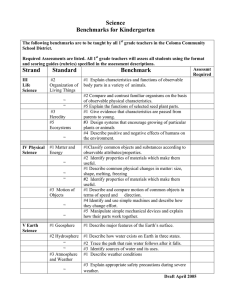
HISTORY AND PHILOSOPY OF SCIENCE Pineda, Reynaldo R. Philosophy Empiricism Proponent Description Positivism Skepticism Is a set of philosophical approaches to building knowledge that emphasizes the importance of observable evidence from the natural world. It is the theory that the origin of all knowledge is the sense of experience. It emphasizes the role of experience and evidence, especially sensory perception, in the formation of ideas and argues that the only knowledge can have is based on experience. Is the view that only authentic knowledge is scientific knowledge, and that such knowledge can only came from positive affirmation of theories through strict scientific method based on gathering observable, empirical and measurable evidence, subject to specific principle of reasoning. A philosophical position that one should refrain from making truth claims and avoid the postulation of truth. It refers to an attitude of doubt or incredulity, either in general or toward a particular subject or to any doubting or questioning attitude or state of mind. Example It can refer to an inquiry, limitations of knowledge, a method of obtaining knowledge through systematic doubt and continual testing, a method of intellectual caution and suspended judgement.