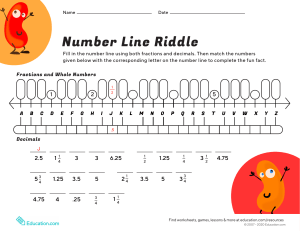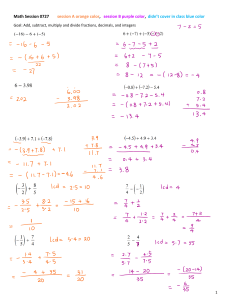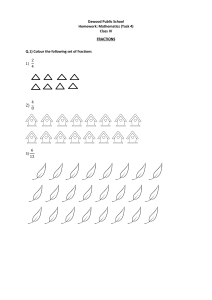
COURSE OUTLINE GRADE 6 MATHEMATICS COURSE: MATHEMATICS GRADE 6 (ORNARY MATHEMATICS) TEXT TITLE: MATHEMATICS AUTHORS: Rhonda Bailey, Roger Day, Ph.D., Patricia Frey, Arthur Howard, Deborah T. Hutchens, Ed.D. Kay McClain, Ed. D. PUBLISHER: Glencoe ISBN: 0-07-829634 – X RESOURCES: Teacher Resources Book: Chapter 1 – 12 Resources Masters, (AND PERSONAL RESOURCES) TEACHING EQUIPMENTS: Computer, measuring equipment Elective/Required: Required Study Time: 5 period weekly for 45 minutes/period Number Credit: 1 (one) Subject Description: A two-semester course on Mathematics covering computational skills, problems solving, mental math and estimation on numeration, exponents, decimals, units of measurement, fractions, probability, statistics, geometry, area, perimeter, converting decimal to fraction, to percentage, and percentage back to fraction or decimal exponent, square roots, power, and circumference COVERAGE: GRADING SYSTER FIRST QUARTER SECOND QUARTER THIRD QUARTER FOURTH QUARTER Chapter 1 – 3 CHAPTER 4 – 6 CHAPTERS 7, 8, AND 10 CHAPTER 9, 11, AND 12 CHAPTER TESTS/QUIZZES 30% Classwork 15% Exam 25% Homework 10% Projects 10 % Participation 10% TOTAL 100% COURSE OUTLINE GRADE 6 MATHEMATICS EKAMAI INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL 2020 – 2021 CHAPTER STANDARDS CC 1.3 CC2.1 CC 2.5 CC 1.3 CC 1.4 CC 1.2 CC 1.1 CC 1.3 CHAPTER 1 CC 1.3 CC 1.1 CC 2.1 COMMON CORE STANDARDS EXPLAINED Determine when and how to break a problem into simpler parts Solve problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of positive fractions and explain why a particular operation was used for a given situation Express the solution clearly and logically by using the appropriate mathematical notation and terms and clear language; support solutions with evidence in both verbal and symbolic work Apply algebraic order of operations and the commutative, associative, and distributive properties to evaluate expressions: and justify each step in the process Write and solve one-step linear equation in one variable Write and evaluate an algebraic expression for a given situation, using up to three variables Write and solve one-step linear equation in one variable TOPICS/CONTENTS 1 - 1 A Plan for problem Solving SKILL Solve problems using the four-step plan 1 - 2 Powers and exponents Use powers and exponents Use Proportions to solve problems Use crossmultiplication as a method for solving problems, understanding it as the multiplication of both sides of an equation by a multiplicative inverse Apply algebraic order of operations and the commutative, associative, and distributive properties to evaluate expressions; and justify each step in the process Analyze problems by identifying relationships, distinguishing relevant from irrelevant information, identifying missing information, sequencing and prioritizing information, and observing pattern Convert one unit of measurement to another 1 – 6 Algebra properties 1 – 3 Order of Operations 1 – 4 Algebra: Variables and Expressions 1 – 5 Algebra: Equation ASSESSMENT Evaluate expressions using the order of operations CHAPTER TEST Evaluate simple algebraic expressions ASSIGNMENT Solve equations using mental math Use addition and multiplication properties to solve problems 1 – 7 Sequences Recognize and extend patterns for sequences 1 – 8 The Metric System Change metric units of length, capacity, and mass CLASS QUIZ CC2.5 Express the solution clearly and logically by using the appropriate mathematical notation and terms and clear language; support solutions with evidence in both verbal and symbolic work 1 – 9 Scientific Notation Write numbers greater than 100 in scientific notation and in standard form CHAPTER 1 DECIMAL PATTERS AND ALGEBRA CHAPTER STANDARD CC2.1 CC 2.4 CC 2.2 CC 1.2 