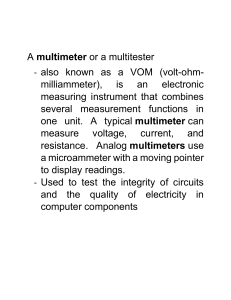
7 TLE-ICT Quarter 0 – Module 1: Using and Maintaining Hand Tools TLE ICT – Grade 7 Alternative Delivery Mode Quarter 1 – Module 1: Using and Maintaining Hand Tools First Edition, 2020 Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work of the Government of the Philippines. However, prior approval of the government agency or office wherein the work is created shall be necessary for exploitation of such work for profit. Such agency or office may, among other things, impose as a condition the payment of royalties. Borrowed materials (i.e., songs, stories, poems, pictures, photos, brand names, trademarks, etc.) included in this module are owned by their respective copyright holders. Every effort has been exerted to locate and seek permission to use these materials from their respective copyright owners. The publisher and authors do not represent nor claim ownership over them. Published by the Department of Education Secretary: Leonor Magtolis Briones Undersecretary: Diosdado M. San Antonio Development Team of the Module Writer: Miraflor V. Banua Editors: Jesusa D. Paladar, Mark Dave M. Vendiola Reviewers: Jesusa D. Paladar, Mark Dave M. Vendiola and Jessie V. Alcala Typesetter: Miraflor V. Banua Management Team: Senen Priscillo P. Paulin, CESO V Rosela R. Abiera Fay C. Luarez, TM, Ed.D., Ph.D. Maricel S. Rasid Adolf P. Aguilar Elmar L. Cabrera Nilita L. Ragay, Ed.D Antonio B. Baguio Jr. Ed.D Printed in the Philippines by ________________________ Department of Education –Region VII Schools Division of Negros Oriental Office Address: Tele #: E-mail Address: Kagawasan, Ave., Daro, Dumaguete City, Negros Oriental (035) 225 2376 / 541 1117 negros.oriental@deped.gov.ph 7 TLE Quarter 1 – Module 1: Using and Maintaining Hand Tools Introductory Message For the facilitator: Welcome to the Technology and Livelihood Education Grade 7 Alternative Delivery Mode (ADM) Module on Using and Maintaining Hand Tools ! This module was collaboratively designed, developed and reviewed by educators both from public and private institutions to assist you, the teacher or facilitator in helping the learners meet the standards set by the K to 12 Curriculum while overcoming their personal, social, and economic constraints in schooling. This learning resource hopes to engage the learners into guided and independent learning activities at their own pace and time. Furthermore, this also aims to help learners acquire the needed 21st century skills while taking into consideration their needs and circumstances. In addition to the material in the main text, you will also see this box in the body of the module: Notes to the Teacher This contains helpful tips or strategies that will help you in guiding the learners. As a facilitator, you are expected to orient the learners on how to use this module. You also need to keep track of the learners' progress while allowing them to manage their own learning. Furthermore, you are expected to encourage and assist the learners as they do the tasks included in the module. ii For the learner: Welcome to the technology and Livelihood Education 7 Alternative Delivery Mode (ADM) Module on Using and Maintaining Hand Tools ! This module was designed to provide you with fun and meaningful opportunities for guided and independent learning at your own pace and time. You will be enabled to process the contents of the learning resource while being an active learner. This module has the following parts and corresponding icons: What I Need to Know What I Know This will give you an idea of the skills or competencies you are expected to learn in the module. This part includes an activity that aims to check what you already know about the lesson to take. If you get all the answers correct (100%), you may decide to skip this module. What’s In This is a brief drill or review to help you link the current lesson with the previous one. What’s New In this portion, the new lesson will be introduced to you in various ways; a story, a song, a poem, a problem opener, an activity or a situation. What is It This section provides a brief discussion of the lesson. This aims to help you discover and understand new concepts and skills. What’s More This comprises activities for independent practice to solidify your understanding and skills of the topic. You may check the answers to the exercises using the Answer Key at the end of the module. What I Have Learned This includes questions or blank sentence/paragraph to be filled in to process what you learned from the lesson. What I Can Do This section provides an activity which will help you transfer your new knowledge or skill into real life situations or concerns. iii Assessment This is a task which aims to evaluate your level of mastery in achieving the learning competency. Additional Activities In this portion, another activity will be given to you to enrich your knowledge or skill of the lesson learned. Answer Key This contains answers to all activities in the module. At the end of this module you will also find: References This is a list of all sources used in developing this module. The following are some reminders in using this module: 1. Use the module with care. Do not put unnecessary mark/s on any part of the module. Use a separate sheet of paper in answering the exercises. 