None Identical Easy Monopolistic competition Many Little Different Easy Oligopoly Few Some/A lot Perfect competition Difficult Different/Identical Monopoly One Total Unique Difficult Classroom Inflation Simulation Each person in this class is a Food Truck owner What are your actions in response to the Foam Ban? www.nytimes.com Business Environment Analysis - PEST tool EXTERNAL POLITICAL ECONOMICAL SOCIAL TECHNOLOGICAL Business Environment Analysis - PEST tool INTERNAL POLITICAL ECONOMICAL SOCIAL TECHNOLOGICAL What is money? Money – anything widely accepted in exchange for goods and services. Auction Rules • A, B, C groups • Five items will be auctioned in each of the 2 rounds • Money left in round 1 can be used in round 2 • The highest bidder will win each item The highest bid is your total minus $1. The lowest bid is $1 You can't spend all your money on one item • The five items represent total output of goods and services produced in the classroom economy • You may not combine your money with anyone else’s in the room Auction Product Total GDP Round 1 price Product Total GDP Round 2 price Discussion What happened to prices in Round 2 compared with those in Round 1? Were the goods in the auctions different in any way? Were there any more items available to buy in Round 2 than in Round 1? Why were prices higher in Round 2? What is inflation Amount of money injected into an economy outstrips the increase in actual output. Each dollar of income will buy fewer goods and services than before People have more money to spend, but there will be the same quantity of product available for them to buy. As they compete with one another to buy available products or services prices go up. Demand-pull and cost-push inflation