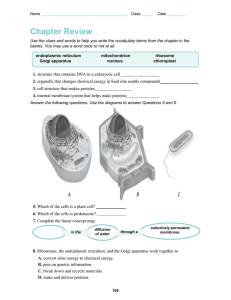
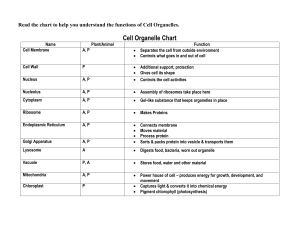
Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7 Prepared by: Angelica Joy T. Serada I. Objectives: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to: a. Identify the parts of the cell and their functions b. Differentiate plant cell and animal cell. II. Subject Matter: a. Topic: Cell parts and their functions. Subtopic: Difference between plant cell and animal cell. b. References: Internet, Science Learners Module p.65-71 c. Materials: visual aids, tape, illustrations of animal and plant cell. III. Learning Procedure: Teachers Activity Students Activity A. Preliminary Activities 1. Prayer To begin the class, let us have our prayer first. Everybody, please stand up. In the name of the Father and of the son.... 2. Greetings Good Morning class! Kindly pick up some pieces of papers and Good Morning Ma’am arrange your chairs properly. (students pick up some papers and arrange their chairs properly) You may now take your seats. B. Review of previous lesson Before we proceed to our new lesson, let’s recall first the lesson we’ve discussed last meeting. So, who among you in the class can Ma’am our lesson last meeting is all about the give a summary of our lesson last meeting? cell. We've learned that cell was first discovered by Robert Hooke through the microscope. Cell is Yes (teacher calls a student to answer) also the basic unit of life. It also has two kinds: plant cell and animal cell. Very Good! Is there any questions about the lesson last None ma’am. meeting? Okay very good! I think all of you here understand our lesson last meeting. It only means that all of you are ready for our new lesson C. Motivation Class, I have a question. Who among you here knows what are the parts of the cell? How about their functions? I have here an illustrations of both animal and plant cell. (teacher shows both illustrations of animal and plant cell) I want all of you to observe these illustrations and take notes of the things you've observed from the illustrations. Later on, we will see if some of your observations are correct. For now, let's proceed to our new lesson for today. Are you all ready? Yes ma'am. D. Lesson Proper Okay class, our lesson for today is all about the parts of the cell and their functions as well as the difference between plant cell and animal cell. As we've discussed last meeting, there are two kinds of cell right? What are those again? It’s the animal cell and plant cell ma’am. Very Good class! Even though they are different, both share the same basic structures. There are 3 basic structure of cell, the first one is the cell membrane, second is the nucleus and the third is the cytoplasm. Do you have any idea on what is a cell No ma’am membrane? Cell membrane is also known as the plasma membrane. It acts as a gatekeeper that protects the cell from the outside environment. It also control’s what material can go in and out of the cell. Again class what does a cell membrane do? (calls a student to answer) Very Good! Let’s continue Cell membrane protects the cell from the outside environment and controls what goes in and out of the cell. Next is the nucleus where the DNA and various proteins and the nucleolus are found. It is also called as "brain of the cell" because it directs all cell activity. Again, why does the nucleus called the brain of the cell? It directs all cell activities. Very Good! Next is the cytoplasm where all organelles are found. It has a jelly-like fluid and it is the material between the nucleus and cell membrane. Are there any questions about the three basic None ma’am structure of the cell? Okay, let’s proceed to the organelles. The first organelle is the mitochondria. It is one of the largest organelle within the cell. It is also called the "powerhouse of the cell" since it is where energy is produced. What is produced in the mitochondria? Very Good! Energy ma’am Next organelle is the ribosome. These are tiny organelles like dots that contain RNA and specific proteins within the cytoplasm. It is directly involved in the manufacture of proteins. Next is the endoplasmic reticulum. It has two kinds: smooth ER and rough ER. Smooth ER lacks ribosome and involved in the synthesis of lipids. Rough ER has ribosome and involved in the manufacture and transportation of proteins. What are the two kinds of endoplasmic Smooth and rough ER reticulum? Very Good! Next is the Golgi apparatus. It is responsible for transporting, modifying and packaging of protein and lipids. Next is the lysosome. It contains chemical that digest waste and worn-out or damaged cells. It also acts as waste disposal system of the cell. Last but not the least is the vacuole. It stores enzymes, water, waste products and food materials. Is there any questions? Clarifications? Activity Class lets have an activity. I want you to divide the class into 2 groups. One for the None ma’am plant cell and the other is for the animal cell. Are you done grouping? Yes ma’am Okay. This is what you'll have to do. You have to put the corresponding organelles to the cells through relays. The first one to finish is the winner. Are you ready class? Okay let the activity begins Very good class. Both teams finished quickly. Let’s see if all of your answers are correct. Yes ma’am (the students are performing the activity) (Teacher checks the students works) Well done class. Both team answer correctly. It seems that all of you understand the lesson today. Now that you have understood the parts of the cell and their functions, we will now talk about the difference between plant and animal cell. (Teacher explains the difference between the animal and plant cell through table.) Do you understand class? Is there any questions? E. Application Now that you have learned about the cell parts and their functions and the difference between animal and plant cell. I want you to connect both cells through their commonly present organelle and give other differences between animal and plant cell. Yes ma’am. None ma’am. F. Generalization Again class, what are the three basic the cell membrane, nucleus and cytoplasm structure if the cell? Very good! and what are the organelles The mitochondria, ribosome, endoplasmic present in both cells? reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, and vacuole. Very well said. How about their functions? (students give the functions of each organelle ) Very good class! So, are there any questions? None ma’am Since there are no more questions let’s have a short quiz. Get 1/4 sheet of paper and answer the following. IV. Evaluation Identify what part if the cell is based on the given function. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Acts as gatekeeper and controls what materials can go in and out of the cell. Also called as "brain of the cell" because it directs all cell activities. Also called "powerhouse of the cell" where energy is produced. It is directly involved in the manufacture of proteins Contains chemicals that digest waste and worn-out or damaged cells. Stores enzymes, water, waste products and food materials Responsible for transporting and packaging of proteins and lipids. Type of endoplasmic reticulum that lacks ribosome and involved in the synthesis of lipids. Type of endoplasmic reticulum that has ribosome and involved in manufacture and transportation of proteins 10. It has jelly-like fluid where all organelles are located. V. Assignment In a short bond paper, draw the animal and plant cell with organelles present.