2. Don’t forget to answer What I Know before moving on to the other activities included in the module. 3. Read the instruction carefully before doing each task. 4. Observe honesty and integrity in doing the tasks and checking your answers. 5. Finish the task at hand before proceeding to the next. 6. Return this module to your teacher/facilitator once you are through with it. If you encounter any difficulty in answering the tasks in this module, do not hesitate to consult your teacher or facilitator. Always bear in mind that you are not alone. We hope that through this material, you will experience meaningful learning and gain deep understanding of the relevant competencies. You can do it! iv What I Need to Know This module contains information and suggested learning activities on Computer Hardware Servicing- Exploratory. It includes training materials and activities for you to accomplish and complete. You are required to go through a series of learning activities in order to complete each of the learning outcomes of the module. Follow these activities on your own and answer the given Task at the end of each learning activity. The module is divided into three topics, namely; Lesson 1 Prepare Hand tools Lesson 2 Use Appropriate Hand Tools and Test Equipment Lesson 3 Maintain Hand Tools After going through this module, you are expected to: 1. Discuss the hardware tools used in computer hardware servicing 2. Identify the different types of hand tools used in computer hardware servicing. 3. Value the importance of following safety precaution while working What I Know A. Choose your answer from the box below. Write your answer in your activity notebook Philips head screwdriver Anti-static wrist strap Compress air Lan tester Cables ties Desoldering tool flat head screwdriver Paint brush Hex driver Anti-static mat Lint free cloth Hand tools Multimeter Crimping tool Torx screwdriver Wire cutter __________1. A Tool used to strip and cut wires. __________2. A tool used to unsoldered unwanted parts or component in the circuit with the support of soldering pencil. __________3. This is use to loosen or tighten crosshead screws. __________4. Sometimes called a nut driver, is used to tighten nuts in the same way that a screwdriver tightens screws. __________5. Its long and soft natural bristles can be used to dust off the surface of circuit boards and its hard-to-reach areas __________6. It is use to loosen or tighten slotted screws. __________7. It is use to test the integrity of circuits and the quality of electricity in computer components __________8. It is use to clean different computer components without scratching or leaving debris. __________9. It is use to connect wires into the metal components of a computer; it is designed to connect or attach a connector at the end of a cable to be able to link or connect to a network of other computers __________10. It is use to prevent ESD damage to computer equipment. B. Matching Type Match column B with the tools being describe in column A. In your notebook copy and answer the table. A B _______1. Use to stand on or place hardware on to prevent static electricity from building up. A. _______2. Tighten / loosen screw B. _______3. Tighten / looses bold with a hexagonal head C. _______4. Retrieve parts that may be hard to reach by your fingers D. _______5. a tool used to join two or more metal conductors with the support of soldering lead melted around it. E. Note: If you get 100% correct in this pre- assessment, skip the lesson but if not and only get 50% to 99% correct, then proceed with the lesson. Lesson USING AND MAINTAINING HAND TOOLS 1 What’s In Why is it important to know the functions and uses of hand tools? What do you observe when using hand tools? What’s New Arrange the scrambled letters to form a word below by understanding the given meaning of the correct term. Write your answer in your activity notebook. TROLLEC-ITATSC SIDGEARCH LOOTS ____________________ Provides the most basic means for the controlled discharge of electrostatic electricity. DNAH TSOLO ____________________ Devices for performing work on a material or a physical system using only hands. NIEACLNG OOLTS ____________________ These tools ensure that computers stay tidy and dirt-free. TINOGASDIC SOOLT ____________________ They are used to test the integrity of circuits and functionality of ports. What is It Proper tool selection A tool is a handheld device that aids in accomplishing a task. Tools range from a traditional metal cutting part of a machine to an element of a computer program that activates and controls a particular function. Preparing for the task to be undertaken includes proper tool selection. 