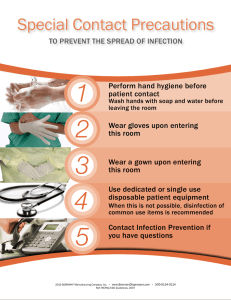
Chapter 21: Concepts of Care for Patients With Infection Ignatavicius: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The nurse learning about infection discovers that which factor is the best and most important barrier to infection? a. Colonization by host bacteria b. Gastrointestinal secretions c. Inflammatory processes d. Skin and mucous membranes ANS: D The skin and mucous membranes are two of the most important barriers against infection. The other options are also barriers, but are considered secondary to skin and mucous membranes. DIF: Understanding TOP: Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning KEY: Infection MSC: Client Needs Category: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation 2. A nursing manager is concerned about the number of infections on the hospital unit. What action by the manager would best help prevent these infections? a. Auditing staff members’ hand hygiene practices b. Ensuring clients are placed in appropriate isolation c. Establishing a policy to remove urinary catheters quickly d. Teaching staff members about infection control methods ANS: A All methods will help prevent infection; however, health care workers’ lack of hand hygiene is the biggest cause of health care–associated infections. The manager can start with a hand hygiene audit to see if this is a contributing cause. DIF: Applying TOP: Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment KEY: Infection, Infection control MSC: Client Needs Category: Safe and Effective Care Environment: Safety and Infection Control 3. An assistive personnel asks why brushing client s’ teeth with a toothbrush in the intensive care unit is important to infection control. What response by the registered nurse is best? a. “It mechanically removes biofilm on teeth.” b. “It’s easier to clean all surfaces with a brush.” c. “Oral care is important to all our clients.” d. “Toothbrushes last longer than oral swabs.” ANS: A Biofilms are a complex group of bacteria that function within a slimy gel on surfaces such as teeth. Mechanical disruption (i.e., toothbrushing with friction) is the best way to control them. The other answers are not accurate. DIF: Understanding TOP: Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning KEY: Infection, Infection control MSC: Client Needs Category: Safe and Effective Care Environment: Safety and Infection Control 4. A client is admitted with possible sepsis. Which action will the nurse perform first? a. Administer antibiotics. b. Give an antipyretic. c. Place the client in isolation. d. Obtain specified cultures. ANS: D Prior to administering antibiotics, the nurse obtains the prescribed cultures. Broad-spectrum antibiotics will be administered until the culture and sensitivity results are known. Antipyretics are given if the client is uncomfortable; fever is a defense mechanism. Giving antipyretics does not occur before obtaining cultures. The client may or may not need isolation. DIF: Applying TOP: Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation KEY: Infection, Medication administration MSC: Client Needs Category: Safe and Effective Care Environment: Management of Care 5. A client is hospitalized and on multiple antibiotics. The client develops frequent diarrhea. What action by the nurse is most important? a. Consult with the primary health care provider about obtaining stool cultures. b. Delegate frequent perianal care to assistive personnel. c. Place the client on NPO status until the diarrhea resolves. d. Request a prescription for an antidiarrheal medication. ANS: A Hospitalized clients who have three or more stools a day for 2 or more days are suspected of having infection with Clostridium difficile. The nurse will inform the primary health care provider and request stool cultures. Frequent perianal care is important and can be delegated but is not the most important action. The client does not necessarily need to be NPO; if the client is NPO, the nurse ensures he or she is getting appropriate IV fluids to prevent dehydration. Antidiarrheal medication may or may not be appropriate as the diarrhea serves as the portal of exit for the infection. DIF: Applying TOP: Integrated Process: Communication and Documentation KEY: Infection, Diagnostic testing MSC: Client Needs Category: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential Copyright © 2021, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 1 6. A nurse is observing as an assistive personnel (AP) performs hygiene and provides comfort measures to a client with an infection. What action by the AP requires intervention by the nurse? a. Not using gloves while combing the client’s hair b. Rinsing the client’s commode pan after use c. Ordering an oscillating fan for the client d. Wearing gloves when providing perianal care ANS: C Fans in client care areas are discouraged because they can disperse airborne or droplet-borne pathogens. The other actions are appropriate. If the client has a scalp infection or infestation, the AP will wear gloves; otherwise, it