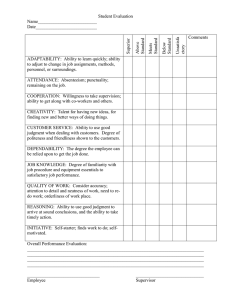
FORMS OF KNOWLEDGE FORM OF KNOWLEDGE Concept Academic Rule DEFINITION COMPONENTS A group or class of items, events, or people that are related through the possession of common characteristics. (Essentially, anything with a definition.) Found in all subjects Categories (way of classifying) Has essential attributes Taught deductively and inductively Examples: main idea, sequence Identify concepts within concepts Established procedures or ways of performing to achieve a desired end. Describes situations Are man-made and found mainly in English and math Issues a command Provides practice Teaching a rule is a matter of providing a situation and issuing a command. Example: Change the “y” to “I” and add “es” Found in natural and social sciences Cause/Effect relationship Example: Air pressure increases (effect) as air velocity increases (cause) Describe situation Issue the command Provide practice for the application of the rule Present formal statement of the law/principle using linking words (if and then) Discuss and explain cause Discuss and explain effect Apply law / principle State value question Develop judgmental criteria Assemble facts Make value judgment Identify the skill Demonstrate/model the skill Have students practice the skill Law or Law-Like Statement Value Knowledge / Judgment Skill MOST EFFECTIVE WAY TO TEACH A statement of the relationship between two concepts; one concept is the condition (cause), one concept is the consequence (effect) Assessment of the value or worth of an object, event, or action Ability to perform an act Found in all subjects A category of knowledge that contains statements that assign value or worth to an object, even, or idea State and explore value questions Develop criteria for value judgments Assemble the facts Test the value judgment Value terms: good, bad, fair, reasonable, worthwhile, beautiful, friendly, interesting, helpful, friendly Production Physical: Involves hands or body Especially in arts, crafts, music, PE, and handwriting State definition/attributes Give examples Give non-examples/distinguish related concepts Test examples Use concept induction when appropriate