1. How do you select the best tool for the job? First, know and understand in detail the scope of work to be accomplished, second, plan for the scope taking into account the sequence of tasks. 2. Selecting the best tool for each task requires training in the proper use of the tools, field experience in their safe use, and following the manufacturer’s guidance and instructions for that specific tool. 3. When obtaining the tool all the associated tooling and consumable parts, as recommended by the manufacturer, must be included. In addition, related consumable parts must also be selected and used according to their manufacturer’s instructions. Safe Use of tools Once selected, use the tool for the purpose for which it was designed. Not all tools come with detailed instructions, but there are those that do spell out the safety ―Do’s and Don’ts for your safety. If there are set-up/use options, operator judgment must always be based on what is the safest way to use the tool. Environmental Safety and Health Program requires the following: Clean tools and equipment work more efficiently. At the end of each working day clean the tools and equipment you used and check them for any damage. If you note and damage, tag the tool as faulty and organize a repair or replacement. Electrical current can travel over oily or greasy surfaces. Keep electrical power hand tools free from dust and dirt and make sure they are free of oil and grease. All workshop hand tools and equipment should have maintenance schedule. Always complete the tasks described on the schedule at the required time. This will help to keep the hand tools in safe working order. Store commonly used hand tools in an easy-to-reach location. If a tool or a piece is too difficult to return, it could be left on a workbench or on the floor where it will become a safety hazard. Keep your work area tidy. This will help you work more efficiently and safely. HARDWARE TOOLS To complete hardware repairs, it is important to have a toolkit that should contain all of the necessary tools. As you gain experience, you will learn which tools to have available for different types of jobs. Hardware tools are grouped into these four categories: • • • • Electro-Static Discharge (ESD) tools Hand tools Cleaning tools Diagnostic tools Electro-Static Discharge (ESD) Tools Static electricity is easily generated by friction on carpets, tile flooring, clothing, hair, fabric, and etc. The friction of moving air alone will charge suspended particles and cause the buildup of static electrical charges on people and objects in the environment. Grounded antistatic work mats used with antistatic wrist straps provide the most basic means for the controlled discharge of electrostatic electricity. Anti-static wrist strap – used to prevent ESD damage to computer equipment. Anti-static mat – used to stand on or place hardware on to prevent static electricity from building up. Anti-static bag- is a packaging material that is specially designed to help prevent static electricity interacting with sensitive electrical components. Hand Tools A hand tool is a device for performing work on a material or a physical system using only hands. The hand tools can be manually used employing force, or electrically powered, using electrical current Flat head screwdriver – used to loosen or tighten slotted screws. Philips head screwdriver – used to loosen or tighten crosshead screws. Torx screwdriver - used to loosen or tighten screws that have a star-like depression on the top, a feature that is mainly found on laptop. Hex driver – sometimes called a nut driver, is used to tighten nuts in the same way that a screwdriver tightens screws. Needle-nose plier – used to hold small parts Wire cutter – used to strip and cut wires Tweezers – used to manipulate small parts. Flashlight or Headlight – used to light up areas that you cannot see well. Soldering Pencil – a tool used to join two or more metal conductors with the support of soldering lead melted around it. Desoldering Tool – a tool used to unsoldered unwanted parts or component in the circuit with the support of soldering pencil. Precision Screwdrivercomes from different interchangeable heads which can be switched; used for tiny screws found in the inner part of the components of a compute