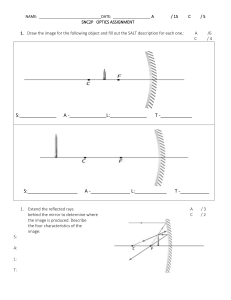
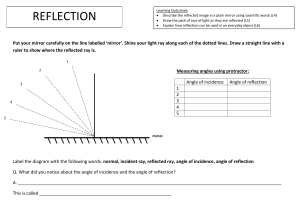
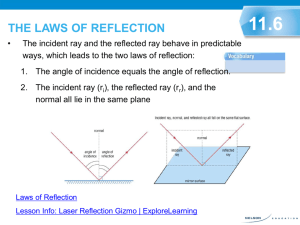
Do now… Describe what you see in this image. Extend: Explain what you see in this image. The Law of Reflection Learning outcomes By the end of this lesson you should be able to: o state the law of reflection o describe the features of a virtual image o draw labelled ray diagrams and use them to explain imaging in mirrors Plane mirrors & virtual images o Plane mirrors reflect light regularly, so they produce a clear image o The image that we see in a plane mirror is called a virtual image o Virtual images are the same size and the same distance behind the mirror as the object in front of it What’s the difference? TASK – In your groups, discuss what is different about the virtual image compared to the object in front of the mirror. Lateral inversion o The type of reversal for which right appears as left and left appears as right is known as lateral inversion o All virtual images are laterally inverted What is a normal line? o A normal line is a line that is perpendicular to a surface (it makes a 90° angle with the surface) o Protractors must always be used when drawing normal lines normal 90° plane mirror o Incident ray – the ray coming into the surface of the mirror (arrow pointing towards the mirror) o Reflected ray – the ray coming out of the surface of the mirror (arrow pointing away from the mirror) o Angle of incidence – the angle between the incident ray and the normal o Angle of reflection - the angle between the normal and the reflected ray Plane mirror Ray diagrams The law of reflection 𝜽𝒊 = 𝜽 𝒓 The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection How do we use reflections? We use our understanding of mirrors and reflection in periscopes. The rest of the PPT will not be in your exam Image formation in plane mirrors The next slides (16 – 20) show the steps for drawing a ray diagram to display the formation of a virtual image on the other side of a plane mirror Step 1 a. Copy the pencil and the plane mirror in your book b. Identify the top and the bottom of the pencil and label these A and B Step 2 a. Draw an incident ray starting at point A b. Draw a normal line where the incident ray meets the mirror c. Use a protractor to draw the reflected ray (remember that i = r) Step 3 Repeat step 2 (a. – c.) with a second incident ray at a different angle Step 4 a. Extend both reflected rays behind the mirror until they meet b. Label the point of intersection Ai Step 5 a. Repeat steps 2 – 4 for point B. b. Draw the virtual image of the pencil using points Ai and Bi as a guide Assessment for learning TASK – Copy the diagrams below in your books. Make sure you leave enough space around the diagrams to complete them. Draw the virtual images of the circle and the heart. mirror mirror