CSEC Chemistry June 2012
,
,,.
t"/
L,
fr/^n,
2
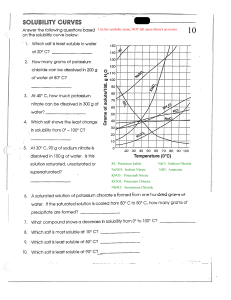
Which of the following features is TRUE
for the particles in a gas?
1
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
The mass oumber of an elemenl
4
Larger when heated
Furthcr aPart when heated
Very closclY Packed together
Strong forces between them
number
of
(A)
(B)
neutrons in an atom o[ the elen]
protons and electrons in an aton
the element
neutrons and Protons in an aton
the element
protons, neutrons and electron
an atom of the element
(c)
(D)
Item 2 refers to the following experiment'
In the diagram below, X
5
Funnel
symbol of
Subllmlte
I
Mirture o[
i
rmmonlum chloride
I
rnd c2lcium sulPhtte
A mixturc of ammonium chtoride
i
i
of
Neutrons
Number
probably b€
I
I
I
I
I
I
i
I
!
i
(A)
(B)
iCl
ammonium chloride
(D)
calcium chloride and ammonium
calcium sulPhatc
calcium sulPhate and ammonium
sUlPhate
6
I
)
Number of
Electrons
(A)
(B)
20
20
20
l8
(c)
60
I8
60
20
(D)
chloride
I
rePrcsents
number of neutrons and electrons in
shown above, until no further change
takes placc. Thc sublimate would MOST
i
X+
Which of the following
and
calcium sulPhate is heated, in the appararus
I
rePresents
positive ion
x0
;
.,
a
40
i
ls
The arrangementofelements in the Peri
Table is based on
i
I
3
i
i
I
!
The atomic strubtures of X and Y are
2, 8,5 and 2,8,6 respectively. Which of
(A)
the following pairs of,properties represents
(c)
X
(D)
and Y?
I
x
I
I
I
I
(A)
(B)
Metal
(c)
Non-metal
Non-metal
(D)
I
I
(B)
Metal
Y
non-metal
metal
metal
non-metal
'1
atomic number
mass number
relative atomic mass
relative molecular mass
The mass concentratioll oI a potasl
r.
chloride solution is 60 g dm What i
mass o[ potassium chloride in 25 cr
this solution?
(A)
(B)
0.001 5 g
0.15 g
1.5 B
(c)
i
;
(D)
l
J.0 s
1
The quantity,
8
'I
to the mass of
mole of atoms of an elemeot" refers
atom of the element
x l01r atoms
the elemenr which contains 6 0
dm' at STP
24'0
occupies
*i,i"tt
tt
" "i"*"nt *ni"n.o-bin"' comPletely with
I
(A)
(B)
(c)
ii,"
(D)
l2
g of carbon -12
"i"-"ri
otlead(Il) nitrate?
correctly rePresents the thermal decomposition
Wbich ofthe following equations
9
10.
2 Pb(No,), (s) + 2o'1(c)
(A)
2Pb(Nor)r(s)
-
(B)
zPu(No,),(sj
-"
2tbo,(s) + 4No'(e)
(c)
2Pb(NO,),(s)
..
2Pbo(s) + 4NO1(g) + o,(C)
(D)
2Pb(No!),(s)
-
2Pb(s) + 4No'(c) +
has
which of the following compounds of
,i"'6"i.or"sr percentage(M'bY mass
= relative
it ine mole?
rt"*"
atomic mass:
-.i""rl"t mass; rblative
H=l;i=lz;o=16)
."ruir
2o'(e)
Items
ll-12
refer lo Compound X' which
-U'
melts at l8 "C and boils at 55
Which of the following statements
1l
;;;;;,
rs
the intermolecular forces of
attraction in ComPound X?
(A)
C,H,O, (M,= 69)
(A)
(B)
(B)
c.H,ro, (M,= 180)
(c)
(C)
C,Huo
(D)
C,H,O (M, = 60)
(D)
TheY are strong.
