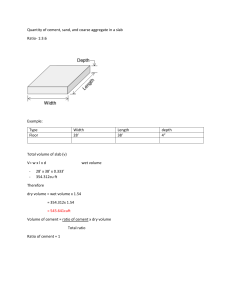
A. Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) is the most widely used cement in the world for producing concrete, mortar, stucco, and non-specialty grouts. Ordinary Portland Cement has 3 grades based on its strength namely 33, 43 and 53 grade that indicates the compressive strength obtained after 28 days of setting. Indian Standard Codes Grade 33 Grade 1.Properties A. Chemical Properties Ratio of Not greater than percentage of lime to percentages of silica, 1.02 and not less than 0.66 alumina and iron oxide Insoluble residue, Not more than 4 percent by mass Magnesia, percent Not more than 6 by mass Chloride content, Not more than 0.1 percent by mass, % Max Not more than alkali content 0.05 B. Physical Properties 3 7 28 Setting Time days Days Days Avg. Compressive Strength in N/mm^2 16 Fineness in m^2 /kg, Min. Soundness a) By Le Chatelier method, mm, Max 22 43 Grade Not greater than Not greater than 1.02 and not less than 1.02 and not less than 0.66 0.8 10 Not more than 2 Not more than 2 Not more than 6 Not more than 6 Not more than 0.1 Not more than 0.1 % Not more than 0.05 Not more than 0.05 3 days 7 Days 28 Days 3 days 7 Days 28 Days 23 33 43 27 37 53 33 225 53 Grade 22 22 5 5 10 10 Setting time a) Initial in minutes, Min b) Final in minutes, Max Code Reference 30 30 30 600 600 600 IS Code – IS 269 : 1989 IS Code – IS 8112: 1989 IS Code – IS 12269 : 1987 B. Rapid Hardening Cement Rapid Hardening Cement (RHC) are also called high early strength cement. The prime difference between the rapid hardening cement and ordinary Portland cement is the lime content. Large proportion of lime is the distinguishing feature of rapid hardening cement. Manufacturing Rapid hardening cement is burnt at a higher temperature than that of the OPC under more controlled conditions. Strength The 3 days strength of rapid hardening cement is equivalent to the 7 days strength of OPC when the water-cement ratio for both the cement is taken to be same. The increased rate of strength is due to the fact that higher proportion of tri-calcium silicate (C3S) is contained in RHC along with finer grinding of the cement clinker. Though, the rate at which RHC gains strength is higher than the rate at which OPC gains strength, the ultimate strength is only a bit higher for RHC. Properties Initial Setting Time: 30 minutes Final Setting Time: 600 minutes The specific surface is greater than 3250 cm2/gm. RHC is lighter than OPC. The curing period for RHC is less. Uses Rapid hardening cement is mostly used in construction of road where the traffic cannot be halted for long period of time. Besides, RHC is used where the formwork need to be removed early for reuse. It is also used on those circumstances where sufficient strength for further construction is wanted as quickly as practicable. These are also used in manufacturing precast slabs, posts, electric poles. Advantages As the curing period for rapid hardening cement is less, it turns out to be economical. Shrinkage during curing and hardening of cement is less in case of RHC. RHC are good at Sulphur resistance. Good speed of construction can be achieved as the strength is gained in relatively shorter time. Disadvantages It is expensive than Ordinary Portland Cement. C. Portland Pozzolana cement Portland Pozzolana cement is integrated cement which is formed by synthesising OPC cement with pozzolanic materials in a certain proportion. It is commonly known as PPC cement. In this article we discuss about the properties, manufacture, characteristics, advantages and disadvantages of Portland Pozzolana cement. What is pozzolana or pozzolanic material? Pozzolana is a volcanic powder found in Italy near Vesuvius. A pozzolanic material can be a natural or artificial which contains silica and aluminous in a reactive form. This materials usually doesnt posses any cementitious properties, but when it is mixed with water or moisture or lime to undergo reaction with calcium hydroxide to form compounds possessing cement properties. Manufacture of Portland pozzolana cement The primary raw materials used for this cement manufacture are limestone (CaCO2) and clay (SiO2,AI2,O3,Fe2O3). Rocks are loaded into trucks and transported to the crushers, where the crushed into fine particles. Fine particles of clay and limestone are fed into the air-swept ball mills in desired proportions as per requirement and mixed very well before it is sent to silos for storing. This mixture is then pre-heated upto 800-1000c where calcinations of CACO3 to CaO takes place. The pre heated mixture is then sent into kiln where the mixture is heated to 1450C in rotary Kiln. The modules formed from the burning process called clinker. The clinker is cooled by a rotary cooler. This clinker is now mixed with gypsum and pozzolana materials in the required proportion and thus the Portland Pozzolana Cement is obtained. Properties of Portland Pozzolana Cement Initial setting time = 30 min (minimum) Final setting time = 600 min (maximum). At 3 days 13MPa (minimum) At 7 days 22 MPa (minimum) At 28 days 33 MPa (minimum) Drying shrinkage should not be more than 0.15% Fineness should not be less than 300 m2/kg Initial strength of PPC is less but final strength is equal to the 28 days strength of OPC PPC has lower rate of development of strength than OPC Uses of Portland Pozzolana Cement 1. Used in hydraulic structures, marine structures, construction near the sea shore, dam construction etc. 2. Used in pre-stressed and post-tensioned concrete members. 