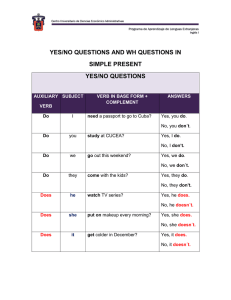
Present Simple
The Present Simple tense is the most basic tense in English and uses the
base form of the verb (except for the verb be). The only change from the base
is the addition of s for third person singular.
How do we make the Present Simple tense?
There are two basic structures for the Present Simple:
1. Positive sentences
subject
+
main verb
Present Simple
2. Negative and question sentences
subject
+
auxiliary do
+
main verb
conjugated in Present Simple
do, does
Look at these examples with the main verb like:
base
subject
+
-
?
auxiliary verb
main verb
I, you, we, they
like
coffee.
He, she, it
likes
coffee.
I, you, we, they
do
not
like
coffee.
He, she, it
does
not
like
coffee.
Do
I, you, we, they
like
coffee?
Does
he, she, it
like
coffee?
From the above table, notice the following points...
For positive sentences:
There is no auxiliary verb.
We conjugate the main verb by adding s to the third person singular.
For negative and question sentences:
The auxiliary verb (do) is conjugated in the Present Simple: do, does
The main verb is invariable in base form: base
For negative sentences, we insert not between the auxiliary verb and
the main verb.
For question sentences, we exchange the subject and the auxiliary
verb.
Emphatic do
Normally, for positive sentences we do not use the auxiliary verb do. But if we
want to emphasize (stress) something, we may use it. For example, instead of
saying "I like your dress", we could say "I do like your dress", just to show how
much we like it. Here are some more examples:
I do wish you'd stop.
I do apologize.
You do look smart today.
Present Simple with main verb be
The structure of the Present Simple with the main verb be is:
subject
+
main verb be
conjugated in Present Simple
am, are, is
Look at these examples with the main verb be:
+
subject
main verb be
I
am
French.
You, we, they
are
French.
-
?
subject
main verb be
He, she, it
is
I
am
not
old.
You, we, they
are
not
old.
He, she, it
is
not
old.
Am
I
late?
Are
you, we, they
late?
Is
he, she, it
late?
French.
From the above table, notice the following points...
There is no auxiliary verb, even for questions and negatives.
The main verb (be) is conjugated in the Present Simple: am, are, is
For negative sentences, we insert not after the main verb.
For question sentences, we exchange the subject and the main verb.
How do we use the Present Simple tense?
We use the Present Simple to talk about:
general time (action verbs)
situations now (stative verbs)
general time and situations now (verb be)
Present Simple for general time
We use the Present Simple tense when:
the action is general
the action happens all the time, or habitually, in the past, present and
future
the action is not only happening now
the statement is always true
John drives a taxi.
past
present
future
It is John's job to drive a taxi. He does it every day. Past, present and
future.
Look at these examples:
I live in New York.
The Moon goes round the Earth.
John drives a taxi.
He does not drive a bus.
We meet every Thursday.
We do not work at night.
Do you play football?
Present Simple for now
For stative verbs, we can use the Present Simple to talk about now. Stative
verbs do not describe action. They describe state, and are verbs such as: like,
sound, belong to, need, seem. We can use these verbs with the Present
Simple tense to talk about a situation at the present time, not general.
I want a coffee.
That sounds interesting.
Do you need some help?
past
present
future
The situation is now.
Present Simple for general time and now
The verb be is always special. It is a stative verb, and we use it in the Present
Simple tense to talk about now situations and about general situations. Look
at these examples of the verb be in the Present Simple tense - some
are general and some are now:
I am not fat.
Why are you so beautiful?
Ram is tall.
past
present
The situation is general. Past, present and future.
future
Am I right?
Tara is not at home.
We are hungry.
past
present
future
The situation is now.
This page shows the use of the Present Simple tense to talk about now and
about general time. But note that there are other uses for the Present Simple,
for example in the zero conditional or to talk about the future.
Present Continuous
(also called Present Progressive)
We often use the Present Continuous tense in English. It is very different
from the Present Simple tense, both in structure and in use.
How do we make the Present Continuous tense?