CC 3.2 CC 2.4 CHAPTER 2 CC 2.3 CC 1.1 CC 1.4 CC 2.4 CC 2.3 COMMON CORE STANDARDS EXPLAINED Compare different samples of a population with the data from the entire population and identify a situation in which it makes sense to use a sample Use variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, graphs, tables, diagrams, and models, to explain mathematical reasoning TOPICS/CONTENTS 2 – 1 Frequency Tables Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, graphs, tables, diagrams, and models, to explain mathematical reasoning Understand how additional data added to data sets may affect theses computations of measures of central tendency Use data to estimate the probability of future events Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, graphs, tables, diagrams, and models, to explain mathematical reasoning Analyze data displays and explain why the way in which the question was asked might have influenced the results obtained and why the way in which the results were displayed might have influenced the conclusion reached Compute the range, mean, median, and mode of data sets Know why a specific measure of central tendency (mean, median, mode) provides the most useful information in a given context Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, graphs, tables, diagrams, and models, to explain mathematical reasoning Analyze data displays and explain why the way in which the question was asked might have influenced the results obtained and why the way in which the results were displayed might have influenced the conclusion reached 2 – 2 Making Predictions SKILLS ASSESSMENT Organize and interpret data in a frequency table Make predictions from graphs 2 – 3 Line Plots Construct and interpret line plots 2 – 4 Mean, Median, Mode 2 – 5 Stem – and – Leaf Plots Find the mean, median, and mode of a set of data Construct and interpret stem-and-leaf plots Chapter test Quiz assignment CC 1.3 Understand how the inclusion or exclusion of outliers affects measures of central tendency Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, graphs, tables, diagrams, and models, to explain mathematical reasoning Analyze data displays and explain why the way in which the question was asked might have influenced the results obtained and why the way in which the results were displayed might have influenced the conclusion reached CC 2.4 CC 2.3 CHAPTER CHAPTER 2 STANDARD CC 2.1 CC 2.4 CC 2.5 COMMON CORE STANDARDS EXPLAINED Compare different samples of a population with the data from the entire population and identify a situation in which it makes sense to use a sample Identify data that represent sampling errors and explain why the sample might be biased Identify claims based on statistical data and, in simple, case, evaluate the validity of the claims 2 – 6 Box – and Whisker Plots 2- 7 Bar Graphs and Histograms Construct and interpret boxand –whisker plots Construct and interpret bar graphs and histograms TOPICS/CONTENTS 2 - 8 Misleading Statistics SKILLS ASSESSMENT Recognize when statistics and graphs are misleading CHAPTER2 STATUSTUCS: Analyzing Data CHAPTER STANDARD COMMON CORE STANDARDS EXPLAINED TOPICS/CONTENTS 3 – 1 Integers and Absolute Value CC 1.1 CC 2.3 CHAPTER 3 CC 2.3 Compare and order positive and negative fractions, decimal, and mixed numbers and place them on a number line. Solve addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division problems, including those arising in concrete situations, that use positive and negative integers and combinations of these operation Solve addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division problems, including those arising in concrete situations, that use positive and negative integers and combinations of these operation 3 – 2 Comparing and Ordering Integers 3 – 3 The Coordinate Plane 3 – 4 Adding Integers SKILLS ASSESSMENT Read and write integers and find the