Crimping tool- used to connect wires into the metal components of a computer; it is designed to connect or attach a connector at the end of a cable to be able to link or connect to a network of other computers Cleaning Tools Having the appropriate cleaning tools is essential when maintaining or repairing computers. Using these tools ensures that computer components are not damaged during cleaning. They also make computers tidy and dirt-free. Lint-free cloth – used to clean different computer components without scratching or leaving debris. Compressed air – used to blow away dust and debris from different computer parts without touching the components. Cable ties – used to bundle cables neatly inside and outside of a computer. Parts organizer – used to hold screw, jumpers, fasteners and other small parts and prevents them from getting mixed together. Paint brush- its long and soft natural bristles can be used to dust off the surface of circuit boards and its hard-toreach areas Rubbing alcohol- used to wipe away sticky substances on the surface of components; its quick evaporation lessens the chance of causing electrical damage to components Diagnostic Tools Computers are easier to use and more dependable with each new generation of hardware and operating system update, but that doesn't mean they're problemfree. Diagnostic tools are used to test the integrity of circuits and functionality of ports. LAN Tester- is a device used to test the network connection. Digital Multimeter- also called Volt-Ohm- Milliammeter (VOM), a handy and battery operated tool used to measure voltge, current and resistance; and effective tool to check or diagnose if the circuits in a component is working or not. Multimeter – used to test the integrity of circuits and the quality of electricity in computer components. Loopback Adapter – used to test the functionality of computer ports. Toner probe – the toner part is connected to a cable at one end using specific adapters, such as an RJ-45, coaxial, or metal clips. The toner generates a tone that travels the length of the cable. The probe part traces the cable. When the probe is in near proximity to the cable to which the toner is attached, the tone can be heard through a speaker in the probe. PROPER USE OF TOOLS Proper Use of ESD Tools The purpose of an antistatic wrist strap is to equalize the electrical charge between you and the equipment. The antistatic wrist strap is a conductor that connects your body to the equipment that you are working on. When static electricity builds up in your body, the connection made by the wrist strap to the equipment, or ground, channels the electricity through the wire that connects the strap. The wrist strap has two parts and is easy to wear: 1. Wrap the strap around your wrist and secure it using the snap or Velcro. The metal on the back of the wrist strap must remain in contact with your skin at all times. 2. Snap the connector at the end of the wire to the wrist strap, and connect the other end either to the equipment or to the same grounding point that the antistatic mat is connected to. The metal skeleton of the case is a good place to connect the wire. When connecting the wire to equipment that you are working on, choose an unpainted metal surface. A painted surface does not conduct the electricity as well as unpainted metal. An antistatic mat is slightly conductive. It works by drawing static electricity away from a component and transferring it safely from equipment to a grounding point: 1. Lay the mat on the workspace next to or under the computer case. 2. Clip the mat to the case to provide a grounded surface on which you can place parts as you remove them from the system. Reducing the potential for ESD reduces the likelihood of damage to delicate circuits or components. Proper Use of Hand Tools A technician needs to be able to properly use each tool in the toolkit. This topic covers many of the various hand tools used when repairing computers. Screws Match each screw with the proper screwdriver. Place the tip of the screwdriver on the head of the screw. Turn the screwdriver clockwise to tighten the screw and counterclockwise to loosen the screw. Screws can become stripped if you over-tighten them with a screwdriver. A stripped screw, may get stuck in the screw hole, or it may not tighten firmly. Discard stripped screws. Flat head screwdriver Use a flat head screwdriver when you are working with a slotted screw. Do not use a flat head screwdriver to remove a Phillips head screw. Never use a screwdriver as a pry bar. If you cannot remove a component, check to see if there is a clip or latch that is securing the component in place. CAUTION: If excessive force is needed to remove or add a component, something is probably