Thev increase above l8'C'
Thev decrease aboYe I8"C
They increase- above 55'C
(M,:46)
12
to be
Compound X is MOST likely
(A)
(B)
(C)
iPj
l3
a gidnt molecute
a liquid metal
a simPle molecule
an ionic comPound
exist
which of the following elements can
state?
in *o,"if,"n on" form in the SAME
(A)
(B)
Carbon
(c)
Iron
Iodine
(D)
Neon
4
becausc
Grcphite can be used as a lubricant
l4
II of
Barium (Ba) rs an elemenl in Group
18
water
ihe Periodic Table- It reacts with cold
of the
,'.-g,";-iydt"g",
loos€ electrons which can
throuBhout the lattice
(^)
formul
move
weak attrac t io n amonB the
hexagonal I aYers of carbon
(B)
BaO
(c)
BaOH
(D)
Ba(OH),
strong attraction among .the
hexagonal layers ot carbon
(c)
strong attraction within.the
hexagonal laYers ot car bon
true of
Wlrich of the following is NOT
knJwn as the harogens?
;J;;;;;;.;;
19
atoms
(c)
a liquid
susoended solids trom
not mrx
do
a oair of liquids that
(^)
(B)
Thev are all non-metals'
tre loss
Thev form negative ions bY
of electrons from thei( atoms'
The boiling Point of the elements
(A)
(B)
in separating
Sublimation can be used
15
Baro
the
atoms
(D)
of
a
(A)
(B)
atoms
and another subslance
components of
(D)
boiling Points
a solid with weak int'erPartrcle
forces from one with strong
a
lncrease
The oxidizing Power o( the
(D)
liquid with similar
(c)
numbers
increases as their atomic
e I
emen
ts decreases as thelr
atomic numbers increase'
forces
Item
2O refers to one mole
ofEACtI oftht
following acids'
16
would
Which of thc following substances
to .t'"* thg LEAST solubilitv
l.
i" .ipJ.a
It.
IIt.
in water?
(A)
(B)
(c)
(D)
t'l
Ammonla
20
Ethanol
lodine
Lithium chloride
'Si'licon (Si) is
in
i"ti"ai" frUf"
as
the
(D)
').7
(A)
SiH,
(B)
SiH.
(c)
silHr
(D)
sirHl
mole of NaoH(aq) for comPlet
neutralization?
;;;;;."
(c)
carbon' The compound
and hydrogen ts
silicon
fonned between
ItkelY to havc the formula
cHrcooH
(cooH)l
mor
Which of the above acids require
(A)
(B)
'same group of the
H)SO.
II only
I and III onlY
II and III onlY
I, lI and III
Which of the following terms BEs
describes strong acids?
(A)
(B)
(c)
(D)
Concentrated
P artial lY icnized
lonized to a larBe extent
tonrz
Concentrated and PartiallY
5
22
A solution, when treated with the gas
sulphur dioxide, becomes green. The
26.
solution contains potassium
4
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
What is the change in th€ oxidation numbor
of nitrogcn in the equation belowf
NH, (g) + 5O, (g)
nitrate
sulphate
(A)
dichromate(Vl)
(B)
manganate(VI!
(c)
(D)
23
Which of the following observations
would be expected when aqueous sodium
hydroxide is. added to an ammonium salt
and the mixture is warmed?
(A)
(B)
Alkaline gas produced
(c)
White precipitatc insoluble in
(D)
Green precipitate insoluble in
.,n
+
a
NO(g) + 6H,O(g)
+3to+2
+3to-2
-3(o+2
-ito-z
Which of the following reactions would
you expect to take place?
Whito precipitate soluble in cxcess
I.
II.
ni.
Zn(s) + Mgr'(aq) -+ Mg(s) + Zn'1*(aq)
Mg(s) + Cu'1'(aq) + Cu(s) + Mgz*169
(A)
(B)
I only
Cu(s) + Mg'*(aq)
-i
Mg(s) + Cui'(aq)
excess
€xcess
(c)
(D)
24
Which of the following pairs of subslances
would be MOST suitable for the Preparation
of copper sulphate crystals?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
.
1.5.
(A)
h base
(B)
an acid
a reducing ag€Dl
an oxidizing agent
(c)
(D)
Itq4s ?E29 refer to lhe following acids
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Copper and dilute sulphruic acid
Copper and concentrated sulPhuric
acid
Copper nitrate and dilute sulphuric
acid
Copper oxide and dilute sulphuric
acid
When chlorine reacts with sodium to form
sodium chloride, the chlorine is acting as
II only
I and III only
II and III only
Sulphuric acid
Hydrochloric acid
Nitric acid
Ethanoic acid
Match EACH item below with ONE of the
options abovc. EACH option may be used
more than once, once or not at all.
Which of the acids above
28-
has a basicity
').9.
is weakly ionised in aqueous solutions?
of2?
-6
I
I
30
Item 34 refers to the graph helow iv hi(
shows the rate ofreaction fo , differeit pa
ticle sizes of the ;ame mass of.nugr,! siu
reacting with dilute acid.