absolute value of an integer Compare and order integers Graph points on a coordinate plane Add Integers 3 – 5 Subtracting Integers Subtract Integers CHAPTER TEST CLASS QUIZZES ASSIGNMENT CUMMULATIVE EXAM COVERS CHAPTERS ONE TILL CHAPTER 3 CC 2.3 CC 2.3 Solve addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division problems, including those arising in concrete situations, that use positive and negative integers and combinations of these operation Solve addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division problems, including those arising in concrete situations, that use positive and negative integers and combinations of these operation 3 – 6 Multiplying Integers Multiply integers 3 – 7 Dividing Integers Divide Integers CHAPTER THREE ALGEBRA INTEGERS CHAPTER TOPICS/CONTENTS SKILLS CC 1.2 STANDARD Write and evaluate an algebraic expression for a given situation, using up to three variables. 4 – 1 Writing Expressions and Equations Write verbal phrases and sentences as simple algebraic expressions and equations CC 1.3 Apply algebraic order of operations and the commutative, associative, and distributive properties to evaluate expressions; and justify each step in the process Write and evaluate an algebraic expression for a given situation, using up three variables Apply algebraic order of operations and the commutative, associative, and distributive properties to evaluate expressions; and justify each step in the process Write and evaluate an algebraic expression for a given situation, using up three variables 4 – 2 Solve Addition and subtraction and Equation CC 1.2 CC 1.3 CHAPTER 4 CC 1.2 COMMON CORE STANDARDS EXPLAINED 4 – 3 Solving Multiplication Equation Solve addition and subtraction problems Solve Multiplication equation 4 – 4 Solving Two – Step Equations Solve two – steps equation 4 – 5 Inequalities Solve Inequalities CC 1.1 Writing and Solve and one-step linear equations in one variable 4 – 6 Functions and Linear Equations Graph a function on a scatter plot CC 1.1 Writing and Solve and one-step linear equations in one variable 4 – 7 Lines and slope Find the slope of a line ASSESSMENTS ASSIGNMENT CLASS QUIZZES CHAPTER TEST CHAPTER 4 ALGEBRA: linear equations and functions CHAPTER STANDARD CC 2.4 COMMON CORE STANDARDS EXPLAINED Determine the least common multiple and the greatest common divisor of whole numbers; use them to solve problems with fractions TOPICS/CONTENTS 5 – 1 Exploring Factors/Prime Factorization 5 – 2 Greatest Common factor 5 – 3 Simplifying Fractions 5 – 4 Fractions and Decimals CHAPTER 5 CC 2.4 Determine the least common multiple and the greatest common divisor of whole numbers; use them to solve problems with fractions (LCM) SKILLS Discover factors of whole numbers ASSESSMENT Find the greatest common factor of two or more numbers 5 – 5 Fractions and Percent Write fractions in simplest forms Write fractions as terminating or repeating decimals and write decimals as fractions Write fractions as percent and percent as fractions 5 – 6 Percent and Decimals Write percents as decimals and decimals as percents 5 – 7 Least Common Multiple Find the least common multiple of two or more numbers CHAPTER TEST CLASS – QUIZZES ASSIGNMET CHAPTER 5 FRACTIONS, DECIMALS, AND PERCENTS CHAPTER STANDARD CC 2.3 CC2.6 CC2.7 CC 2.4 COMMON CORE STANDARDS EXPLAINED Estimate unknown quantities graphically and solve for them by using logical reasoning and arithmetic and algebraic techniques Indicate the relative advantages of exact and approximate solutions to problems and give answers to a specified degree of accuracy Make precise calculation check the validity of the results from the context of the problem Determine the least common multiple and the greatest common divisor of whole numbers; use them to solve problems with fractions (LCM) TOPICS/CONTENTS 6 – 1 Estimating with Fractions 6 – 2 Adding and subtracting