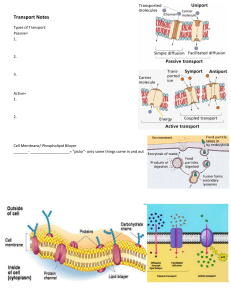
MICERE DAN MWIRIGI J23/2664/2017 EBM300 Assesment 1 Organelle Nucleus Nucleolus Cytoplasm Cytosol Cytoskeleton Ribosome Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus Structure A nuclear membrane, nucleoplasm, nucleolus, and chromosomes make up the nucleus. The nucleoplasm is the matrix that surrounds the nucleus. The nuclear membrane is a double membrane that surrounds the entire organelle and isolates nucleus contents from cytoplasm. Function Controls and regulates the cell's processes (e.g., growth and metabolism), as well as carrying the genes, which are structures that contain hereditary information. A spherical structure in the nucleus of a cell that creates cell's ribosomes. Gel-like substance found between the cell membrane Contains the contents of the cell that serves and nucleus, mainly as a platform for other organelles within the composed of water, cell to operate. organic and inorganic compounds. water-based solution in which organelles, proteins, Gel-like matrix that forms the cytoplasmic and other cell structures medium float Comprises fibres, organizes the cell's other constituents, namely microtubules, maintains the cell's shape, and is in charge actin filaments, and of the cell's locomotion as well as the intermediate movement of the many organelles within it. filaments. Tiny particles made up of By connecting amino acids together, it aids RNA and related proteins in protein synthesis from messenger RNA that are responsible for (mRNA). protein synthesis. A collection of flattened forms membranes and secretory proteins, sacs with numerous whereas ribosomes linked to the rough ER ribosomes on their exterior use the translation process to create surface proteins. Meshwork of fine disk-like synthesizes lipids, steroids hormones, and tubular membrane phospholipids as in those in plasma comprising tubular membranes structures called cisternae. Comprises of many Transports, modifies, and packages proteins parallelly stacked discand lipids into vesicles for delivery to shaped sacs known as specific locations. cisternae and associated vesicles. Lysosome Peroxisome Vacuoles Vesicles Cell Membrane responsible for the breakdown and membrane-bound sphere- digestion of macromolecules shaped sacs containing (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic hydrolytic enzymes capable acids) within the cell, cell membrane of breaking down a wide repairs, and reactions to external substances range of biomolecules including bacteria, viruses, and other antigens. Single membrane-bound vesicles consisting of a engaged in lipid metabolism and the phospholipid bilayer with conversion of reactive oxygen species like multiple membrane-bound hydrogen peroxide to less dangerous proteins important in molecules like water and oxygen energy metabolism and lipid production. membrane-bound sacs within the cytoplasm that are filled with fluid and any Theytake in and dispose of waste. compounds they take in. They both take in and dispose of waste. The lipid bilayer is a thinThey are in charge of transporting walled structure made up of commodities from one location to another. fluid or gas that is encircled Vesicles are also involved in metabolism and enclosed by an outer and enzyme storage. membrane. Made of phospholipid bilayers with hydrophobic, fatty acid tails in touch with one another, as well as proteins. The plasma membrane's particular A thin flexible barrier that separates the cell tasks, such as selective from its environment. It regulates the molecular transport and movement of materials into and out of the cell-cell identification, are cell carried out by proteins embedded inside the phospholipid bilayer. There are also some carbohydrates present.