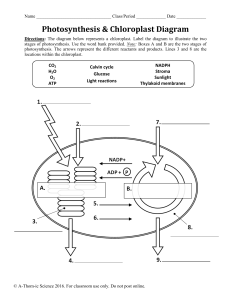
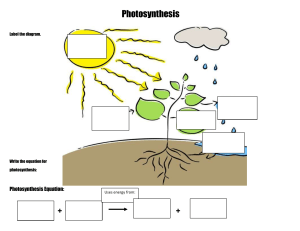
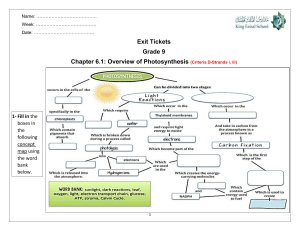
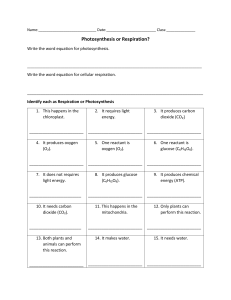
AS BIOLOGY PHOTOSYNTHESIS FACILITATOR: SRC Scope of topic • explain how photosynthesis transfers energy from light to carbohydrate molecules • describe how the structure of a chloroplast is related to its functions • describe the roles of chloroplast pigments, and interpret absorption spectra and action spectra • describe how to use chromatography to separate chloroplast pigments and calculate Rf values • describe the reactions of the light-dependent stage of photosynthesis, including cyclic photophosphorylation and noncyclic photophosphorylation Scope of topic • describe the light-independent stage of photosynthesis • explain the main limiting factors for photosynthesis, and interpret graphs showing the effects of these on the rate of photosynthesis • describe how to investigate the effects of limiting factors on the rate of photosynthesis using aquatic plants • describe how to investigate the effect of light intensity and light wavelengths on a chloroplast suspension, using a redox indicatoR • In Chapter 12 you learnt how all organisms use ATP as their energy currency. • They make ATP by using the chemical potential energy contained in glucose and other organic molecules to join a phosphate group to ADP. • This is done by respiration, which is a series of enzymecontrolled reactions that take place in every living cell. • In this chapter you will find out how the glucose that is used in respiration is produced. • It is done by photosynthesis, in which energy in sunlight is transferred to carbohydrates such as glucose An outline of photosynthesis Structure and function of chloroplasts