Fractions SKILLS ASSESSMENT Estimate sums, differences, products, and quotients of fractions and mixed numbers Add and subtract fractions ASSIGNMENT CHAPTER TEST CHAPTER 6 CC 2.4 Determine the least common multiple and the greatest common divisor of whole numbers; use them to solve problems with fractions (LCM) 6 – 3 Adding and Subtracting Mixed Numbers Add and subtract mixed numbers CC 2.2 Explain in the meaning of multiplication and division of positive fractions and per-form the calculations Multiply fraction and mixed numbers CC 1.3 Apply algebraic order of operations and commutative, associative, and distributive properties to evaluate expressions; and justify each step in the process Explain the meaning of multiplication and division of positive fractions and per-form the calculations Apply algebraic order of operations and commutative, associative, and distributive properties to evaluate expressions; and justify each step in the process Explain the meaning of multiplication and division of positive fractions and per-form the calculations Convert one unit of measurement to another Demonstrate an understanding that rate is a measure of one quantity per unit value of another quantity Use variables in expressions describing geometric quantities (the formulas for the perimeter of a rectangle, the area of a triangle, and, and the circumference of a circle , …. Use variables in expressions describing geometric quantities (the formulas for the perimeter of a rectangle, the area of a triangle, and, and the circumference of a circle , …. Know common estimates of p (3.14; 22/7) and use these values to estimate and calculate the circumference and the area of circles; compare with actual measurements 6 – 4 Multiplying Fractions and Mixed Numbers 6 – 5 Solving Equations 6 – 6 Dividing Fractions and Mixed Numbers Divide fractions and mixed numbers 6 – 7 Changing Customary Units Change units in the customary systems 6 – 8 Perimeter and area Find the perimeters and areas of figures 6 – 9 Circles and Circumferences Find the circumferences of a circle CC 2.2 CC 1.3 CC 2.2 CC 2.1 CC2.2 CC 3.1 CC 3. CC 1.91 CLASS – QUIZZES EXAM COVERS FROM CHAPTERS 1 - 6 Solve equations with rational numbers solution CHAPTER 6 APPLYING FRACTION CHAPTER STANDARD COMMON CORE STANDARDS EXPLAINED TOPICS/CONTENTS SKILL CC 1.2 Interpret and use ratios in different contexts 7 – 1 Ratios CC 1.2 CC 2.3 Interpret and use ratios in different contexts Solve problems involving rates, average speed, distance and time Interpret and use ratios in different contexts 7 – 2 Rates Write ratios as fractions and determine whether two ratios are equivalent Determine unit rates 7 – 3 Solving Proportions Use proportions to estimate CC 1.2 ASSESSMENT 7 – 4 Scale Drawings CC 3.3 CHAPTER 7 CC1.4 CC 3.3 CC1.4 CC 3.3 CC1.4 Represent probabilities as ratios, proportions, decimals between 0 and 1, and percentages between 0 and 100 and verify that the probabilities computed are reasonable; know that if P is the probability of an events Calculate given percentages of quantities and solve problems involving discounts at sales, interest earned, and tips Represent probabilities as ratios, proportions, decimals between 0 and 1, and percentages between 0 and 100 and verify that the probabilities computed are reasonable; know that if P is the probability of an events Calculate given percentages of quantities and solve problems involving discounts at sales, interest earned, and tips Represent probabilities as ratios, proportions, decimals between 0 and 1, and percentages between 0 and 100 and verify that the probabilities computed are reasonable; know that if P is the probability of an events Calculate given percentages of quantities and solve problems involving discounts at sales, interest earned, and tips 7 – 5 Fractions, Decimal, and Percents Solve problems involve scale drawing Write