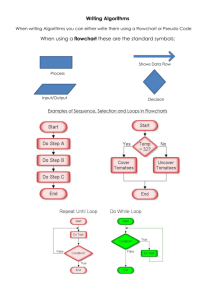
ALGORITHMS What are Algorithms? Algorithms can be defined as the process or set of rules to be followed in calculation or other problem-solving operations, especially by a computer. The first step in every programming language is used to write an algorithm. The algorithm is the step-by-step process for doing a task Why do we follow the algorithm? ✓ It produces an ordered sequence of steps that provide a solution to a problem. ✓ It is also an effective method of solving a problem using a frequency of instructions it forms a fundamental part of Computing. Advantages of Algorithms: 1. It is a step-wise representation of a solution to a given problem, which makes it easy to understand. 2. An algorithm uses a definite procedure. 3. It is not dependent on any programming language, so it is easy to understand for anyone even without programming knowledge. 4. Every step in an algorithm has its logical sequence so it is easy to debug (spot errors). 5. By using an algorithm, the problem is broken down into smaller pieces or steps hence, it is easier for a programmer to convert it into an actual program. Disadvantages of Algorithms: 1. Algorithms are Time consuming. 2. Not suitable for all problems. Difficult to show Branching and Looping in Algorithms. 3. Big tasks are difficult to put in Algorithms as they are very timeconsuming. Tools of algorithms There are mainly two tools to understand the programming logic. These are: 1. Flowchart 2. Pseudocode Flow charts Flowcharts are a pictorial or graphical representation of algorithms. Flowcharts use shapes symbols to represent an activity. The flow of lines with arrows are used to depict(represent) the flow of data within a program The various symbols used in the flowchart are given in the table below Name Symbol Description Terminator box Oval Represent the beginning or end of a flowchart Input/output box Parallelogram Represent the input and output operations in a flowchart Process box Rectangle Represent the process of instructions to be carried out example calculation Decision box Diamond This symbol is used in branching when a decision is to be made Connector box Circle Disconnect one part of the flowchart to another Flow lines This represents the flow of information from one point to another Rules to be followed when writing flowchart 1. The listing of all requirements should be done in a logical order. 2. Ensure that the flowchart has a logical start and finish. 3. The flow of information in a flowchart should be from top to bottom or from left to right. 4. Only one-floor line should come out from the process symbol. 5. In a decision symbol only one flow line should enter it where is there can be any number of outgoing flow lines 6. The Terminator symbol can have only one flowline. 7. The connectors reduce the number of flowlines. This should be used to make the flowchart simple. avoid intersection of long lines. 8. A flowchart should be clear and easy-to-follow START Collect Leaves Wrap the leaves for drying Dry the leaves STOP Advantages of flowchart i. ii. iii. The symbols are self-explanatory and easier to understand. Graphic symbols make the process of explaining an algorithm quite straightforward. With the help of a flowchart problems can be analyzed more effectively. Disadvantages of flowcharts i. ii. iii. iv. Diagrammatic representation takes a lot of time. Difficult to handle complex programs. Standard rules need to be followed for making a flowchart. If changes are required the flowchart may need to be completely redrawn. CHARACTERISTICS OF ALGORITHMS: Precision – the steps are precisely stated(defined). Uniqueness – results of each step are uniquely defined and only depend on the input and the result of the preceding steps. Finiteness – the algorithm stops after a finite number of instructions are executed. Input – the algorithm receives input. Output – the algorithm produces output. Generality – the algorithm applies to a set of inputs PSEUDOCODE It is an informal language that helps programmers to develop algorithms it is generally written in simple English statements to represent the logic of a program pseudocodes help a non-programmer to understand how a program works one person’s pseudocode can differ from that of the other.