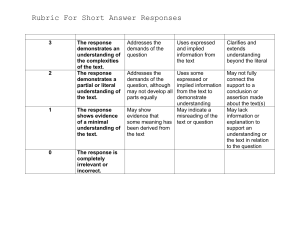
Agency vs Trust AGENCY TRUST Agent represents and acts for his principal Title and control of the property under trust instrument passes to the trustee who acts in his own name Agency may in general be revoked at any time Trust may be terminated only by fulfillment of its purpose Article 1869. Agency may be express, or implied from the acts of the principal, from his silence or lack of action, or his failure to repudiate the agency, knowing that another person is acting on behalf without authority. Agency may be oral, unless the law requires a specific form. Kinds of Agency 1. As to manner of its creation: a. Express – orally or in writing (authority) b. Implied – (enumeration is NOT exclusive) i. one which is implied from the acts of the principal ii. from his silence or lack of action, or iii. his failure to repudiate the agency knowing that another person is acting on his behalf without authority or iv. from the acts of the agent which carry out the agency v. from his silence or inaction according to the circumstances 2. As to its character: a. Gratuitous b. Compensated or onerous 3. As to extent of business covered: a. General – one which comprises all the business of the principal b. Special – one which comprises one or more specific transactions 4. As to authority conferred: a. Couched in general terms – one which is created in general terms and is deemed to comprise only acts of administration b. Couched in specific terms – one authorizing only the performance of a specific act/s. 5. As to its nature and effects: a. Ostensible or representative – agent acts in the name and representation of the principal b. Simple or commission – agent acts in his own name but for the account of the principal Form of Agency General rule: It is created by contract which may be oral, written or implied. Exceptions: a. When form is required for the validity of the contract b. When it is required to make the contract effective against third person c. When it is required for the purpose of proving the existence of a contract such as those provided in the Statute of Frauds Appointment of Agent It is not essential that an agent should be appointed directly by the principal, but the appointment may be made through another, as by referring an applicant to another and representing that he has authority to act, or the relation may arise out of an agreement to employ the agent of another, such person then becoming the agent of the first party. Presumption of Agency General rule: Agency is not presumed. The relation between principal and agent must exist as a fact. Burden of proof rests upon the person alleging the agency to show, not only the fact of its existence, but also its nature and extent. Exception: Presumption may arise in those cases where an agency may arise by operation of law or to prevent unjust enrichment. Authority of attorney to appear on behalf of his client 1. Authority in an action presumed – Rule 138, ROC Section 21, Section 22, Section 23. (Authority to represent is presumed) 2. Scope of authority – an act performed by counsel within the scope of a “general or implied authority” is regarded as an act of the client.