3. Used in masonry mortars and plastering. 4. As it gives better surface finish, it is used in decorative and art structures. 5. Used in manufacture of precast sewage pipes. 6. Used under harsh concreting conditions. Advantages of Portland Pozzolana Cement 1. It is an eco-friendly cement as the material used in the manufacture are made of natural recycled waste. 2. It is very fine cement hence very good when used for plastering works. 3. Pozzolano consists of silica material which makes it cheap and hence reduces the cost of the cement making it economical to use. 4. Pozzolana cement has very good resistance against sulphate attack hence is used in hydraulic structures, marine structures, construction near the sea shore, dam construction etc. 5. PPC used in pre-stressed and post-tensioned concrete members. 6. Pozzolano consists of silica material which makes it cheap and hence reduces the cost of the cement making it economical to use. 7. Pozzolana cement has very good resistance against sulphate attack hence is used in hydraulic structures, marine structures, construction near the sea shore, dam construction etc. 8. PPC used in pre-stressed and post-tensioned concrete members. Disadvantages of Portland Pozzolana Cement 1. The initial strength obtained is less, which effect the de-shuttering of supports early. 2. As it contains more fine material, handing of concrete is difficult. 3. When compared to the OPC setting time is less for PPC 4. Reduction in alkanity reduces the resistance to corrosion of steel reinforcement 5. As the strength of this concrete gains slowly, curing process is very important. Any error in this could cause durability problems. D. Quick Setting Cement It is one of the type of cements where the initially set in 5 mins and final set is achieved in 30 mins, which is used in the special conditions of construction like in running water. In this article we study about the properties, phenomenon, uses, advantages and disadvantages of quick setting cement. Phenomenon of Quick setting cement Generally, when the water is added into the cement hydration takes places and the chemical reaction occurs which make the cement to harden where the initial setting time is 30 mins and final setting time being 10hrs. In this special type of cement, where the setting time of the cement is to be less and hardening of cement to be fast. The cement clinkers are grinded with aluminium sulphate, which accelerates the setting time of cement. aluminium sulphate is used as accelerating admixture in the dosage range of 1% to 3% by weight of cement clinkers .The mechanism of function of aluminium sulphate is that it increases the rate of hydration of tricalcium silicate (C3S) and tricalcium aluminate (C3A) phases of cement, thereby providing earlier heat evolution and strength development. It acts as a catalyst in the hydration of tricalcium silicate (C3S) and tricalcium aluminate (C3A). Concrete specimens with varying percentage of aluminium sulphate were tested for compressive strength, splitting tensile strength and flexural strength. The results obtained were compared with results of normal M-20 concrete mix and it was found that maximum increase in compressive strength, splitting tensile strength and flexural strength occurred for quick setting cement concrete at 3 days age and 7 days age. However, there was no considerable increase in compressive strength, splitting tensile strength and flexural strength at 28 days age. Uses of Quick setting cement 1. 2. 3. 4. It is used in under water construction. It is also used in rainy & cold weather conditions. Where, quick strength is needed in short span of time. Used higher temperature where water evaporates easily. 5. Used for anchoring or rock bolt mining and tunnelling 6. Used for fixing concrete steps. 7. For the anchorage of Rock Bolt in Tunnel & all works underground, quick setting cement is required. Disadvantages of Quick setting cement 1. Due to content of sulphates in the aluminium sulphate, there are major chance of sulphate attack on the reinforcement corrosion and durability is compromised. 2. When water is added the work should be completed fast or else it sets and difficult to mix. 3. In quick setting cement, if the heat is not dissipated properly it can result in cracks in the cement after setting. 4. It is not widely available. 