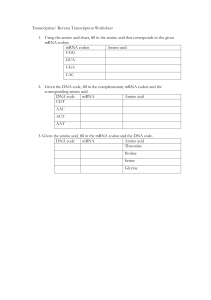
Republic of the Philippines Department of Education Caraga Administrative Region Province of Surigao del Sur Cortes II District MATHO INTEGRATED SECONDARY SCHOOL Matho, Cortes, Surigao del Sur Lesson Plan in Science 10 Third Quarter (Amino Acid Coded from DNA-Base & mRNA Codon) Content Standard: The information stored in DNA as being used to make proteins Performance Standard: Identify the amino acids coded for by the mRNA codon using the Genetic Code Table. Learning Competency: Explain how protein is made using information from DNA (S10LT-IIId37). I. Objectives Along with the teaching-learning process, students shall have: 1. identified the DNA bases and mRNA codons; 2. recognized the role of DNA and mRNA codons that corresponds to the amino acids in proteins; and 3. completed the amino acids coded for by the messenger RNA codon using the Genetic Code Table. II. Subject Matter Topic: Reference: Materials: Values Integration: Amino Acid Coded from DNA-Base & mRNA Codon Alvarez, Liza A., et.al. (2015). Science 10. 1st edition. Department of Education PC Tablet, Reference Book, Paper, Genetic Code Table (Tarpaulin) Determination in building! III. Procedure A. Preparation Prayer Create conducive environment Checking of attendance and tasks Republic of the Philippines Department of Education Caraga Administrative Region Province of Surigao del Sur Cortes II District MATHO INTEGRATED SECONDARY SCHOOL Matho, Cortes, Surigao del Sur B. Review/Drill Initiate practice test/exercise on related topic on nitrogenous bases on the previous lesson. Sample Activity: Each combination of three nitrogenous bases on the messenger RNA molecule is a codon, a three letter code for a specific amino acid. Use the table below to identify the specific amino acid for each messenger RNA codon. DNA SEQUENCE: m RNA: Amino Acid: GCA CGU Arginine AGT UCA Serine ACC TGA UGG ACU Tryptophan Threonine C. Presentation Activity Directions: Perform the activity below through identify the amino acids coded for by the m RNA codon using the Genetic Code Table. Trace the Code Objective: Identify the amino acids coded for by the mRNA codon. Use the Genetic Code Table for translation of codons to amino acid/protein. Materials: Genetic Code Table Activity Sheets Procedure: 1. Copy and fill in the table. 2. Refer to the Genetic Code Table to identify the amino acid. Republic of the Philippines Department of Education Caraga Administrative Region Province of Surigao del Sur Cortes II District MATHO INTEGRATED SECONDARY SCHOOL Matho, Cortes, Surigao del Sur Order of bases in DNA TAG CAT Order of bases in m RNA (codon) AUC Order of bases in t RNA Amino Acid Coded into Proteins GUC CCA Methionine Valine ACA AAA GAA ACU UGU CUU 3. To determine the order of bases in the column (DNA), second column (codon), and third column (anticodon), consider the complementary base pairs in DNA: adenine pairs with thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine. While in RNA, adenine pairs with uracil and guanine pairs with cytosine. 4. To identify the amino acid, look at the bases in the mRNA codon, e.g., AUG using the Genetic Code Table. Look for the first letter of the mRNA codon on the left side of the genetic code table (A), the second letter of the mRNA on the second letter column (U), and the third letter on the right side column (G). AUG codes for the amino acid-methionine. 5. Do the same with the other codons in the chart. Fig. 1 Genetic Code Table https://byjus.com/biology/genetic-code/ Republic of the Philippines Department of Education Caraga Administrative Region Province of Surigao del Sur Cortes II District MATHO INTEGRATED SECONDARY SCHOOL Matho, Cortes, Surigao del Sur Analysis Directions: The students will have shared their perceived ideas or learning from the concrete performance they have done. Guide Questions: 1. Why is specific base pairing essential to the processes of transaction and translation? 2. How many codon/s codes for one amino acid? Abstraction Directions: The teacher will have facilitated the discussion and some enrichments to the class to enhance student’s understanding of the lesson on Amino Acid Coded from DNA-Base & mRNA Codon. Amino Acid Coded from DNA-Base & mRNA Codon - - DNA Replication is a process in which the DNA is copied. - mRNA is a messenger RNA; brings information from the DNA in the nucleus to the cytoplasm. - Transcription is a process of copying DNA sequence into mRNA. - rRNA is a ribosomal RNA; hold tightly to the mRNA and use its information to assemble amino acids. Fig. 2 Process of DNA coding to Amino Acid - Nucleotide is a carbon ring structure that contains one or more atoms of nitrogen. In DNA, there are four possible nitrogen bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). Codon is a set of three nitrogenous bases in mRNA representing an amino acid or a start/stop codon. Anticodon is the complement of the mRNA; triplet code in the tRNA. Republic of the Philippines Department of Education Caraga Administrative Region Province of Surigao del Sur Cortes II District MATHO INTEGRATED SECONDARY SCHOOL Matho, Cortes, Surigao del Sur - Translation is a process of converting information in m RNA into a sequence of amino acids in a protein. - t RNA is a transfer RNA; a type of RNA that attach the correct amino acid to the protein chain that is being synthesized in the ribosome. - Genetic Code is a set of rules that specify the codons in DNA or RNA that corresponds to the amino acids in proteins. Application Directions: Read the concept of normal and missense mutation and complete the figure below. The figure below shows changes in the sequences of bases in normal hemoglobin and the one affected by mutation. A recessive gene causes sickle-cell anemia, where most of the red blood cells stiffen and become sickle shape in affected people. These diseased cells carry less oxygen than normal cells. People affected by the disease eventually die. Fig. 3 Normal and Missense Mutation of Red Blood Cells Republic of the Philippines Department of Education Caraga Administrative Region Province of Surigao del Sur Cortes II District MATHO INTEGRATED SECONDARY SCHOOL Matho, Cortes, Surigao del Sur Points 9-10 6-8 3-5 0-2 Descriptions Understanding of concept is clearly evident, uses strategies to get accurate results and uses logical thinking to arrive at conclusion. Understanding of the concept is evident, uses appropriate strategies to arrive at a results and shows thinking skills to arrive at the conclusion. Has a limited understanding of the concept, uses strategies that are ineffective and attempts to show thinking skills. Has a complete lack of understanding of concept and makes no attempt to use a strategy. Table 2. Scoring Rubrics for Figure Analysis (Adopted from http://www.google.com/search?q=+rubric+in+science) Agreement Directions: Research on the chromosomal mutation and its explain examples. (10 points each) Guide Questions: 1. What does chromosomal mutation infer? 2. Cite examples of chromosomal mutation and provide figures of each? Prepared by: Noted by: EMMANUEL II L. GADDAO Science Teacher MARIA ELENA F. MORALES, Ed. School Head Republic of the Philippines Department of Education Caraga Administrative Region Province of Surigao del Sur Cortes II District MATHO INTEGRATED SECONDARY SCHOOL Matho, Cortes, Surigao del Sur Trace the Code Objective: Identify the amino acids coded for by the mRNA codon. Use the Genetic Code Table for translation of codons to amino acid/protein. Materials: Pen, Paper, and Genetic Code Table SCORE: /27 Order of bases in DNA Order of bases in m RNA (codon) TAG AUC Order of bases in t RNA Amino Acid Coded into Proteins CAT GUC CCA Methionine Valine ACU ACA UGU AAA GAA CUU