The structure of the Present Continuous tense is:
subject
+
auxiliary be
+
main verb
conjugated in Present Simple
am, are, is
present participle (-ing)
The auxiliary verb (be) is conjugated in the Present Simple: am, are, is
The main verb is invariable in present participle form: -ing
For negative sentences we insert not between the auxiliary verb and the main
verb.
For question sentences, we exchange the subject and the auxiliary verb.
Look at these example sentences with the Present Continuous tense:
subject
auxiliary verb
main verb
+
I
am
speaking
to you.
+
You
are
reading
this.
-
She
is
not
staying
in London.
-
We
are
not
playing
football.
?
Is
he
watching
TV?
?
subject
auxiliary verb
main verb
Are
they
waiting
for John?
How do we use the Present Continuous tense?
We use the Present Continuous to talk about:
action happening now
action in the future
Present Continuous for action happening now
a) for action happening exactly now
I am eating my lunch.
past
present
future
The action is happening
now.
Look at these images. Right now you are looking at this screen and at the
same time...
the pages are
turning
the candle is
burning
the numbers are
spinning
b) for action happening around now
The action may not be happening exactly now, but it is happening just before
and just after now, and it is not permanent or habitual.
John is looking for a new job.
past
present
future
The action is happening
"around" now.
Look at these examples:
Muriel is learning to drive.
I am living with my sister until I find an apartment.
Present Continuous for the future
We can also use the Present Continuous tense to talk about the future - if we
add a future word!! We must add (or understand from the context) a future
word. "Future words" include, for example, tomorrow, next year, in June, at
Christmas etc. We only use the Present Continuous tense to talk about the
future when we have planned to do something before we speak. We have
already made a decision and a plan before speaking.
I am taking my exam next month.
past
present
future
!!!
A firm plan or programme exists
now.
The action is in
the future.
Look at these examples:
We're eating at Joe's Cafe tonight. We've already booked the table..
They can play tennis with you tomorrow. They're not working.
When are you starting your new job?
In these examples, a firm plan or programme exists before speaking. The
decision and plan were made before speaking.
How do we spell the Present Continuous tense?
We make the Present Continuous tense by adding -ing to the base verb.
Normally it's simple: we just add -ing. But sometimes we have to change the
word a little. Perhaps we double the last letter, or we drop a letter. Here are
the rules to help you know how to spell the Present Continuous tense.
Basic rule
Just add -ing to the base verb:
Exception
work
→
working
play
→
playing
assist
→
assisting
see
→
seeing
be
→
being
If the base verb ends in consonant + stressed vowel +
consonant, double the last letter:
s
t
o
p
consonant
stressed
vowel
consonant
vowels = a, e, i, o, u
stop
→
stopping
run
→
running
begin
→
beginning
Note that this exception does not apply when the last syllable
of the base verb is not stressed:
open
Exception
Exception
→
opening
If the base verb ends in ie, change the ie to y:
lie
→
lying
die
→
dying
If the base verb ends in vowel + consonant + e, omit the e:
come
→
coming
mistake
→
mistaking
Note that continuous tenses are also called progressive tenses. So the
Present Continuous tense is sometimes called the Present Progressive tense.
What's the difference?
Present Simple and Present Continuous
Present Simple
Present Continuous
Things which are always true:
Things which are happening at the
moment of speaking:
Water boils at 100 degrees.
Permanent situations (or nearly permanent;
true for a few years at least):
Temporary situations:
The water is boiling now, so you can
put in the pasta.
Julie lives in London.
Julie is living in Paris for a few
months (usually she lives in London).
Situations which are slowly changing:
Habits or things we do regularly:
I drink coffee every morning.
I'm getting better and better at
speaking English.
Temporary or new habits:
I'm drinking too much coffee these
days because I'm so busy at work.
Annoying habits (usually with
'always'):
Future events which are part of a timetable:
My plane leaves at eight tonight.
My flatmate is always leaving the
kitchen in a mess!
Definite future plans:
I'm meeting John after class today.
To talk about the future after certain words
('when' 'until' 'after' 'before' 'as soon as'):
I'll call you when I get home.
To talk about what happens in books, plays
and films:
To talk about people in pictures and
photos:
At the end of the book, the
detective catches the killer.
In this photo, my mother is
walking beside a lake.
Remember:
We use the present simple with stative verbs. We can't use any continuous tense
(including the present continuous tense, of course) with stative verbs.