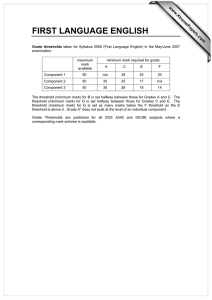
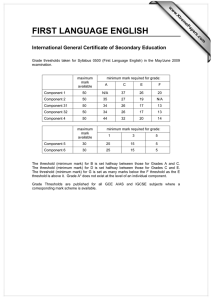
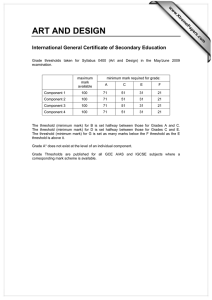
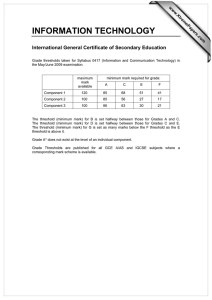
Sensory Thresholds: Absolute, Recognition, Difference, Terminal
advertisement

DETERMINING THRESHOLDS DETERMINING THRESHOLDS - Absolute threshold Recognition threshold Difference threshold Terminal threshold - Thresholds can be used to determine the point at which some substances begin to reduce acceptability. - Hindi na malamsahan, no more stimulus, no perceptible sensory experience - Beyond acceptability - experience pain Thresholds may also be used as means of selecting or testing panelists. - Determine the thresholds of the panelists before conducting panelist esp if needs a highly trained panel - - - Thresholds - limits of sensory capacities - Beyond threshold, wither di na madetect or - pain na madetect Measurement of thresholds is the most common procedure for studying the psychophysics of taste - Study of the relationship between physical stimuli and a person’s sensory experience Thresholds may differ: - Among panelists - Training of each panelists - Within panelists - Within ourselves - Among sensory stimuli - Bawat stimuli (sweetness, sour, etc) pwede iba iba stimuli natin per component - ABSOLUTE THRESHOLD Detection threshold Lowest stimulus capable of producing a sensation - Ex: the dimmest light that we can perceive - Pinaka bland na kaya natin mapercieve It is usually set as the stimulus magnitude at which the subject can identify a difference in taste. - Lowest level or concentration of stimuli that we can detect a difference/ perceive - Pwedeng di pa natin madistinguish ano yung stimuli na yon - Ex: lowest concentration of salt conc - We detect a difference or perceive something/ a stimuli , but cannot distinguish it as saltiness - Not distinguishable but you can perceive it RECOGNITION THRESHOLD Level of stimulus at which the specific stimulus can be recognized and identified. - Higher than your absolute threshold - - You can distinguish the specific stimuli already DIFFERENCE THRESHOLD least amount of change of a given stimulus necessary to produce a change in sensation - Example - 2 samples with the same solution - Ex: S1 has a lower concentration than S2, example absolute thresh - S1 very low conc but detectable - S2 higher, so more detected - The difference Conc1 and Conc 2 is the difference threshold - level/amt/conc of change na dedetect padin ❖ The interval unit used ➢ JND (Just Noticeable Difference) ■ Noticeable difference between sx ➢ JNND (Just Not Noticeable Difference) ■ No noticeable difference between sx DETERMINING THRESHOLDS - TERMINAL THRESHOLD magnitude of a stimulus above which there is no increase in perceived intensity of the appropriate quality of the stimulus. - Above terminal, pain na experience - - Too sweet; high conc of sugar conc, di na malasahan na sweet, usually pain na, beyond acceptability . beyond appreciation Ex; sound, too much, too loud sounds FACTORS INFLUENCING THRESHOLD MEASUREMENTS INCLUDE: ● ● ● ● ● Purity of stimuli ○ There should be no other interfering stimuli to detect the threshold ○ Other tastants will have an effect Level of “noise” in the blank ○ Blank sample will help to distinguish ■ Blank must be pure or else mag iiba basis Physiological state of panelist ○ Medica, physical, medical conditions affects the threshold ○ Mas amtaas threshold needed if may sakit Panelist attentiveness Panelist motivation ○ More motivated and concentrated, more sensitive