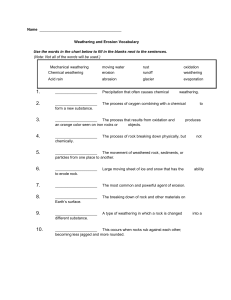
5 Minutes duration What causes the cracks ? Observations What did you observe? Observations What did you observe? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gz4DBn_FFak "why did we watch this? Module E Unit 1 Lesson 2 Weathering Objective 1 Recognize that there are two kinds of weathering. Identify and list the agents of physical weathering. •How can a small crack in a rock eventually split the rock into two or more pieces? What is weathering? •Weathering is the breakdown of rock material by physical and chemical processes. •Two kinds of weathering are physical weathering and chemical weathering. Lab: Limestone Weathering ● You are a member of the city council in a medium sized city in New England, where acid precipitation is a tremendous problem. Acid precipitation is rain, snow, or sleet that is polluted with sulfuric acid, nitric acid, or both. In recent years, the precipitation in some northeastern cities, such as Poughkeepsie, New York, has been as acidic as a cola drink. ● The mayor wants to build a new city hall on the edge of a limestone cliff. You feel that this would be a big mistake because f the acidity of the precipitation in the area would weather away the limestone and damage the building. When you tell this to the mayor, he responds by laughing and saying, “Well yeah, maybe in a million years!” He then tells you to bring proof of the problem to the next city council meeting. ● Using the materials listed below, design an experiment to demonstrate to the mayor just how drastically acid rain can damage limestone in a relatively short period of time. MATERIALS FOR THE EXPERIMENT: (for each group) Limestone Chips (Chalk) Labels for the jars Vinegar Lab Balance 3 Jars with lids Paper Towels Graph Paper True or False Rocks can change shape and composition over time. · _____________Rocks can’t be weathered by wind and chemicals in the air. · _____________A rusty car is an example of weathering. · ______________________ ____________Plants and animals can cause weathering of rocks. Rocks can change shape and composition over time. ( T ) · Rocks can’t be weathered by wind and chemicals in the air.( F) · A rusty car is an example of weathering. ( T ) · Plants and animals can cause weathering of rocks.( T ) True or false Answers Wrap up Warm up weathering Warm up pressure, temperature, biological activity Objective 2 Describe the agents of physical weathering Activity 1 Watch then solve the worksheet 10-15 minutes https://studyjams.scholastic.com/studyjams/jams/science/rocks-minerals-landforms/weatheringand-erosion.htm Video & Notes Activity 2 10 Minutes duration Search for the Agents of physical weathering •Physical weathering is the process by which rock is broken down into smaller pieces by physical changes. •The composition of the material does not change during physical weathering. •Agents of physical weathering include 1. temperature changes 2. pressure changes 3.plant and animal actions 4. Water 5. wind 6. gravity. •Changes in temperature can cause a rock to break apart by weakening the structure of the rock. •Heat causes the rock to expand; cold causes it to contract. 5 Minutes duration Find the meaning of the following terms Exfoliation Abrasion •Rocks that formed under pressure deep within Earth can be exposed to the surface. •As material is removed above the rock, the pressure decreases and the rock expands. •Exfoliation is the process by which the outer layers of rock slowly peel away due to pressure changes. •Abrasion is the breaking down and wearing away of rock material by the mechanical action of other rocks. •Three agents of physical weathering that can cause abrasion are moving water, wind, and gravity. •Rocks suspended in a glacier can also cause abrasion of other rocks on Earth’s surface. •Animals can cause physical weathering by digging burrows. •New rocks, soils, and other materials become exposed at the surface as a result of animal actions. • Materials exposed at the surface are more likely to undergo weathering than those below •Roots of plants start out as tiny strands that may grow in small cracks in rocks. •As the roots grow, they put more pressure on the rock, causing the rock to expand and eventually break apart. Class activity 10-15 Minutes duration Solve the assignment ( weathering, erosion and deposition) Group work Online quiz https://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/story.php?title=Weathering-Quiz-1 Warm up burrowing animals Warm up Smooth, shiny rocks that have tumbled along the river bottom have been rounded and polished by Warm up Physical weathering by ABRASION is usually caused by friction due to Warm up Plants usually break open small cracks in rocks with their Objective 3 •To identify and list the agents of chemical weathering Chemical weathering Watch the video then answer the questions 10-15 minutes duration https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6VnVRHIV6j4 1.What are the three types of chemical weathering ? 2. What is oxidation? Give example 3. What is carbonation? Give examples 4. What is hydrations? Give examples 5. How does climates play major role in chemical weathering? What causes chemical weathering? •Chemical weathering is the breakdown of rocks by chemical reactions. •Chemical weathering changes both the composition and appearance of rocks. Agents of chemical weathering include: •Oxidation oxygen in the air •acidification (acid rain). What causes chemical weathering? •Oxidation is the process by which chemicals in rock combine with oxygen in the air or in water. •Rock surfaces sometimes change color, indicating that a chemical reaction may have occurred. • Acid rain is caused by a chemical reaction that begins when compounds like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides are released into the air. These substances can rise very high into the atmosphere, where they mix and react with water, oxygen, and other chemicals to form more acidic pollutants, known as acid rain. Acids can cause chemical weathering by breaking down minerals faster than water alone. •Acids in the atmosphere are created when chemicals combine with water in the air. •Acid precipitation occurs when strong acids fall to Earth as rain, sleet, or snow. What causes chemical weathering? •Acids in groundwater can cause rock to dissolve. • •A small crack in the rock can result in the formation of extensive cave systems carved out over time. •Rock material dissolved in groundwater can be carried and deposited in new locations over time. Have you ever heard about Jeita cave? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5-NCiLpgN6g Let us discover the beauty of stalactites and stalagmites Question: What is the difference between stalactites and stalagmites? Stalactites: is a type of formation that hangs from the ceiling of caves A stalagmite is a type of rock formation that rises from the floor of a cave. Solve the following 10 minutes duration Warm up Objective 4 •To identify the difference between physical and chemical weathering by constructing a Venn diagram. Compare and contrast between physical and chemical weathering using Venn Diagram Click and solve live worksheet https://www.liveworksheets.com/vl823139qm Solve The assignment If time allows Weathering sorting Class activity Duration 15 Minutes In small groups of 2-3, have students sort the weathering cards as either mechanical (physical) weathering or chemical weathering. Groups must be able to describe why the statement or image is a particular form of weathering. Wrap up •How does chemical weathering change Earth’s surface? • •What are some similarities between Frost wedging and plant root growth in a rock?