is not required for grooming the hair. DIF: Analyzing TOP: Integrated Process: Communication and Documentation KEY: Infection, Infection control MSC: Client Needs Category: Safe and Effective Care Environment: Safety and Infection Control 7. A client is to receive a fecal microbiota transplantation tomorrow (FMT). What action by the nurse is best? a. Administer bowel cleansing as prescribed. b. Educate the client on immunosuppressive drugs. c. Inform the client he/she will drink a thick liquid. d. Place a nasogastric tube to intermittent suction. ANS: A The usual route of delivering an FMT is via colonoscopy, so the client would have a bowel cleansing as prescribed for that procedure. The client will not need immunosuppressant drugs, to drink the material, or have an NG tube inserted. DIF: Applying TOP: Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation KEY: Infection MSC: Client Needs Category: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 8. A nurse manager is preparing an educational session for floor nurses on drug-resistant organisms. Which statement below indicates the need to review this information? a. “Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus can be hospital- or community-acquired.” b. “Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus can live on surfaces and be infectious for weeks.” c. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae is hard to treat due to enzymes that break down antibiotics.” d. “If you leave work wearing your scrubs, go directly home and wash them right away.” ANS: D To help prevent the transmission of an MDRO, wear scrubs and change clothes before leaving work. Keep work clothes separate from personal clothes. The nursing manager would need to correct his or her knowledge if he or she is letting staff know that wearing scrubs home is alright. The other statements are correct about multi-drug resistant organisms. DIF: Analyzing TOP: Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation KEY: Infection, Infection control MSC: Client Needs Category: Safe and Effective Care Environment: Safety and Infection Control 9. The nurse caring for clients admitted for infectious diseases understands what information about emerging global diseases and bioterrorism? a. Many infections are or could be spread by international travel. b. Safer food preparation practices have decreased foodborne illnesses. c. The majority of Americans have adequate innate immunity to smallpox. d. Plague produces a mild illness and generally has a low mortality rate. ANS: A Increased global travel has resulted in the spread of many emerging diseases and has the potential to spread diseases caused by bioterrorism. Foodborne illnesses are on the increase. Many people in the United States have never been vaccinated against smallpox, and those who have are not guaranteed life-long protection. Plague can be fatal. DIF: Analyzing TOP: Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation KEY: Infection, Infection control MSC: Client Needs Category: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation 10. A client has been placed on Contact Precautions. The client’s family is very afraid to visit for fear of being “contaminated” by the client. What action by the nurse is best? a. Explain to them that these precautions are mandated by law. b. Show the family how to avoid spreading the disease. c. Reassure the family that they will not get the infection. d. Tell the family it is important that they visit the client. ANS: B Visitors may be apprehensive about visiting a client in Transmission-Based Precautions. The nurse would reassure the visitors that taking appropriate precautions will minimize their risks. The nurse would then demonstrate what precautions were needed. The other options do nothing to ease the family’s fears. DIF: Applying TOP: Integrated Process: Communication and Documentation KEY: Infection, Transmission-based precautions MSC: Client Needs Category: Psychosocial Integrity Copyright © 2021, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 2 11. A nurse is caring for a client who has methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection cultured from the urine. What action by the nurse is most appropriate? a. Prepare to administer vancomycin. b. Strictly limit visitors to immediate family only. c. Wash hands only after taking off gloves after care. d. Wear a respirator when handling urine output. ANS: A Vancomycin is one of a few drugs approved to treat MRSA. The others include linezolid and ceftaroline fosamil. Delafloxacin is a new antibiotic approved to treat MRSA. Visitation does not need to be limited to immediate family only. Hand hygiene is performed before and after wearing gloves. A respirator is not needed, but if splashing is anticipated, a face shield can be used. DIF: Remembering TOP: Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation KEY: Infection, Antibiotics MSC: Client Needs Category: Physiological Integrity: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies 12. A hospitalized client