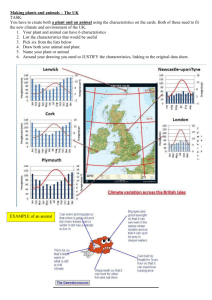
Snow Leopard Thick, white coat for camouflage Thick fur on soles of feet to help them walk in the cold conditions Long tail can store fat reserves for use in times when food is difficult to find Long, furry tail to use as a blanket Layers of fur of different lengths and thickness to provide added insulation Enlarged nasal cavity to help take in as much oxygen as possible in higher altitudes where oxygen is low Thick, white coat for insulation Shortened body parts legs, ears neck - to reduce heat loss Adaptations of a Snow Leopard • Thick white coat to keep warm and blend in with surroundings. • Thick fur on soles of feet to aid walking in cold conditions. • Enlarged nasal cavity helps breathing in high altitude conditions. • Long tail stores fat and can be coiled up for warmth. • Shortened body parts – limb and ears – reduce potential for heat loss. • Small pupils aid sight and reduce glare in bright conditions. • Ability to eat an animal three times its size means food can last several days at a time. Small pupils to minimise glare from the snow and help with hunting Can eat an animal three times its size and make it last several days