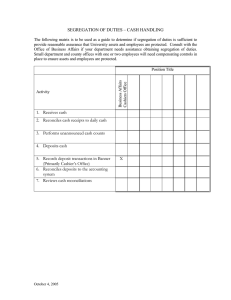
Financial management controls and risk management Internal Control Internal controls are all the policies and procedures adopted by management to assist in achieving the entity’s objectives. An internal control structure should improve the accuracy and reliability of accounting and other forms of information, provide management with the facility to safeguard assets, detect errors, fraud and other irregularities. In doing so an internal control structure provides assurances that a business is properly managed. The main purpose of an effective internal control structure is to assist management by ensuring that, as far as practicable: – The business is conducted in an orderly and efficient manner, – Ensure compliance with all financial and operational requirements, – Irregularities are prevented, or detected and corrected should they occur, – Assets are safeguarded from unauthorised use or disposition, – Financial records and other relevant data bases completely and accurately reflect the entire operational activities of the entity and permit the timely preparation of financial information. Internal control objectives aim to ensure transactions are: – Complete; – Valid and relate to the business; – Properly authorised; – Properly valued; – Properly classified; – Properly recorded, and – Recorded on a timely basis. Financial controls The purpose of financial controls is to ensure: – Specified individuals are held accountable for transactions under their control; – Accounting records are accurately and reliably maintained; – There is adequate segregation of record keeping duties from the custodianship of an entity’s assets; – Transactions are properly authorised; – There are adequate segregation of duties, and – There are adequate checking and reconciliation procedures. Administrative controls Relate to the establishment of a sound operational environment within which accounting (financial) controls may efficiently operate. Examples would include: – Establishment of physical safeguards (eg closed off area) that restrict access to inventory, cash on hand, computers, building, etc., and – Establishment of an organisational chart that depicts areas of responsibility;