I
Which of the following is a weak electrolyte?
(A)
(B)
Molten lead
Molten lead bromide
(c)
Aqueons ethanoic acid
Dilute hydrochloric acid
(D)
I
I
I
c
I]
III
3l
During thc electrolysis ofaqueous copper(If)
sulphate solution using inert electrodes, the
ious migrating to the cathode are
(A)
Cu't (aq) and SOI;(aC)
(B)
H. (aq) and OH-(aq)
IV
E
Time
32
(C)
Sol
(D)
Cu'- (aq) and H* (aq)
(aq) and oH- (aq)
34.
magnesium?
(C)
(D)
I
)
(B )
In the anodizing ofan aluminium pot, which
of the following is TRUE?
(A)
(B)
u
Which line on the graph,l,II, III or M
po
dert
BEST represent the reaction with
C)
(D )
Hydrogen is given offat the anode-
II
I
IV
A layer of aluminium hydroxide
forms on the .Pot.
The aluminium.pot is the anode in
the cell-
The electr.olyte is a solution of
sodium chloride.
35.
which of the following statements tn
about the reactants and products rn e
exothermic reaction?
(A)
Products have morc storcd
er[
than the reactants33
How many coulombs (C).of ele ctricity
passes through an electrolyte when a
current o[ 100 A flows for l0 minutes?
(B)
(c)
(D)
(A)
(B)
600
(c)
l0 000
(D)
60 000
100
erI
Reactants have more stored
than the products.
Products and reactanls lta ett
same amount oI stored en cy
Reactants have lesb energ thz
the products since ene cv
absorbed from lhe surrortn lne
7
36.
When crystals of potassium nirale are
dissolved in water, the temperature of the
Items 40-42 refer to the properties of
four melals, W, X, Y and Z, which are
summarised in the following table.
solution decreases because
(A)
eDergy is required to break down the
Metal
crystal struchle ofthe Potassiurn
(B)
nikate
heat is always absorbed when
(c)
substance dissolYes
the water absorbs the energY from
a
There is no reaction
x
the potassium nitrate
(D)
Reaction With Water/Steam
Reacts with steam but not with
cold water.
the energy content of digsolved
. potassium nitrato is lower than
that of solid Potassium hitrate
Y
Reacts rapidly with cold water
Reacts slowly with cold water.
31.
In which of the followint industrial
preparations is a catalyst NOT used?
I.
40.
Sulphuric acid
II
III
Chlorine
Ammonia
(A)
(B)
I only
II only
(c)
I and II onlY
(D)
II and III onlY
Which of the metals is NOT likely to
react with dilute hydrochloric acid to give
,hydrogen?
(A)
(B)
x
(c)
Y
(D)
4t
Which of the metals is likely to form
a
soluble hydroxide?
38
A meral, M, can be extracted by roasting
its ore in air with carbon. Metal M could
(A)
(B)
be
(A)
(B)
Mg
AI
(c)
Ca
(D)
Fe
42
(c)
Y
(D)
z
For which of the following pairs of metals
is the firs!. MOST likely to.disrlace-the
39
Which of the following metals can be
extracted bY electrolYsis?
(A)
(B)
K
(c)
AI
(D)
Fe
Ca
second soltition?
(A)
(B)
X,Y
(c)
w,x
z,v
(D)
8
Which of the following compounds will
NOT evolve carbon dioxide upon heating?
43
Which of the following obsetvations is
Iikely when EXCESS aqueous arnmonra is
added to a solution of coppe(Il) sulphate
and the mixture is shaken?
44
Calcium carbonate
(A)
(B)
Copper(II) carbonate
Lead(II) carbonate
Sodium carbonate
(c)
(D)
(c)
Creen solution
Green precipitate
Deep blue solution
(D)
Light blue PreciPitate
(A)
(B)
required for the fcrmsnta(ion of
which of the foltowing arc the raw materials and conditions
d5
sugars?
(A)
(B)
(c)
(D)
46.
:.t !i
i!
Temperature
ClUcoSe + yeast
Starch + yeas(
Sucross + yeast
Sucrose + glucose
room temPerature
30 .C above room temPerature
i ii
I .:
itr
iti
i.i
il
l
41
rl
'il'
i,i
l 1!
llt
lir
lrl
lri
room temPeraturc
(A)
(B)
(c)
(D)
ll
H-C ll
}I
C
//_o
-C
HH
(A)
(B)
Acids
(c)
Alkenes
(D)
Alcolrols
A.lkanes
o-H
'1
Iess than 7
less than 7
c,H.
c,H.
