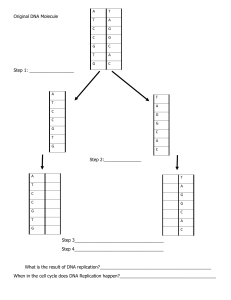
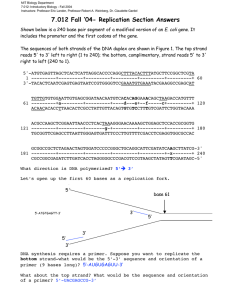
Some of the DNA replication enzymes: 1. 2. Topoisomerase- unwind DNA helix structure (change DNA topography); DnaA protein opens replication origin to form replication bubble; DNA – helicasebreak H-bonds between base pairs; this creates a replication fork; Y-shaped structure; with single stranded DNA section; 3. 4. DNA polymerase IIIfor polymerisation in prokaryote Delta DNA polymerase: for polymerisation in eukaryote 5. NB: 4 & 5 above also proof read a nucleotide they just added 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Leading strand; daughter strand continuously made towards a growing replication fork; because 3’ 5’ direction of reading parent template is towards the growing Replication fork; so its synthesised just behind the leading strand Lagging strand; daughter strand discontinuously made in opposite direction of a growing replication fork; - because 3’ 5’ direction of reading the parent template - is away from the growing Replication fork; Okazaki fragments; several short DNA strands; joined to primers; growing away from replication fork; later join to make the daughter DNA lagging strand; DNA Primase; - add short RNA nucleotides called RNA primers; RNA primers; - short RNA nucleotide used to make double strand & provide initial 3’ C- OH for polymerising DNA polymerase like 5 & 5 above to start work; DNA polymerase I – remove of RNA primers then replace them with DNA nucleotides; 11. 12. DNA ligase- join DNA fragments like Okazaki fragments to form the continuous DNA strand;