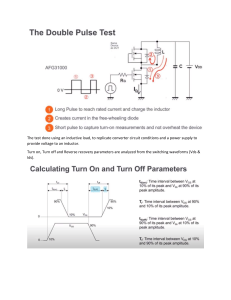
SUKKUR INSTITUTE OF BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION SUKKUR Example sheet #1: DC-DC Converter CCM Example 1: Analyze and design a Buck-Boost converter in continuous conduction mode (CCM): A buck-boost converter is illustrated in Fig: 1(a), and practical implementation using transistor and diode is shown in Fig: 1(b). Fig: 1(a) Fig: 1(b) (a) Derive the expressions for the dc components of each capacitor voltage and inductor current, as a function of the duty cycle D, the input voltage Vg and the load resistance R. ANS: V= -DVg/(1-D), IL= DVg/R(1-D)2 (b) Derive the expression for the inductor peak current ripple and the capacitor peak voltage ripple. ANS: i = VgDTs/2L, v = VgD2Ts/2RC(1-D) Example 2: Given the following values for the boost converter Input voltage Vg = 12V Output voltage V = -5V Switching frequency fs = 200 kHz Load resistance R = 2.5Ω (a) Calculate the values of D and I. ANS: D=0.294, IL=2.831 (b) Choose the value of L that will make the peak inductor current ripple i equal to fifteen percent of the average inductor current I. ANS: L=20.75 μH (c) Choose C such that peak output voltage ripple v is 25 mV. ANS: C=58.82μF (d) Calculate & sketch the MOSFET current and voltage waveforms, including ripples. ANS: IQ= 3.255A, VQ =17.025v