percent as fractions and vice versa 7 – 6 Percents Greater than 100% and percents Less Than 1% Write percents greater than 100% and percents less than 1% as fractions and as decimals and vice versa 7 – 7 Percent of a number Find the percent of a number CHAPTER TEST MATHEMATICS CLASS – QUIZZES ASSIGNMENT CHAPTER 7 RATIOS AND PROPORTIONS CHAPTER STANDARD COMMON CORE STANDARDS EXPLAINED TOPICS/CONTENTS CC 2.0 Use estimation to verify the reasonableness of calculated results 8 – 1 Percent and estimate CC 1.2 Write and evaluate an algebraic expression for a given situation, using up to three variable 8 – 2 percent and Equations CC 2.2 Use a variety of methods, such as words, numbers, symbols, charts, graphs, tables, diagrams, and models, to explain mathematical reasoning Understand how additional data added to data sets may affect theses computations of measures of central tendency Use data to estimate the probability of future events Represent probabilities as ratios, proportions, decimals between 0 – 1 and percentages between 0 and 100 and verify that the probabilities computed are reasonable 8 – 3 Use statistics to predict CHAPTER 8 CC 1.2 CC 3.2 CC 3.3 8 – 4 Percent of Change SKILL Estimate percent by using fractions and decimals Solve problems by using the percent equations Predict actions of larger group by using a sample Find the percent of the increase or decrease ASSESSMENT CHAPTER TEST ASSIGNMENT CLASS QUIZZES CC 1.4 Calculate given percentages of quantities and solve problems involving discount of sales, interest earned, and tips 8 – 5 Sales Tax and Discount CC 1.4 Calculate given percentages of quantities and solve problems involving discount of sales, interest earned, and tips 8 – 6 Simple Interest Solve problems involving sales tax and discount Solve problems involving sample interest CHAPTER 8 APPLYING PERCENT CHAPTER STANDARD COMMON CORE STANDARDS EXPLAINED TOPICS/CONTENTS 9 – 1 Simple - Events 9 – 2 Tree Diagrams CC 9 - 3 Understand that the probability of either of two disjoint evens occurring is the sum of the two individual probabilities and that the probability of one events following another, in independent trials, is the product of the two probabilities Understand that the probability of either of two disjoint evens occurring is the sum of the two individual probabilities and that the probability of one events following another, in independent trials, is the product of the two probabilities Understand that the probability of either of two disjoint evens occurring is the sum of the two individual probabilities and that the probability of one events following another, in independent trials, is the product of the two probabilities 9 – 3 The fundamental Counting Principle CC 3.1 CC 3.5 CC 9 - 3 CHAPTER 9 CC 9 – 3 CHAPTER 9 PROBABILITY SKILLS Find the probability of simple events Use tree diagrams to count outcomes and find probabilities Use Multiplications to count outcomes 9 – 4 Permutations Find the number of permutations of a set of objects 9 – 5 Combination Find the number of combinations of set of objects Represent all possible outcomes for compound events in an organized way and express the theoretical probability of each outcomes 9 – 6 Theoretical and Experimental Probability Understand the difference between independent and dependent events 9 – 7 Independent and Dependent Events Find and compare experimental and theoretical probabilities Find the probability of independent and dependent events ASSESSMENT TEST CLASS QUIZZES HOMEWORK PROJECT CHAPTER STANDARD CC 2.1 CC2.2 CHAPTER 10 CC2.2 CC 2.1 CC 2.3 CC 2.3 COMMON CORE STANDARDS EXPLAINED Identify angles as vertical, adjacent, complementary, or supplementary and provide descriptions of these terms Identify different ways of selecting a sample and which method makes a sample more representative for a populations Identify different ways of selecting a sample