5. It is expensive. E. Sulphate Resisting Cement Sulphate Resisting Cement is a type of Portland cement in which the amount of tricalcium aluminate (C3A) is restricted to lower than 5% and (2C 3A +C4AF) lower than 25%, which reduces the formation of sulphate salts. The reduction of sulphate salts lowers the possibility of sulphate attack on the concrete. In this article we study about the composition, properties, characteristics, uses, advantages and disadvantages of sulphate resisting cement. Composition of Sulphate Resisting Cement Due to very low range of tricalcium aluminate in sulphate resisting cement, a very small quantity of calcium aluminate is formed on hydration. The formation of calcium sulpho- aluminates which formed due to reaction of calcium sulpho-aluminates which formed due to reaction of calcium sulphoaluminate and sulphate salts is considerably reduced with use of sulphate resisting cement. The sulphate aluminates are highly expansive in nature and cause maximum damage to the concrete. Properties of Sulphate Resisting Cement Property Values Fineness 280+ or -10 sq m /kg Setting time Initial 80 min Final 240 min Soundness Lechatelier (mm) 2 (max) Compressive strength 3 days 30 + or - 3 7 days 45 + or - 3 28 days 65 + or - 3 Tri calcium aluminate 0.035 Magnesia 0.02 Loss on ignition 0.02 Characteristics of Sulphate Resisting Cement 1. This cement provides maximum resistance to chloride ions - minimising the risk of corrosion of reinforced steel. 2. It also provides high level of concrete performance and structural integrity in highly aggressive sulphate and acidic environments. 3. It also has increased workability and pumpability. 4. This cement has significantly improved later-age concrete strengths. Uses of Sulphate Resisting Cement Sulphate Resisting Cement is recommended for following type of constructions: 1. Foundations. 2. Piling works. 3. Construction in contact with soils or ground water having more than 0.2% or 0.3 % g/l sulphate salts respectively. 4. Concrete surfaces subjected to alternate wetting and drying such as bridge piers, concrete surface in tidal zone, apron etc. 5. Effluent treatment plans. 6. Chimney, cooling towers. 7. Coastal protective works such as sea walls, break waters, tetrapods etc. 8. Building near seacoast. 9. Chemical industries, water storage, sumps, drainage works. 10. Suitable for underground works where Sulphate is present in the Soil and water. Advantages of Sulphate Resisting Cement 1. The use of sulphate resisting cement provides excellent protection against the formation of sulpho-aluminates and consequent resistance to concrete against sulphate attack. 2. Very high compressive strength by economic concrete mix design. 3. Very low heat of hydration helps to avoid shrinkage cracks. 4. Improves life and durability of structures under aggressive conditions. 5. Improves corrosion resistance of steel by preventing sulphate attack. Disadvantages of Sulphate Resisting Cement 1. Sulphate resisting cement is not suitable where there is danger of chloride attack. This will cause corrosion of rebar. 2. If both Chlorides and Sulphates are present, Ordinary Portland Cement with C3A between 5 & 8 should be used. 3. Curing process should be done properly with great care for min of 8-10 days. 4. It is not prescribed to use it in marine construction. F. Blast furnace slag cement Blast furnace slag cement is the mixture of ordinary Portland cement and fine granulated blast furnace slag obtained as a by-product in the manufacture of steel with percent under 70% to that of cement. Ground granulated blast furnace slag cement (GGBFS) is a fine glassy granules which contain cementatious properties. In this article we discuss about the manufacture, constituents, properties, uses, advantages and disadvantages of Blast-furnace slag cement. Blast furnace slag cement is the mixture of ordinary Portland cement and fine granulated blast furnace slag obtained as a by product in the manufacture of steel with percent under 70% to that of cement. Ground granulated blast furnace slag cement (GGBFS) is a fine glassy granules which contain cementatious properties. In this article we discuss about the manufacture, constituents, properties, uses, advantages and disadvantages of Blast-furnace slag cement. Manufacture and Constituents of Blast-Furnace Slag Cement GGBFS is obtained as a by-product in the extraction of iron from it ore. The process of extraction of iron is blast furnace. The slag that is obtained on the iron ore is separated and cooled down slowly, which results in the formation of nonreactive crystalline material. Constituents of the Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag Constituents % by mass SiO2 27-39% Al2O3 8- 20% CaO 38-50% MgO <10% Further this slag is grounded finely as that of cement and mixed in the proportion as per the requirement. Different percentage of GGBFS is added for different type of construction. Proportion of slag percentage for different applications. Application in Type of Construction Slag Proportion in % General construction 20-40 Reduction of heat hydration 50-80 Structures exposed to chloride attack 50-81 Structures exposed to sulfate attack 50-82 Marine structures 60-80 Properties of Blast-Furnace Slag Cement Properties Values Density (g/cm3) 3.04 Specific Surface Area (cm2/g) 4050 Setting Time Initial Setting 60min Final Setting 600min Compressive Strength (N/mm2) 3days 23.5 7days 36.1 28days 62.4 Chemical Composition (%) Magnesium oxide 2.88 Sulphur tri oxide 2.19 Ignition loss 1.47 Uses of Blast-Furnace Slag Cement 1. Used in ready mix concrete plants. 