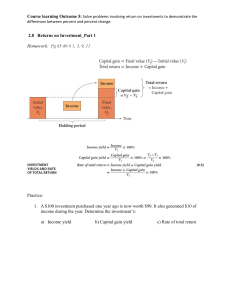
Advanced Time Value of Money Yield to Maturity Print version of the lectures in MA270 Financial Mathematics I presented in Winter, 2021 by c Adam Metzler from The Department of Mathematics at Wilfrid Laurier University Advanced Time Value Motivating Example • The City of Guelph has an outstanding bond that matures on July 11, 2030, paying a semi-annual coupon of 2.45% on a face value of $100. – Assume today is January 11, 2021 and that today’s coupon was just paid. Relationship Between Price and Yield for the Guelph Bond 140 120 Price ($) 100 80 60 40 20 0 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.1 Per-Period Yield Advanced Time Value Buying the Guelph Bond • I’m interested in buying the bond, and my broker tells me I can purchase it for $106.30. – This price is non-negotiable. • What is the corresponding yield? 1 MA270 Financial Mathematics I (Advanced Time Value of Money) c Adam Metzler, Page 20212 Relationship Between Price and Yield for the Guelph Bond 140 120 Price ($) 100 80 60 40 20 0 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.1 Per-Period Yield Advanced Time Value Who Cares? • In practice, bonds are bought and sold in the secondary market at market prices. – Individual investors and issuers have essentially no control over these prices. • Given the market price of a bond, the corresponding yield is of great importance to both investors and issuers. – Gives investors an indication of what they might earn on their investment, if they were to purchase the bond. – Gives issuers an indication of the interest rate they would have to pay, if they decided to borrow money through the bond market. • Yield is so much more than a number we plug into a formula to get a price. – Bond yields have significant economic content. Advanced Time Value Formal Definition • Consider a bond with price function P . – Since P is strictly decreasing, it is one-to-one. • Let $B be an observed market price for the bond. • Then there is a unique number Y T M such that P (Y T M ) = B. – i.e. Y T M = P −1 (B). • We call Y T M the bonds yield to maturity. – Of considerable importance to both investors and issuers. Advanced Time Value MA270 Financial Mathematics I (Advanced Time Value of Money) c Adam Metzler, Page 20213 Yield as a Function of Price • In the last video we looked at price as a function of yield. – i.e. we considered the function P . • Today we are thinking about yield as function of price. – i.e. we are considering the function P −1 . • Unfortunately there is no formula for P −1 . – How do we compute something if we don’t have a formula for it? – We use numerical methods to approximate yields. • That being said, there are some things we can say about yields, without a formula for them. Advanced Time Value Yield is a Decreasing and Convex Function of Price • So Yield = P −1 (Price). • From calculus, we know how to differentiate inverse functions. – dYield 1 1 = 0 −1 = 0 . dPrice P (P (Price)) P (Yield) – P 00 (P −1 (Price)) d2 Yield P 00 (Yield) = − = − . [P 0 (P −1 (Price))]3 [P 0 (Yield)]3 dPrice2 • So yield is a decreasing and convex function of price. Advanced Time Value Example 1 Concordia University has an outstanding bond that matures in 3.5 years and pays a semiannual coupon of 4.4% on a face value of $100. The bond is currently trading at $107.11. Prove that its yield does not exceed 3%. Advanced Time Value Example 2 Sketch the yield on the Guelph bond, as a function of its price. Advanced Time Value Computing Yields • There are a small number of special cases where we can compute yields explicitly. • If price equals face value, then yield equals – This is because . . MA270 Financial Mathematics I (Advanced Time Value of Money) c Adam Metzler, Page 20214 • If price equals dollar value of remaining cash flows, then yield equals – This is because . . • If there are two or fewer coupons remaining, yield can be computed using the quadratic formula. Example 3 Nova Scotia Power Inc. has an outstanding bond maturing on January 10, 2020, and paying a semi-annual coupon of 9.90% on a face value of $100. The current market price of the bond is $106.77. What rate is the bond market charging NSP to borrow money for one year? Advanced Time Value Advanced Time Value Final Thought - Terminology • If the market price of a bond is greater than its face value, we say it is trading at a premium. – Occurs if, and only if, coupon exceeds yield. • If the market price of a bond is less than its its face value, we say it is trading at a discount. – Occurs if, and only if, yield exceeds coupon. • If the market price of a bond is equal to its face value, we say it is trading at par. – Occurs if, and only if, yield equals coupon. Advanced Time Value