wrong. Take a second look to make sure that you have not missed a screw or a locking clip that is holding the component in place. Refer to the device manual or diagram for additional information. Phillips head screwdriver Use a Phillips head screwdriver with crosshead screws. Do not use this type of screwdriver to puncture anything. This will damage the head of the screwdriver. Hex driver Use a hex driver to loosen and tighten bolts that have a hexagonal (six-sided) head. Hex bolts should not be over-tightened because the threads of the bolts can be stripped. Do not use a hex driver that is too large for the bolt that you are using. CAUTION: Some tools are magnetized. When working around electronic devices, be sure that the tools you are using have not been magnetized. Magnetic fields can be harmful to data stored on magnetic media. Test your tool by touching the tool with a screw. If the screw is attracted to the tool, do not use the tool. Part retriever, Needle-nose pliers, or tweezers The part retriever, needle-nose pliers, and tweezers can be used to place and retrieve parts that may be hard to reach with your fingers. Do not scratch or hit any components when using these tools. CAUTION: Pencils should not be used inside the computer to change the setting of switches or to pry off jumpers. The pencil lead can act as a conductor and may damage the computer components. Proper Use of Cleaning Materials Keeping computers clean inside and out is a vital part of a maintenance program. Dirt can cause problems with the physical operation of fans, buttons, and other mechanical components. On electrical components, an excessive buildup of dust will act like an insulator and trap the heat. This insulation will impair the ability of heat sinks and cooling fans to keep components cool, causing chips and circuits to overheat and fail. CAUTION: When compressed air is used to clean inside the computer, the air should be blown around the components with a minimum distance of four inches from the nozzle. The power supply and the fan should be cleaned from the back of the case. CAUTION: Before cleaning any device, turn it off and unplug the device from the power source. Computer Cases and Monitors Clean computer cases and the outside of monitors with a mild cleaning solution on a damp, lint-free cloth. Mix one drop of dishwashing liquid with four ounces of water to create the cleaning solution. If any water drips inside the case, allow enough time for the liquid to dry before powering on the computer. LCD Screens Do not use ammoniated glass cleaners or any other solution on an LCD screen, unless the cleaner is specifically designed for the purpose. Harsh chemicals will damage the coating on the screen. There is no glass protecting these screens, so be gentle when cleaning them and do not press firmly on the screen. CRT Screens to clean the screens of CRT monitors, dampen a soft, clean, lintfree cloth with distilled water and wipe the screen from top to bottom. Then use a soft, dry cloth to wipe the screen and remove any streaking after you have cleaned the monitor. Clean dusty components with a can of compressed air. Compressed air does not cause electrostatic buildup on components. Make sure that you are in a wellventilated area before blowing the dust out of the computer. A best practice is to wear a dust mask to make sure that you do not breathe in the dust particles. Blow out the dust using short bursts from the can. Never tip the can or use the compressed air can upside down. Do not allow the fan blades to spin from the force of the compressed air. Hold the fan in place. Fan motors can be ruined from spinning when the motor is not turned on. Component Contacts Clean the contacts on components with isopropyl alcohol. Do not use rubbing alcohol. Rubbing alcohol contains impurities that can damage contacts. Make sure that the contacts do not collect any lint from the cloth or cotton swab. Blow any lint off the contacts with compressed air before reinstallation. Keyboard Clean a desktop keyboard with compressed air or a small, hand-held vacuum cleaner with a brush attachment. CAUTION: Never use a standard vacuum cleaner inside a computer case. The plastic parts of the vacuum cleaner can build up static electricity and discharge to the components. Use only a vacuum approved for electronic components. Mouse Use glass cleaner and a soft cloth to clean the outside of the mouse. Do not spray glass cleaner directly on the mouse. If cleaning a ball mouse, you can remove the ball and clean it with glass cleaner and a soft cloth. Wipe the rollers clean inside the mouse with the same cloth. Do not spray any liquids inside the mouse. What’s More Task 1. Direction: Choose at least 10 hand tools available at home and conduct a