is placed on Contact Precautions. The client needs to have a computed tomography (CT) scan. What action by the nurse is most appropriate? a. Ensure that the radiology department is aware of the Isolation Precautions. b. Plan to travel with the client to ensure appropriate precautions are used. c. No special precautions are needed when this client leaves the unit. d. Notify the primary health care provider that the client cannot leave the room. ANS: A Clients in isolation will leave their rooms only when necessary, such as for a CT scan that cannot be done portably in the room. The nurse will ensure that the receiving department is aware of the Isolation Precautions needed to care for the client. The other options are not needed. DIF: Applying TOP: Integrated Process: Communication and Documentation KEY: Infection, Transmission-based precautions MSC: Client Needs Category: Safe and Effective Care Environment: Management of Care 13. A nurse receives report from the laboratory on a client who was admitted for fever. The laboratory technician states that the client has “a shift to the left” on the white blood cell count. What action by the nurse is most important? a. Document findings and continue monitoring. b. Notify the primary health care provider and request antibiotics. c. Place the client in protective isolation. d. Tell the client this signifies inflammation. ANS: B A shift to the left indicates an increase in immature neutrophils and is often seen in infections, especially those caused by bacteria. The nurse will notify the primary health care provider and request antibiotics (and cultures). Documentation and teaching need to be done, but the nurse needs to do more. The client does not need protective isolation. DIF: Applying TOP: Integrated Process: Communication and Documentation KEY: Infection, Laboratory values MSC: Client Needs Category: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential MULTIPLE RESPONSE 1. The nurse caring for clients understands that which factors must be present to transmit infection? (Select all that apply.) a. Colonization b. Host c. Mode of transmission d. Portal of entry e. Reservoir f. Poor hygiene ANS: B, C, D, E Factors that must be present in order to transmit an infection include a host with a portal of entry, a mode of transmission, and a reservoir. Colonization is not one of these factors. Poor hygiene may or may not contribute to infection. DIF: Remembering TOP: Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning KEY: Infection MSC: Client Needs Category: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation Copyright © 2021, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 3 2. Which statements are true regarding Standard Precautions? (Select all that apply.) a. Always wear a gown when performing hygiene on clients. b. Sneeze into your sleeve or into a tissue that you throw away. c. Remain 3 feet (1 m) away from any client who has an infection. d. Use personal protective equipment as needed for client care. e. Wear gloves when touching clients’ excretions or secretions. f. Cohorting clients who have infections caused by the same organism. ANS: D, E Standard Precautions implies that contact with bodily secretions, excretions, and moist mucous membranes and tissues (excluding perspiration) is potentially infectious. Always wear gloves when coming into contact with such material. Other personal protective equipment is used based on the care being given. For example, if face splashing is expected, you will also wear a mask. Wearing a gown for hygiene is not required. Sneezing into your sleeve or tissue is part of respiratory etiquette. Remaining 3 feet (1 m) away from client is also not part of Standard Precautions. Cohorting infectious clients can be used for deciding room/bed placement, but is not part of Standard Precautions. DIF: TOP: KEY: MSC: Remembering Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation Infection, Standard precautions Client Needs Category: Safe and Effective Care Environment: Safety and Infection Control 3. The nurse learns that effective antimicrobial therapy requires which factors to be present? (Select all that apply.) a. Appropriate drug b. Proper route of administration c. Standardized peak levels d. Sufficient dose e. Sufficient length of treatment f. Appropriate trough levels ANS: A, B, D, E In order to be effective, antimicrobial therapy must use the appropriate drug in a sufficient dose, for a sufficient length of time, and given via the appropriate route. Some antimicrobials do require monitoring for peak and trough levels, but not all. DIF: Remembering TOP: Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning KEY: Infection, Antibiotics MSC: Client Needs Category: Physiological Integrity: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies 4. A client is being admitted with suspected tuberculosis (TB). What actions by the nurse are best? (Select all that apply.) a. Admit the client to a negative-airflow room. b. Maintain a distance of 3 feet (1 m) from the client at all times. c. Obtain