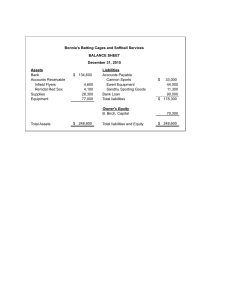
Accounting 101 Comprehensive Exam Reviewer Accounting Scope of Practice of Accountancy Is a SERVICE ACTIVITY Is an INFORMATION SYSTEM Is a PROCESS Is an ART Phases of Accounting 1. 2. 3. 4. Professional Accountant – an individual who holds a valid certificate issued by the Board of Accountancy. Fundamental Principles of an Ethical Professional Accountant Memorandum – book where all transactions are recorded Journal – Merchant’s private book. Ledger – alphabetical listing of the accounts. A grouping of accounts. Entity Concept Periodicity Concept Stable Monetary Unit Concept GAAP Stands for Generally Accepted Accounting Principles. It encompasses the conventions, rules and procedures necessary to define accepted accounting practices at a particular time. Relevance Objectivity Feasibility Basic Principles of GAAP General Knowledge Organizational and Business Knowledge Information Technology Knowledge Accounting Knowledge Intellectual Skills Interpersonal Skills Communication Skills Professional Ethics - Values Moral Values Branches of Accounting Criteria in selecting GAAP Integrity Objectivity Professional Diligence and Due Care Confidentiality Professional Behavior Core Competencies for Accountants Fundamental Concepts under the Accounting Process Public Accountancy Commerce and Industry Education / Academe Government Ethics Measuring Classifying Summarizing Interpreting Books in Summa Jovi Vonn Balcita Objectivity Principle Historical Cost Revenue Recognition Principle Expense Recognition Principle Adequate Disclosure Materiality Consistency Principle Accountancy in the Philippines PRC – stands for Professional Regulation Commission. R.A. 9298 – the Philippine Accountancy Act of 2004 by Former president Gloria Arroyo signed on May 13, 2004. PICPA – Philippine Institute of CPAs PAS – Philippine Accounting Standards 1 Auditing – most significant service of accountants to the public. Bookkeeping – mechanical task involving the collection of basic financial data. Cost Bookkeeping, Costing, and Cost Accounting – involves the recording of cost data in books of accounts. Financial Accounting – focused on recording business transactions and preparation of reports on financial position and results of operations. Targets the owners of the entity and other parties. Financial Management – involves setting financial objectives and making plans using those objectives. Management Accounting – incorporates cost accounting data and adapts them for specific decisions for the management. Taxation – includes the preparation of tax returns Government Accounting – concerned with the identification of the source and uses of resources in compliance with the provisions of existing laws. Accounting 101 Comprehensive Exam Reviewer Jovi Vonn Balcita Accountancy around the World Elements of Financial Statements IASB – stands for International Accounting Standards Board. Its objective is to achieve convergence in the accounting principles used around the world. IFRSF – stands for International Financial Reporting Standards Foundation. An independent private sector organization working in the public interest. They use the IASB as the standard setting body for principles. Elements directly related to the measurement of financial position in the balance sheet: Assets Liabilities Equity Elements directly related to the measurement of performance in the income statement: Income Expenses Accounting Standards – authoritative statements of how particular types of transactions and other events should be reflected in financial statements. Recognition – the process of incorporating in the balance sheet or income statement an item that meets the definition of an element and satisfies the criteria for recognition. Criteria for recognition are as follows: It is probable that any future economic benefits associated with the item would flow to or from the enterprise; and The item has a cost or value that could be measured with reliability. IFRS Framework – describes the basic concepts that underlie the preparation and presentation of financial statements for external users. Users of Financial Information* Primary Users – need information about the resources and claims against the entity to assess the management. External Users – has current or potential financial interest in the reporting entity but are not involved in the daily operations of the entity. Other Users – Employees, Customers, Government and their agencies, and the public Measurement of the Elements of Financial Statements Measurement – the process of determining the monetary amounts at which the elements of the financial statements are to be recognized and carried in the balance sheet and income statements. Basis of measurement are as follows: Historical Cost – assets are measured at the amount of cash paid at the time of acquisition. Current Cost – assets are carried at the amount of cash if the same or equivalent asset was acquired currently. Realizable Value – assets are carried at the amount of cash that could currently be obtained by selling an asset in an orderly disposal. Settlement Value – liabilities are carried at the undiscounted amounts of cash expected to be paid to satisfy the liabilities required in the normal course of business. Present Value – assets/liabilities are carried at the present discounted value of the future net cash inflow/outflow that is expected to be required. *this classification is not part of the IFRS Framework Qualitative Characteristics of Useful Financial Information Fundamental Qualitative Characteristics Relevance – capable of making a difference in the decisions made by users. Could have a predictive or a confirmatory value, or both. Faithful Representation – seeks to maximize the completeness, neutrality, and freedom from error. Enhancing Qualitative Characteristics Comparability Verifiability Timeliness Understandability Underlying Assumptions Concepts of Capital and Capital Maintenance Going Concern – presuming that the entity has neither the intention, nor the need to liquidate or curtail materially the scale of its operations. 