CH](CH,)ICOOH
cH,(cH,)]COH
thr
Match EACH item below with ONE of
uset
options above. Each option may be
more than once, once or not at all'
polymerisation
I{
1
Item s 48-{9 refer to the following options
condensation
hydrolYsis
neutralisation
followin g structure belgng?
rl
t;
'C above room temPerature
To which homologous ssries does the
t:
li
3O
During the digestion of polysaccharides
by the human body, the main Process
occurring is
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
r1!
pH
Raw Materials
48.
An alcobol
49.
'An alkane
9
The compound ethene is descnbed as being
50
Ethanol can be converted to ethanoic acid
using the apparatus shown belo\',/.
53
unsaturated. This means that the
carbon atoms in ethene are linked
(A)
Ethanol
by single bonds
carbon atoms in the molecule are
very reactiye
molecule has insufficient hYdrogen
(B)
(c)
atoms
molecule contaiDs at least one
(D)
double bond
51.
Thc frrnctional group presenl
il
carboxylic
acids is
(A)
Watrr bath
H
Rei8enl X
I
-c:o
(B)
t+
llea t
OH
Reagent X could.bc
_c:o
(c)
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
H
aqueous bromine
concentrated sulPhuric acid
acidifredPotassiumdichromate(Vl)
aqueous sodium hYdroxide
I
-c-:ou
Items 54-55 refer to the following
I
compounds.
H
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
H
(D)
I
-C=C-OH
H
52.
(A)
(B)
(c)
(D)
dilute sulPhuric acid
dilute hydrochloric acid
concentrated hYdrochi6ric aciti
concentrated sulPhirric acid
Staich
Protein
Polyester
Match EACH item below with ONE of the
options above. Each option may be used
more than once, once or not at all.
I
When ethanoic acid and ethanol react to
form ethyl ethanoate, the catalyst used is
Fat
54
Which comPound produces amino-acids
when hydrolysed?
55
Which compound is NOT considered to be
a polymer?
I
I
- l0
I
56
I
-
A polyamide is formed by a condensation
reaction between a molecule containing
(A)
Item 59 refers to the following srructu
HHH
at least one -OH groupwith another
ttt
H-C - C _
I
containing at least one -NH2
tlr
HIH
grouP
(B)
I
(C)
I
(D)
at least onc -OH group with another
C
H
H-C-H
containing at least one -COOH
group
at least one -COOH group with
another containing at least one
I
H
H
I
-NHr group
two -OH groups with another
containing two -COOH groups
H-C_H
II
lnH
,ll
H-C*C_C_tI
tlt
I
5'l
}IHII
Wlrich of the following statements about
polymers are true?
I
II
are long-chain moleculcs
Pol)mers
I
llt
made byjoining together a large
H
-C- H
lH
H
_C _
oumber of monomer units.
II
Condensation po'lymers are
gcnerally madc up from one
III.
Addition polymerisation invo.lves
the breaking of a C = C double
I
il
li.
tl;
Il
(^)
I
tl
(B)
,l;,
ll
(c)
(D)
: ll'
H
lI only
I and III only
II and III only
I, II and III
I
and
I
H_C-H
IV
lH
lt
H _C
ttlH
i:,
l:
58
i
r:,
H
i'l:
,ll:
H-
ti
I
C - COOH
I
NH
:i
I
lrt,
'lr,
ll;
rll
lil,
(A)
(B)
Polyamide
Polyalkene
(c)
Polyester
Polysaccharide
(D)
_
H
I
H
one below?
;l
C
H_C-H
Which of the following types of polyme i
may be derived liom compounds like the
- li:
_H
H
bond in the monomer,
rlit;l
C
HI
H-c-H
type ofmonomer.
rl
i:i,
Ir
s9
Which of the structures above represt
branched alkanes?
(A)
(B)
I
I
(c)
and II only
and fV on)y
Ill and IV on)y
(D)
I, II and
It I
only
,
60
ll
-
Which of the following compounds can
decolourizc potassium manganate(Vll)?
E
E
C:C
(A)
Il
H
I
I
EH
ll
(B)
H-c-c-H
ll
HE
HIIII
(c)
llr
E-c-c-c-H
rll
I{HII
HII
(D)
ll
llHl
H- C
.
C-
I
I
I
I
I
H
E_ C_H
I
H
END OF TEST
WORK 9N THIS TEST'
IFYOU FINISII BEFORE TIME IS CALLED' CIIECKYOUR
t
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
T
t
I