specialized respirators for caregiving. d. Other than wearing gloves, no special actions are needed. e. Wash hands with chlorhexidine after providing care. f. Assure client has a respirator for moving between departments. ANS: A, C A client with suspected TB is admitted to Airborne Precautions, which includes a negative-airflow room and special N95 or PAPR masks to be worn when providing care. A 3-foot (1 m) distance without a mask is required for Droplet Precautions (a nurse providing direct care cannot ensure that he or she will never need to be within 3 feet of the client). Chlorhexidine is used for clients with a high risk of infection. When moving between departments, the client wears a surgical mask. DIF: Applying TOP: Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation KEY: Infection, Transmission-based precautions MSC: Client Needs Category: Safe and Effective Care Environment: Safety and Infection Control 5. A nurse asks the supervisor why older adults are more prone to infection than other adults. What reasons does the supervisor give? (Select all that apply.) a. Age-related decrease in immune function b. Decreased cough and gag reflexes c. Diminished acidity of gastric secretions d. Increased lymphocytes and antibodies e. Thinning skin that is less protective f. Higher rates of chronic illness ANS: A, B, C, E, F Older adults have several age-related changes making them more susceptible to infection, including decreased immune function, decreased cough and gag reflex, decreased acidity of gastric secretions, thinning skin, fewer lymphocytes and antibodies, and higher rates of chronic illness. DIF: Remembering TOP: Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning KEY: Infection, Older adult MSC: Client Needs Category: Health Promotion and Maintenance Copyright © 2021, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 4 6. A client with an infection has a fever. What actions by the nurse help increase the client’s comfort? (Select all that apply.) a. Administer antipyretics around the clock. b. Change the client’s gown and linens when damp. c. Offer cool fluids to the client frequently. d. Place ice bags in the armpits and groin. e. Provide a fan to help cool the client. f. Sponging the client with tepid water. ANS: B, C, F Comfort measures appropriate for this client include offering frequent cool drinks, and changing linens or the gown when damp. Fever is a defense mechanism, and antipyretics will be administered only when the client is uncomfortable. Ice bags can help cool the client quickly but are not comfort measures. Fans are discouraged because they can disperse microbes. Sponging the client’s body with tepid water is also helpful. DIF: Applying TOP: Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation KEY: Infection, Comfort measures MSC: Client Needs Category: Physiological Integrity: Basic Care and Comfort 7. A nurse plans care for a client who is at risk for infection. Which interventions will the nurse implement to prevent infection? (Select all that apply.) a. Administer prophylactic antibiotics. b. Monitor white blood cell count and differential. c. Screen all visitors for infections. d. Implement Transmission-Based Precautions. e. Promote sufficient nutritional intake. ANS: B, C, E Nursing interventions for clients at risk for infection include monitoring white blood cell count and differential, screening visitors for infections and infectious disease, and promoting sufficient nutritional intake. Standard Precautions are required but not Transmission-Based Precautions. Prophylactic antibiotics are not generally used to prevent infections. DIF: Understanding TOP: Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation KEY: Infection, Infection control MSC: Client Needs Category: Health Promotion and Maintenance 8. A nurse cares for several clients on an inpatient unit. Which infection control measures will the nurse implement? (Select all that apply.) a. Wear a gown when contact of clothing with body fluids is anticipated. b. Teach clients and visitors respiratory hygiene techniques. c. Obtain powered air purifying respirators for all staff members. d. Do not use alcohol-based hand rub between client contacts. e. Disinfect frequently touched surfaces in client-care areas. ANS: A, B, E Infection control measures appropriate to all clients include hand hygiene with alcohol-based hand rub or soap between client contact, procedures for routine care, cleaning and disinfection of frequently contaminated surfaces, and wearing personal protective equipment when contamination is anticipated. Client and visitors would be instructed on appropriate respiratory hygiene and cough etiquette. No information in the stem indicates the clients need anything more than Standard Precautions. DIF: Understanding TOP: Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation KEY: Infection, Infection control MSC: Client Needs Category: Safe and Effective Care Environment: Safety and Infection Control Copyright © 2021, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 5