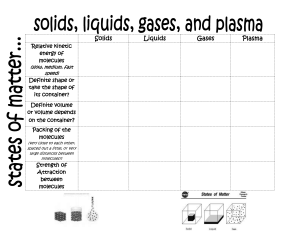
What are the three different state of matter SOLID, LIQUID, GAS What is matter? Anything that has mass and occupies space (E.g. Everything and anything around us : Water , gas , rocks, table , juice, plants , animals) Example of SOLID Table , key , bottle Example of LIQUID Water , juice , glue , oil , Examples of GAS Oxygen, CO2 , neon ,Hydrogen , Air (mixture of gas) Properties of SOLID Properties of LIQUID Definite shape Definite volume Molecules are tightly packed. Very little space between molecules. Strongest force of attraction Molecules vibrate in its position. Takes shape of the container Definite volume Less closely packed Molecules can slide over each other Weaker force of attraction compared to solid Properties of GAS Definite mass Takes the shape of the container. Fills the volume of container. Molecules are randomly spread throughout the container. Molecules are least closely packed Weaker force of attraction compared to liquid and solid. More space between molecules. SOLID --- LIQUID Process is called melting. When heat is applied Solid changes to liquid by melting. LIQUID -- GAS Process is called Evaporation / boiling. When heat is applied liquid changes to gas by the process of evaporation. GAS--- LIQUID Process is called condensation. When heat is removed from gas it changes to liquid by the process of condensation. LIQUID ---SOLID Process is called Freezing. When heat is removed from a liquid it changes to solid by the process of freezing. Kinetic Energy Energy of movement. Kinetic molecular theory All matter is composed of small particles (atoms, molecules or ions) They are in constant, random motion (either vibrating, sliding or moving away) constantly collide with each other and with the walls of their container. Diffusion Spontaneous mixing of the particles of two substances caused by their random motion The kinetic energy of gas molecules is proportional to their? Temperature What causes a gas to exert pressure when confined in a container From collisions As the temperature of a gas decreases what change occurs in the amount of kinetic energy Energy decreases as it slows down What is the relationship between temperature & molecular motion when hot molecules move fast , colder molecules move slow Increase in the temperature of a gas confined in a rigid container cause an increase in the pressure of the gas . Why? Cause molecules to move faster which increases the no. of collisions & pressure According to the kinetic molecular theory, which substances are made of particles All matter According to the kinetic- molecular theory particles of a gas Neither attract nor repel each other but collide Which is an example of gas diffusion The odor of perfume spreading throughout a room By which process do gases take shape of their container Diffusion If a gas with an odor is real eased in a room, it quickly can be detected across the room because it Diffuses Diffusion between two gasses occurs most rapidly if the gasses are at a High temperature & molecules are small slope of heating curve temperature⬆️ kinetic energy⬆️ potential energy↔️ particle motion⬆️ plateau of heating curve temperature↔️ kinetic energy↔️ potential energy⬆️ particle motion (moves apart)= phase change HEATING CURVE a plot of temperature vs time when the system is heated and energy is transferred into it ie: liquid - - gas, solid - - liquid COOLING CURVE a plot of temperature vs time when the heating system is allowed to cool. energy is released and bonds are formed. ie: liquid - - solid, gas - - liquid TEMPERATURE related to the average kinetic energy of the molecules of a substance HEAT a measurement of the total energy in a substance, which is made up of not only the kinetic energies but also potential energies of the molecule SOLID --> LIQUID Melting LIQUID --> SOLID Freezing / Solidification LIQUID --> GAS Evaporation GAS --> LIQUID Condensation Change of state Conversion of a substance from one physical form to another Melting Solid to liquid Liquid to solid Evaporation Liquid to gas Boiling Liquid to vapour Condensation Gas to liquid Sublimation Solid directly to gas Deposition Gas to solid What is diffusion? Diffusion is the net movement of particles from a area of higher concentration to a area of lower concentration. It does not require energy. Why when there is a higher temperature will there be a faster diffusion rate? More energy so move faster In terms of gas what happens in a sealed container that is filled with gas? Gas particles are colliding with each other so they then smash onto the walls of the container creating an outward force. What happens if the container size is increased? If the same amount of gas is put into a larger container there will be fewer Collisions with the walls of the container, so the pressure will decrease What happens if the same amount of gas is poured into a smaller container? There will be Collisions on the walls as particles are being squashed together. The reassure will increase Diffusion In everyday life includes ? Smelling scents Oxygen getting into bodies Chlorine moving through the swimming pool. How do pollen grains move in water? They move in a zig zag A random pattern Pollen grains move in zig zag random pattern. Why does this happen? Smaller molecules are bouncing into bigger ones which creates a pattern Define diffusion The net movement of particles from high to low concentration. What affects the rate of diffusion Temperature Surface area concentration Why Can’t Diffusion occur in solids The bonds between solids’ particles are too strong Gas molecules are always in what type of motion ? Constant and random motion The kinetic energy of gas molecules is proportional to their? Temperature What causes a gas to exert pressure when confined in a container From collisions As the temperature of a gas decreases what change occurs in the amount of kinetic energy Energy decreases as it slows down What property of gas particles is measured by temperature The movement of particles What is the relationship between temperature & molecular motion when hot molecules move fast, colder molecules move slow In the temperature of a gas confines in a rigid container cause an increase in the pressure of the gas Cause molecules to move faster which increases the # of collisions & pressure According to the kinetic molecular theory , which substances are made of particles All matter According to the kinetic- molecular theory particles of a gas Neither attract nor repel each other but collide If a gas with an odor is real eased in a room, it quickly can be detected across the room because it Diffuses Diffusion between two gasses occurs most rapidly if the gasses are at a High temperature & molecules are small Boiling point of pure water 1000C Melting point of pure water O0 C What is the boiling temperature of iron in the heating curve below? 2550 0C