2. Used for structures meant for water retaining such as retaining wall, rivers, ports, tunnels for improvement in impermeability. 3. Used in mass concreting works such as dams, foundations which require low heat of hydration. 4. Used in the places susceptible to chloride and sulphate attacks such as substructure, bored piles, pre-case piles and marine structures. Advantages of Blast-Furnace Slag Cement 1. The initial strength achieved is lesser than that of conventional concrete, but the higher ultimate strength gained is equal and sometimes higher that conventional concrete. 2. As the slag is grounded finely, it has the capacity to fill the pores efficiently, workability is high and bleeding is low. 3. It has good resistance towards sulphate and chloride attack and even less risk of alkali-silica reaction with aggregates. 4. Due to slow hydration process, the slump retention and initial setting time is more. 5. Greater durability and reduced permeability due to fineness. 6. The hydration process if slag is an exothermic process, thus the generation of heat of hydration is slow. Due to this property, this type of cement can be used where the problem of thermal cracking is foreseen. 7. As the colour of GGBFS is white, the cement colour obtained is lighter coloured when compared to conventional cement. 8. The production cost this cement is less when compared to OPC. Disadvantages of Blast-Furnace Slag Cement 1. Initial Strength is low, due to this it cannot be used in RCC works. 2. As the initial setting time is high, this cement is not used for emergency or repair works G. High Alumina Cement High Alumina Cement is manufactured by grinding the clinkers of alumina and calcareous material such as lime by fusing or sintering process. This cement is also known as calcium aluminum cement. In this article we discuss about the history, composition, manufacture, characteristics, uses, advantages and disadvantages. History of High Alumina Cement High Alumina Cement was first developed in United Kingdom in 1925 by a cement producer by name Lafarge. As it was found to be resistant to chemical attacks it was primarily used for marine construction. Its popularity rose when the properties of this cement such as rapid strength gain and easy to manufacture were found out and widely used for precast concreting. Fig 1: High Alumina Cement. Composition of High Alumina Cement Table 1 : Composition percentage of constituents. Constituents Content Percentage Silica 3-8% Alumina 37-41% Lime 36-40% Iron Oxide 9-10% Titanium 1.5-2% Magnesium 1% Insoluble Resides 1% Manufacture of High Alumina Cement The process of manufacture of High Alumina Cement is different compared to that of ordinary portland cement. Bauxite and lime are used as the raw material. The raw materials are mixed in the required proportion and grinded into small fragments of 100 mm. These lumps are fed in kiln and heated up-to their fusion point which is 1600°C. The molten material fall down on the steel plate and it is send to cool down in rotary kiln. These clinkers are then grounded finely in tube mills unto the fineness not less than 2250 cm2/gram is achieved. Characteristics of High Alumina Cement The characteristics of this cement are, It is very resistant to chemical attacks. The pH level is low. High resistant to chemical corrosion, due to which it is used for construction of water pipes, sewage pipes, factory drains, coastal constructions and in factory chimneys. The refractive index of this cement is high. It has high durability in sulphuric acid. Hardening property of this cement is fast. It acts as a bonding material when added in refractory castables because it forms ceramic bond at high temperatures. Uses of High Alumina Cement 1. Due the property of rapid hardening and strength, it is widely used in marine construction and sewer infrastructure. 2. High alumina cement is also used in refractory concretes where it requires more strength at very high temperature. Advantages of High Alumina Cement The advantages of High Alumina Cement are as follows, 1. Due to the more setting time, time for mixing and placing is more. 2. The resistance for the chemical action is good. 3. Can withstand high temperature. 4. Frost action is low as the heat evolved is more during setting. 5. High alumina cement is very reactive and has very high compressive strength. 6. High resistant to fire. Disadvantages of High Alumina Cement The disadvantages of high alumina cement are as follows, 1. As the heat required for the manufacture of this cement is more, the manufacturing cost of this cement is high. 2. As the fineness is kept not less than 2250 cm2/gram, which is very fine. Care to be taken that it doesn't come in contact with human eye or mouth. 3. As the heat evolution while setting is high, it cannot be used in mass concreting works