maintenance activity. TOOLS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Flat Head Screwdriver Philips Head Screwdriver Torx Screwdriver Hex Driver Needle-nose Plier Wire Cutter 7. Tweezer 8. Part Retriver 9. Flashlight 10. Multimeter 11. Philips Head Screwdriver 12. Crimping Tool 13. Soldering Tool 14. Digital Multimeter 15. LAN Tester MAINTENANCE ACTIVITY Clean and Magnetize Clean and Magnetize Clean and Magnetize Clean and Magnetize Clean and Lubricate Clean and Lubricate And Sharpen if necessary Clean Clean Clean and change batteries if drained Clean and calibrate Clean and Magnetize Clean and Lubricate Remove the residue Clean, calibrate, change battery Clean, calibrate, change battery Score Card Activity Excellent 5 Very Satisfactory 3 Satisfactory Score 1 Cleaning Hand tools Magnetizing hand tools Calibrating hand tools Changing batteries Lubricating hand tools Sharpening hand tools Storing hand tools What I Have Learned Direction: Answer the K-W-L chart. Write your answer in your notebook. K W L What do you think you What do you WANT to What did you LEARN KNOW about Hand know about Hand about Hand Tools? Tools? Tools? What I Can Do Activity 1 Direction: Identify the correct tool that is being described by the following statements. After identifying the tool, classify it as ESD, Hand Tool , Cleaning Tool or Diagnostic Tool. Write your answer in your activity notebook. 1. Used to strip and cut wires. (_______________, ______________) 2. Used to retrieve parts from location that are to small for your hand to fit. (_______________, ______________) 3. Used to loosen or tighten slotted screws. (_______________, ______________) 4. Used to loosen or tighten screws that have a star-like depression on the top, a feature that is mainly found on laptop. (_______________, ______________) 5. Used to blow away dust and debris from different computer parts without touching the components. (_______________, ______________) 6. Used to light up areas that you cannot see well. (_______________, ______________) 7. Used to hold small parts. (_______________, ______________) 8. Used to test the integrity of circuits and the quality of electricity in computer components. (_______________, ______________) 9. Used to clean different computer components without scratching or leaving debris. (_______________, ______________) 10. Used to test the functionality of computer ports. (_______________, ______________) 11. Used to connect an RJ-45 to the end of a cable. (_______________, ______________) 12. Used to test LAN/Internet cable. (_______________, ______________) Activity 2 Direction: Complete the computer cleaning chart shown below. Write your answer in your activity notebook. COMPUTER MAINTENANCE COMPONENTS TO CLEAN Computer case and outside monitor Keyboard Mouse LCD Screen CRT Screen Heat Sink RAM CLEAN WITH: Mild cleaning solution and lint free cloth (sample) Assessment Fill in the blanks. Choose your answer from the box. Write your answers in your activity notebook. Hex driver Four counter clockwise isopropyl insulator Clockwise distilled Philips equalize lead hand tools safety 1. The purpose of an antistatic wrist strap is to ________ the electrical charge between you and the equipment. 2. Turn the screwdriver _________ to tighten the screw 3. Turn the screwdriver ________________ to loosen the screw. 4. Use a ________ head screwdriver with crosshead screws. 5. On electrical components, an excessive buildup of dust will act like an _________ and trap the heat. 6. When compressed air is used to clean inside the computer, the air should be blown around the components with a minimum distance of ______ inches from the nozzle. 7. Pencils should not be used inside the computer to change the setting of switches or to pry off jumpers because the tip contains _____ which can act as a conductor and may damage the computer components. 8. To clean the screens of CRT monitors, dampen a soft, clean, lint-free cloth with _______ water and wipe the screen from top to bottom. 9. Clean the contacts on components with _________ alcohol. 