and which method makes a sample more representative for a populations Identify angles as vertical, adjacent, complementary, or supplementary and provides descriptions of these terms Draw quadrilaterals and triangles from given information about them Draw quadrilaterals and triangles from given information about them TOPICS/CONTENTS SKILLS 10 – 1 Measuring Angles Measure angles 10 – 2 Making Circle Graphs Construct and interpret circle graphs 10 – 3 Angle Relationship Identify and apply angle relationships 10 – 4 Triangles Identify and classify triangles Identify and classify quadrilaterals Determine whether figures are similar and find a missing length in a pair of similar figure Classify polygons and determine which polygons can form a tessellations Graph translation of polygons on a coordinate plane Identify figure with line symmetry and graphs reflection on a coordinate plane 10 – 5 Quadrilaterals 10 – 6 Similar Figures 10 – 7 Polygons and Tessellations 10 – 8 Translations 10 – 9 Reflections ASSESSMENT CHAPTER TESTT CLASS QUIZZ ASSIGNMENT EXAM COVERS CHAPTERS 1 – 8 AND 10 CHAPTER 10 GEOMETRY CHAPTER STANDARD COMMON CORE STANDARDS EXPLAINED TOPICS/CONTENTS SKILLS ASSESSMENT 11 – 1 Squares and Square roots 11 – 2 Estimating Square Roots Find squares of numbers and square roots of perfect squares Estimate square roots CC 1.3 Know and use the formulas for the volume of triangular prisms and cylinder 11 – 3 The Pythagorean Theorem CC 1.3 Know and use the formulas for the volume of triangular prisms and cylinder Know and use the formulas for the volume of triangular prisms and cylinder Use variables in expressions describing geometric quantities. Area of Triangles,, polygons and circle Know common estimates of 3.14 and use these values to estimate and calculate the circumference and the area of circle Use variables in expressions describing geometric quantities. Area of Triangles,, polygons and circle 11 – 4 Area of Parallelograms 11 – 5 Area of Triangles and Trapezoids 11 – 6 Area of circles Find the relationship among the sides of a right triangle Find the areas of parallelograms Find the areas of triangles and trapezoids Find the areas of circles 11 – 7 Area of Complex figures Find the areas of complex figures CC 1.3 CC 3.1 CHAPTER 11 CC 1.2 CC 3.1 CHAPTER TEST PROJECT CLASS QUIZZES ASSIGNMENTS HAND – ON ACTIVITY CHAPTER 11 GEOMETRY MEASURING DIMENSIONAL FIGURES CHAPTER STANDARD COMMON CORE STANDARDS EXPLAINED TOPICS/CONTENTS 12 – 1 Drawing Three – dimensional figures CC 1.3 CC 1.3 Know and use the formulas for the volume of triangular prisms and cylinder Know and use the formulas for the volume of triangular prisms and cylinder 12 - 2 Volume of Rectangular Prisms 12 – 3 Volume of Cylinder SKILL Draw a three-dimensional figure given the top, side, and front view Find the volumes of rectangular prisms Find the volumes of cylinders ASSESSMENT CC 1.3 CHAPTER 12 CC 2.3 CC 2.6 Know and use the formulas for the volume of triangular prisms and cylinder Estimate unknown quantities graphically and solve for them by using logical reasoning and arithmetic and algebraic techniques Indicate the relative advantages of exact and approximate solutions to problems and give answers to a specified degree of accuracy 12 – 4 Surface Area of Rectangular Prisms 12 – 5 Surface area of Cylinder Find the surface area of rectangular prisms Find the surface areas of cylinder 12 – 6 Precision and Measurement Determine and apply significant digits in a real – life context HOMEWORK CLASS – QUIZZES CHAPTER TEST ASSIGNMENT HAND – ON ACTIVITY CHAPTER 12 GEOMETRY; MEASURING THREE – DIMENSIONAL FIGURES COVERAGE: GRADING SYSTER FIRST QUARTER SECOND QUARTER THIRD QUARTER FOURTH QUARTER Chapter 1 – 3 CHAPTER 4 – 6 CHAPTERS 7, 8, AND 10 CHAPTER 9, 11, AND 12 CHAPTER TESTS/QUIZZES 30% Classwork 15% Exam 25% Homework 10% Projects 10 % Participation 10% TOTAL 100%