2 Financial Concept – capital is synonymous with the net assets or equity of an enterprise. Physical Concept – capital is regarded as the productive capacity of the enterprise, based on, for example, units of output per day. Accounting 101 Comprehensive Exam Reviewer Jovi Vonn Balcita Elements of Financial Statements Double Entry System Financial Position Assets – resources controlled by an enterprise as a result of past events and from which future economic benefits are expected to flow to the enterprise Liabilities – present obligations of the enterprise arising from past events, the settlement of which is expected to result in an outflow from the enterprise of resources embodying economic benefits. Equity – the residual interest in the assets of the enterprise after deducting all its liabilities. Performance Income – increases in economic benefits during the accounting period in the form of inflows or enhancement of assets, or decreases in liabilities that results in increases in equity. Encompasses both Revenue and Gains. Expenses – decreases in economic benefits in the accounting period in the form of outflows or depletion of assets, or incurrences of liabilities that result in decreases in equity. Loss represents other items that meet the definition of expenses and may or may not arise in the course of ordinary activities. A debit side entry must always have a corresponding credit entry. For every transaction, there must always be one or more accounts debited and one or more accounts credited. Each transaction affects at least two accounts. Total debits must always equal total credits. Normal Balance of an Account The normal balance of an account refers to the side of an account where increases are recorded. Accounting Events and Transactions Accounting Event – an economic occurrence that causes changes in an enterprise’s assets, liabilities, and/or equity. Transaction – an event that involves the transfer of something of value between two entities. Types and Effects of Transactions The Account Source of Assets Exchange of Assets Use of Assets Exchange of Claims Accounting for Business Transactions The basic summary device of accounting. A separate account is maintained for each element that appears in the balance sheet and income statement. “T” Account – the simplest form of the account. Business Transaction – the occurrence of an event or a condition that affects financial position and can be reliably recorded. The Accounting Equation 𝐴𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑡𝑠 = 𝐿𝑖𝑎𝑏𝑖𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑒𝑠 + 𝑂𝑤𝑛𝑒𝑟 ′ 𝑠 𝐸𝑞𝑢𝑖𝑡𝑦 3 Accounting 101 Comprehensive Exam Reviewer The Journal Jovi Vonn Balcita Accrual Basis A chronological record of transactions. It shows transactions in debits and credits. The book of original entry. The General Journal is the simplest journal. The standard contents of the journal are as follows: Date Account Titles and Explanation Posting Reference Debit Credit Journalizing – the process of recording a transaction. The effects of transactions and other events recognized when they occur and not as cash is received or paid. The accountant records revenues when earned and expenses when they are incurred. In the Cash Basis, the accountant does not record a transaction until cash is received or paid. Periodicity Concept This is done by dividing the economic life of a business into artificial time periods. Most basic accounting period is one year. Simple entry – only two accounts are affected. Compound entry – three or more accounts are affected. Liquidation – process of going out of business. Kinds of Accounting Years Fiscal year – period of any twelve consecutive months Natural year – a twelve-month period that ends when business is at their lowest level. Calendar year – annual period ending on December 31 Interim period – a period of less than one year The Ledger Grouping of the entity’s accounts. The General Ledger is the “reference book” of the accounting system and is used to classify and summarize transactions, and to prepare data for basic financial statements. Classification of the accounts in the general ledger Balance Sheet - permanent accounts. Income Statement - temporary/nominal accounts. Deferrals and Accruals The Chart of Accounts Deferrals – postponement of the recognition of “an expense already paid, but not yet incurred”, or of “revenue already collected but not yet earned. e.g. Prepaid Expenses, Supplies, Depreciation, Revenues received in advance A listing of all of the accounts and their account numbers in the ledger. Posting Transferring the amounts from the journal to the appropriate accounts in the ledger. Trial Balance Accruals – recognition of “expense already incurred, but unpaid”, or of “revenue earned, but uncollected”. e.g. Accrued Expenses (Salaries, Interest), Accrued Revenues (Uncollectible Accounts) A list of all accounts with their respective debit and credit balances. It is prepared to verify the equality of debits and credits in the ledger at the end of each accounting period. The Worksheet A document that provides an efficient way to summarize the data for financial statements. It simplifies the adjusting and closing process. It can also reveal errors. 4 Accounting 101 Comprehensive Exam Reviewer The Financial Statements Statement of Financial Position Also called the Balance Sheet, this statement lists all the assets, liabilities, and equity of an entity as at a specific date. Users analyze the balance sheet to evaluate an entity’s liquidity, financial flexibility, and solvency. Report format – lists the assets, followed by liabilities, then by the owner’s equity. Account format – lists the assets on the left and the others on the right. Statement of Comprehensive Income In Basic Accounting, only the Income Statement is discussed further. The Income Statement presents a summary of the revenues and expenses for a period. Statement of Changes in Owner’s Equity This statement presents a summary of the changes in capital such as investments, profit or loss, and withdrawals during a specific period. Statement of Cash Flows This statement reports the amount of cash received and disbursed during the period. It is a formal statement that classifies cash receipts and payments into operating, investing, and financing activities. Activities undertaken by an entity Operating activities – involves providing services, and producing and delivering goods. Investing activities – includes making and collecting loans, acquiring and disposing of investments, property, equipment, and other assets. Financing activities – includes obtaining resources from owners and creditors. Accounting Policies This statement lists the specific principles, bases, conventions, rules, and practices adopted by an enterprise in preparing and presenting financial statements. Notes to Financial Statements This statement provides narrative descriptions of items presented in the statements and information about items that do not qualify for recognition in the statements. 5 Jovi Vonn Balcita