10. Use a __________ to loosen and tighten bolts that have a hexagonal (six-sided) head. Multiple Choice Select the letter of the correct answer. Write your answer in your activity notebook. ______ 1. What do you call this kind of ESD Tool that works by drawing static electricity away from a component and transferring it safely from equipment to a grounding point? A. Anti-static wrist strap C. Electro-Static Discharge (ESD) Tools B. Anti-static mat D. Diagnostic tools _____ 2. The following are the proper way of cleaning the component contacts except____. A. Clean the contacts on components with isopropyl alcohol. B. Blow out the dust using short burst from the can. C. Do not use rubbing alcohol. D. Make sure that the contacts do not collect any lint from the cloth or cotton swab. ______ 3. Which tool is used to manipulate small parts? A. Wire cutter B. Tweezers C. Part retriever D. Hex driver ______ 4. Which tool is used to prevent ESD damage to computer equipment? A. Anti-static wrist strap C. Electro-Static Discharge (ESD) Tools B. Anti-static mat D. Diagnostic tools _____ 5. A Tool used to unsoldered unwanted parts or component in the circuit with the support of soldering pencil A. Desoldering Tool C. Crimping Tool B. Soldering Tool D. part Retriever ______ 6. Which tool is used to test the integrity of circuits and the quality of electricity in computer components? A. Multimeter B. Tweezers C. Anti-static wrist strap DLoopback Adapter ______ 7. Which hand tool is used to driver to loosen and tighten bolts that have a hexagonal (six-sided) head? A. Needle-nose pliers C. Phillips head screwdriver B. Tweezers D. Hex driver ______ 8. Among the four categories of hardware tools, which tool is used for performing work on a material or a physical system using only hands? A. Hand Tool B. ESD Tool C. Cleaning Tool D. Diagnostic Tool _____ 9. Is a device used to test the network connection A. LAN Tester C. Loopback adapter B. Multimeter D. Crimping Tool ______ 10. Which cleaning tool is used to clean different computer components without scratching or leaving debris? A. Lint-free cloth B. Cable ties C. Compressed air D. Part retriever Additional Activities Direction: Creating acrostic poem about Computer Hardware Tools. Choose a particular tool to be the subject of your poem. Write the letters of that word vertically on your paper. Now write about the subject using words that start with the letters in your column. All lines of the poem should relate to or describe the poem. Acrostic poems maybe made of single words, phrases or sentences. The poem does not need to rhyme. Be creative and use your imagination. References https://www.bing.com/images/search?view=detailV2&ccid=IYVNQlVF&id=A071E73B965F4EF6C518 286E5FAF01EE4CB88233&thid=OIP.IYVNQlVFM6kHxP1ffTk_OgAAAA&mediaurl=https%3a%2f%2fww w.gamingscan.com%2fwp-content%2fuploads%2f2019%2f01%2fanti-static-wrist-strap-how-touse.jpg&exph=420&expw=420&q=anti+static+strap&simid=607997679151417319&ck=ACAA9C797C A3B29B5957C37185D05C3C&selectedIndex=69&ajaxhist=0 https://ndcllano.blogspot.com/2017/01/tools-for-computer-hardware-servicing.html https://teachergelo.blogspot.com/2017/01/grade-7-lesson-2-use-of-tools-in-pc.html http://ndcmartinez.blogspot.com/2017/01/1.html http://www.deped.com/resources/9/k_to_12_pc_hardware_servicing_learning_module.pdf#:~:text =Welcome%20to%20the%20world%20of%20Computer%20Hardware%20Servicing%21,like%20you% 20ought%20to%20possess%2C%20namely%3A%20%20. https://www.bing.com/images/search?view=detailV2&ccid=xFr4Vt9V&id=A310899B876CBB518E58 927FFA4633A2CB00BF5C&thid=OIP.xFr4Vt9VlyHmt56Lsrh4pgHaE8&mediaurl=https%3a%2f%2fmarl acummins.com%2fwp-content%2fuploads%2f2013%2f12%2fadhd-and-using-the-righttool.jpg&exph=352&expw=528&q=Proper+Tool+Use+Poster&simid=608028632932486907&ck=156 D3E4F72114FE4BE5B8DB61B1B1D2F&selectedIndex=64&ajaxhist=0 https://www.bing.com/images/search?view=detailV2&ccid=mwdTMVJb&id=11C3C19C1F088B9B42 8A5BBC2EF1732D441DF3C6&thid=OIP.mwdTMVJbh0kWMOZ7RUCd0gHaEw&mediaurl=https%3a%2 f%2ffthmb.tqn.com%2fjZpZAT8YKOjNKpYCj5uluMBKKVg%3d%2f3963x2549%2ffilters%3afill(auto%2c 1)%2fscrewdriver-flat56a056d65f9b58eba4aff0cf.jpg&exph=2549&expw=3963&q=screwdriver&simid=608053801423471 332&ck=5CDBA3205F151E7D4245026812324CBA&selectedIndex=32&ajaxhist=0 https://www.bing.com/images/search?view=detailV2&ccid=H%2FXAax3F&id=C8895B70D0314C587 428BCB29D96F42592138AFA&thid=OIP.H_XAax3Ftu8OWIUBA9UiQHaHa&mediaurl=http%3A%2F%2Fi.ebayimg.com%2Fimages%2Fi%2F261549093889-01%2Fsl1000.jpg&exph=1000&expw=1000&q=screwdriver&simid=608011899829880832&ck=9C79B5C905E 21037827E0C5E9D6741CA&selectedindex=33&ajaxhist=0&vt=0&sim=11 https://www.bing.com/images/search?view=detailV2&ccid=BvO1M09J&id=D0BF66788A7757E9A02 5D3419BEFEF03F5C9B8AA&thid=OIP.BvO1M09JTILAn818LpvfIwHaHa&mediaurl=https%3a%2f%2fae 01.alicdn.com%2fkf%2fHTB1NOUpegKTBuNkSne1q6yJoXXab%2fMulti-Function-Mini-KeyboardCleaning-brush-Vehicle-Anti-Static-Dust-Brush-Desktop-Sweeper-Cleaning-HomeDusting.jpg&exph=841&expw=841&q=Keyboard+Cleaning+Brush&simid=608038674591842660&ck =37FFB6DE657D0F68581B0942D4263A76&selectedIndex=0&ajaxhist=0 https://www.slideshare.net/kenjoyb/k-to-12-pc-hardware-servicing-learning-module For inquiries or feedback, please write or call: Department of Education – Schools Division of Negros Oriental Kagawasan, Avenue, Daro, Dumaguete City, Negros Oriental Tel #: (035) 225 2376 / 541 1117 Email Address: negros.oriental@deped.gov.ph Website: lrmds.depednodis.net