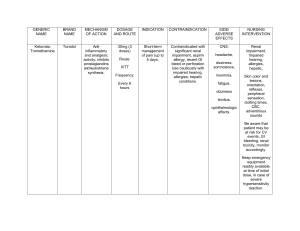
Patient Education on Medication Name of the Drug Trade and Generic Trade: Kefzol, Ancef Generic: Cefazolin Classification Therapeutic: Anti-infectives Action Bind to bacterial cell wall Pharmacologic: membrane, first generation causing cell cephalosporins death. Adult dosing Side effects Contraindications Special precautions IM, IV (Adults): Moderate to severe infections— 500 mg– 2 g q 6–8 hr (maximum 12 g/day). Mild infections with gram-positive cocci — 250 – 500 mg q 8 hr. Uncomplicated urinary tract infections — 1 g q 12 hr. Pneumococcal pneumonia — 500 mg q 12 hr. Infective endocarditis or septicemia — 1 – 1.5 g q 6 hr. Perioperative prophylaxis — 1 g given 30 – 60 min prior to incision. Additional 500 mg – 1 g should be given for surgeries �2 hr. 500 mg – 1 g should then be given for all surgeries q 6 – 8 hr for 24 hr postoperatively. CNS: SEIZURES (high doses). GI: CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA (CDAD), diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, cramps. Hypersensitivity to cephalosporins; Serious hypersensitivity to penicillin. Derm: STEVENSJOHNSON SYNDROME, rashes, pruritis, urticaria. Hemat: agranulocytosis, eosinophilia, hemolytic anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia. Local: pain at IM site, Renal impairment (dosage increase and/or increase dosing interval recommended for: cefadroxil and cephalexin, if CCr less than or equal to 50 mL/min, and cefazolin, if CCr less than 30 mL/min; History of GI disease, especially colitis; Geri: Dose adjustment due to age-related decrease in renal function may be necessary; OB, Lactation: Halflife is shorter and blood levels lower during Patient Education on Medication phlebitis at IV site. pregnancy; have been used safely. Misc: allergic reactions including ANAPHYLAXIS and SE- RUM SICKNESS, superinfection. Name of the Drug Trade and Generic Trade: Toradol Generic: ketorolac Classification Therapeutic: nonsteroidal antiinflammatory agents, nonopioid analgesics Action Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis, producing peripherally mediated analgesia. Also has Pharmacologic: antipyretic and antipyrazoline carboxylic acid inflammatory properties Adult dosing Side effects Contraindications Special precautions PO (Adults less than 65 yr): 20 mg initially, followed by 10 mgq4– 6hr(nottoexceed40mg/day). CNS: drowsiness, abnormal thinking, dizziness, euphoria, headache. Hypersensitivity; Cross-sensitivity with other NSAIDs may exist; Preoperative use; Active or history of peptic ulcer disease or GI bleeding; Known alcohol intolerance (injection only); Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery; Cerebrovascular bleeding; PO (Adults greater than or equal to 65 yr, less than 50 kg, or with renal impairment): 10 mg q 4 – 6 hr (not to exceed 40 mg/day). IM (Adults less than 65 yr): Single dose — 60 mg. Multiple dosing — 30 mg q 6 hr (not to exceed 120 mg/day). EENT: increases lacrimation (spray), nasal discomfort (spray), throat irritation (spray). Cardiovascular disease or risk factors for cardiovascular disease (may increase risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke, especially with prolonged use or use of higher doses); avoid use in patients Patient Education on Medication IM (Adults greater than or equal to 65 yr, less than 50 kg, or with renal impairment): Single dose — 30 mg. Multiple dosing — 15 mg q 6 hr (not to exceed 60 mg/day). IV (Adults less than 65 yr): Single dose — 30 mg. Multiple dosing — 30 mg q 6 hr (not to exceed 120 mg/day). IV (Adults greater than or equal to 65 yr, less than 50 kg, or with renal impairment): Single dose — 15 mg. Multiple dosing Intranasal (Adults less than 65 yr): 1 spray in each nostril q 6 – 8 hr (not to exceed 4 sprays in each nostril/day). Intranasal (Adults greater than or equal to 65 yr, less than 50 kg, or with renal impairment): 1 spray in only one nostril q 6 – 8 hr (not to exceed 4 sprays in one nostril/day). Resp: asthma, dyspnea. CV: HF, MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION, STROKE, edema, pallor, vasodilation. GI: GI BLEEDING, abnormal taste, diarrhea, dry mouth, dyspepsia, GI pain, increases liver enzymes, nausea. GU: oliguria, renal toxicity, urinary frequency. Derm: EXFOLIATIVE DERMATITIS, STEVENSJOHNSON SYNDROME, TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECROLYSIS, Advanced renal impairment or at risk for renal failure due to volume depletion; Concurrent use of pentoxifylline or probenecid; OB: Chronic use in 3rd trimester may cause constriction of ductus arteriosus. May inhibit labor and increase maternal bleeding at delivery. with recent MI or HF; Heart failure; Coagulation disorders; Mildto- moderate renal impairment (decrease dose may be required); Hepatic impairment Patient Education on Medication pruritus, purpura, sweating, urticaria. F and E: hyperkalemia. Hemat: prolonged bleeding time. Local: injection site pain. Neuro: paresthesia. Misc: allergic reactions including, anaphylaxis. Name of the Drug Trade and Generic Classification Action Adult dosing Side effects Contraindications Special precautions Patient Education on Medication Trade: Sodium Chloride Generic: Normal Saline Therapeutic: Crystalloid Fluid Pharmacologic: treat or prevent sodium loss caused by dehydration, excessive sweating, or other causes. reduce some types of bacteria. clean out an intravenous (IV) catheter, Average normal adult daily requirements range from two to three liters (1.0 to 1.5 liters each for insensible water loss by perspiration and urine production). febrile response, infection at the site of injection, venous thrombosis or phlebitis extending from the site of injection, extravasation, and hypervolemia evaluated clinically from patient to patient. If the implementation of normal saline results in dilution of serum electrolyte concentrations, overhydration, congested states, or pulmonary edema, then its use is strongly discouraged Store Normal Saline at room temperature away from moisture and heat.