Post-Op Mastectomy Care: Case Study & Interventions
advertisement

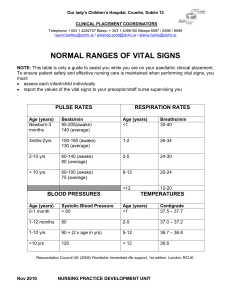
Chapter 37 – Care of the Surgical Patient Learning Outcomes: - Select interventions to prevent each of the potential postoperative complications Prepare to perform an immediate postoperative assessment when a patient returns to the nursing unit Case Scenario: T.S. is a 37-year-old female that had a double mastectomy performed this morning. She is being admitted to your unit for post-operative care and patient education. She had a double mastectomy because she has a family history of breast cancer and the BRCA gene. She arrives from the PACU and appears drowsy but comfortable. Her vital signs are: Temperature 36.40 C, HR 76, BP 128/86, RR 14, oxygen saturation 97% on 2L/min oxygen via nasal cannula, pain 2/10 upon arrival to the unit. Her dressings are clean, dry, intact. She has 2 drains on each side of her chest for a total of 4 drains. Use an X to indicate which actions listed in the left column would be included in the plan of care to help prevent T.S. from developing post-operative complications Actions Perform vital signs every 4 hours Encourage T.S. to use the incentive spirometer every hours she is awake Do not have T.S. drink water or eat to help prevent nausea for 48 hours Encourage T.S. to take pain medication only when her pain gets to really bad Have T.S. wear sequential pneumatic compression devices in bed and to begin walking when she feels strong enough Plan of Care Answers/Rationale: Actions Perform vital signs every 4 hours Encourage T.S. to use the incentive spirometer every hours she is awake Do not have T.S. drink water or eat to help prevent nausea for 48 hours Encourage T.S. to take pain medication only when her pain gets to really bad Have T.S. wear sequential pneumatic compression devices in bed and to begin walking when she feels strong enough Plan of Care Copyright © 2022, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. x x Chapter 37 – Care of the Surgical Patient T.S. needs to use her incentive spirometer every hour while she is awake to help prevent respiratory complications like pneumonia. T.S. can also cough and deep breath. The important thing is to prevent the development fluid in the lungs that can lead to pneumonia. T.S. needs to wear sequential pneumatic compression devices while in bed and begin to walk when she feels strong enough to help prevent the development of blood clots or venous thromboembolism. Walking will also help decrease the risk of getting pneumonia from remaining in bed. The nurse needs to perform vital signs more frequently on a post-operative patient. Vital signs are usually taken q15 minutes x 4, q30 minutes x 2, q1h x 4, and then q4h for 24-48 hours depending on hospital policy. The time immediately after anesthesia is when the patient is most at risk for complications so close monitoring is required. You want T.S. to maintain fluid balance after surgery, once she is awake and is able to swallow without difficulties T.S. should be offered ice chips or sips of water. She would be allowed to drink water once she is fully awake. Food should be withheld until bowel sounds return to prevent the development of a paralytic ileus, however the patient can still have water while waiting for bowel sounds to return as long as the water does not make her nauseous and vomit. T.S. should take pain medication n a regular basis immediately after surgery to prevent the pain for being so bad T.S. is unable to function. Once pain gets severe it is really difficult to get the pain under control and make the patient comfortable. It is important that you explain to T.S. that taking pain medication regularly for a couple of days after surgery will not lead to addiction and is beneficial because when T.S. does not have a significant amount of pain, she is more likely to walk and do her respiratory exercise to prevent postoperative complications. Reference: Williams: Fundamental Concepts and Skills for Nursing, 6th edition, Chapter 37 Copyright © 2022, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved.