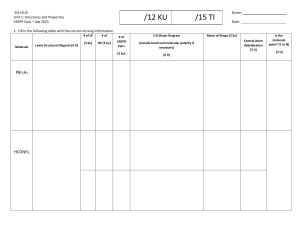
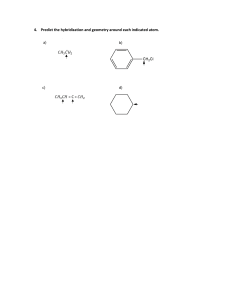
Chemistry Grade 11 Term 2 - 2020-2021 Chemistry Grade11 Term 3: 2020-2021 Week 2 Day 2 Section 5: Mollecular geometry HOLT McDOUGAL Modern Chemistry Chapter 6: chemical bonding Section 5: Mollecular geometry GRADE 11– CHEMISTRYWEEK 3 - DAY 2 AY 2020 – 2021 Chapter 6: chemical bonding Section 5: Molecular Geometry ALWAYS KEEP THESE IN MIND. NEVER FORGET THE CLASS RULES AND REGULATIONS! Section 5: Mollecular geometry Section 5: Mollecular geometry AMBITION . Grade 10: Chapter 15: section# 2 : PH meter #492,493 HS-PS1-3 Plan and conduct an investigation individually and collaboratively to produce data to serve as the basis for evidence, and in the design: decide on types, how much, and accuracy of data needed to produce reliable measurements and consider limitations on the precision of the data and refine the design accordingly. Topic: Molecular Geometry Students will be able to explain VESPR Theory, Predict the shapes of molecules or polyatomic ions using VSEPR theory. Section 5: Mollecular geometry Chapter 6 Chemical Bonding Section 5: Mollecular geometry Elaborate (SC: I can Predict the shapes of molecules or polyatomic ions using VSEPR theory.) Evaluate:(SC: I can answer application questions in Learning Check.) Section 5: Mollecular geometry Section 5: Mollecular geometry Section 5: Mollecular geometry Poly atomic ions • According to the VSEPR theory, the NH4+ molecule ion possesses tetrahedral molecular geometry. Because the center atom, nitrogen, has four N-H bonds with the hydrogen atoms surrounding it. The H-N-H bond angle is 109.5 degrees in the tetrahedral molecular geometry. Nitrate ion The nitrate has 3 electron domains and no lone pairs. Therefore, NO3– molecular geometry is slightly bent and is trigonal planar. The bond angle is 120o. Geometry: Trigonal Planar Bond Angle: 120o Section 5: Mollecular geometry Section 5: Mollecular geometry VSEPR Theory • VSEPR theory can also account for the geometries of molecules with unshared electron pairs. • examples: ammonia, NH3, and water, H2O. • The Lewis structure of ammonia shows that the central nitrogen atom has an unshared electron pair: HNH H • VSEPR theory postulates that the lone pair occupies space around the nitrogen atom just as the bonding pairs do. VSEPR Theory • Taking into account its unshared electron pair, NH3 takes a tetrahedral shape, as in an AB4 molecule. • The shape of a molecule refers to the positions of atoms only. • The geometry of an ammonia molecule is that of a pyramid with a triangular base. • H2O has two unshared pairs, and its molecular geometry takes the shape of a “bent,” or angular, molecule. VSEPR Theory • Unshared electron pairs repel other electron pairs more strongly than bonding pairs do. • This is why the bond angles in ammonia and water are somewhat less than the 109.5° bond angles of a perfectly tetrahedral molecule. VSEPR Theory • The same basic principles of VSEPR theory that have been described can be used to determine the geometry of several additional types of molecules, such as AB2E, AB2E2, AB5, and AB6. • Treat double and triple bonds the same way as single bonds. • Treat polyatomic ions similarly to molecules. • The next slide shows several more examples of molecular geometries determined by VSEPR theory. VSEPR and Molecular Geometry Chapter 6 Section 5 Molecular Geometry VSEPR and Molecular Geometry VSEPR Theory • Sample Problem F a. Use VSEPR theory to predict the shape of a molecule of carbon dioxide, CO2. b. Use VSEPR theory to predict the shape of a chlorate ion, ClO3 . VSEPR Theory • Sample Problem F Solution a. Draw the Lewis structure of carbon dioxide. O • C O There are two carbon-oxygen double bonds and no unshared electron pairs on the carbon atom. • This is an AB2 molecule, which is • linear. VSEPR Theory • Sample Problem F Solution, continued b. Draw the Lewis structure of the chlorate ion. Cl O O O • There are three oxygen atoms bonded to the central chlorine atom, which has an unshared electron pair. • This is an AB3E molecule, which is • trigonal-pyramidal. Explain • • • Click on the link below and wait for the teacher to give you the link. Activity 1: https://nearpod.com/ Activity 2: in MS forms Differentiated strategy (in process) (Note: students can choose the activities according to their choice.) Section 5: Mollecular geometry