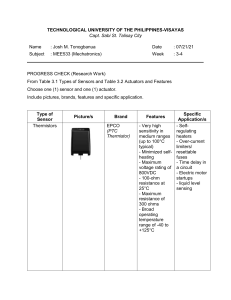
Types of motors Electric motors can be classified in a variety of ways Operating characteristics such as The source of electric power, Type of rotor winding, Type of motion, Control pattern, The magnetic flux orientation, Structure topology, Power rating, The cooling methods. Types of Electric Motors used in Electric Vehicles: DC Series Motor Brush-less DC Motor Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) Three Phase AC Induction Motors Switched Reluctance Motors (SRM) 1. DC Series (DC Brushed ) Motor : High starting torque capability Advantages Easy speed control It can also withstand a sudden increase in load. Drawback high maintenance due to brushes and commutators. Frictional losses Applications Electric Vehicles Drones Robots and Some other Electronics Devices. 2. BLDC (Brush-less) Motor : Same as Dc motor but it does not have the commutator and brush arrangement. Elimination of brushes over armature for switching (commutation) it becomes more complex and is performed electronically using additional set of electronic components (like an amplifier triggered by a commutating component like an optical encoder) to achieve motion. Commutation algorithms for Brush-less DC motors can be divided into two: Sensor-based senseless commutation. Sensors based (e.g hall sensor) are placed along the poles of the motor to provide feedback to the control circuitry to help it estimate rotor position. There are three popular algorithms employed for sensor-based commutation. Trapezoidal commutation Advantages i. Control Algorithm is simple ii. Only two phase is needed to active at time iii. Less switching losses Disadvantages a. Torque ripple at every commutation b. Torque produced is less c. Acoustic and electric noise Sinusoidal commutation Advantages i. No torque ripple in commutation ii. Smooth motion iii. Maximum Torque is produced Disadvantages a. Possible to have three phase on same time b. Higher Switching losses c. Control Algorithms are complex and mathematically intensive Vector (or field-oriented) control. Each of these control algorithm has its pros and cons and the algorithms can be implemented in different ways depending on the software and the design of the electronics hardware to make necessary changes. Senseless commutation. instead of sensors being placed within the motors, the control circuitry is designed to measure the back EMF to estimate rotor position. This algorithm performs pretty well and is at a reduced cost as the cost of the hall sensors is eliminated but its implementation is a lot more complex compared to the sensor based algorithms. Advantages High starting torque High efficiency around 95-98% BLDC motors are maintenance free as the commutation is done electronically. Factors to consider when selecting between the Brush-less and Brushed DC Motors Duty Cycle/ Service Life Efficiency Control/Actuation Cost BLDC motors further have two types: Out-runner type BLDC Motor (Hub motor): Rotor of the motor is present outside and the stator is present inside. does not require external gear system In few cases, the motor itself has inbuilt planetary gears. motor makes the overall vehicle less bulky This motor is widely preferred by electric cycle manufacturers like Hullikal, Tronx, Spero, light speed bicycles, etc. It is also used by two-wheeler manufacturers like 22 Motors, NDS Eco Motors, etc. In-runner type BLDC Motor: The rotor of the motor is present inside and the stator is outside like conventional motors. Motor require an external transmission system to transfer the power to the wheels, The out-runner configuration is little bulky when compared to the in-runner configuration. Many three- wheeler manufacturers like Goenka Electric Motors, Speego Vehicles, Kinetic Green, Volta Automotive use BLDC motors. Low and medium performance scooter manufacturers also use BLDC motors for propulsion. 3. Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) Similar to BLDC motor which has permanent magnets on the rotor. Characteristics like high power density and high efficiency. The difference is that PMSM has sinusoidal back EMF whereas BLDC has trapezoidal back EMF. PMSM is the best choice for high performance applications like cars, buses. Stiff competition between PMSM & induction motors due to increased efficiency PMSM is also costlier than BLDC motors. They have a constant magnetic field in the rotor. So induction cannot be used. Most of the automotive manufacturers use PMSM motors for their hybrid and electric vehicles For example, Toyota Prius, Chevrolet Bolt EV, Ford Focus Electric, zero motorcycles S/SR, Nissan Leaf, Honda Accord, BMW i3, etc use PMSM motor for propulsion. 4. Three Phase AC Induction motor : Asynchronous motor is a machine whose rotor rotates at the speed less than the synchronous speed. N < NS Simple and rugged construction Low cost and minimum maintenance High dependability and sufficiently high proficiency Needs no additional starting motor and necessity not to be synchronized Advantages: Low Cost Low Maintenance Cost Ease of Operation due to no connection to rotor Speed Variation constant High Starting Torque Durability is high Disadvantages: Throughout the light load situation, the power factor is extremely less and it draws a huge current. So, the copper loss can be high which decreases the efficiency throughout the light load situation. The squirrel cage induction motor’s initial torque is not low. This is an invariable speed motor and this motor is not applicable where uneven speed needs This motor speed control is not easy This motor includes a high starting inrush current which will cause a reduction within voltage at the beginning of time. Applications Pumps Compressors Small fans Mixers Toys High-speed vacuum cleaners Electric shavers Drilling machines Lifts Cranes Hoists Large capacity exhaust fans Driving lathe machines Crushers Oil extracting mills Textile and etc. 5. Switched Reluctance Motors (SRM) Torque pulsations are inherent in SRM’s due to the doubly salient structure. Minimized torque ripple design of a SRM of the machine and its sequential excitation. Advantages A switched reluctance motor offers many benefits against other types of electric motors because of its control flexibility, simple structure, Lower cost High efficiency. The lack of winding or permanent magnet on the rotor means that an SRM is appropriate for extremely high speed applications, and can withstand high temperatures. Rugged and simple structure and low manufacturing cost if a fault occurs in any one winding or phase, the motor can still work but at a reduced load. Disadvantages non-linear characteristics of magnetic saturation makes it complicated to accurately control its torque. high noise, vibrations and torque ripple. requires advanced control methods when compared with other AC and DC motor drives. Motors Rotor BLDC Permanent magnet on rotor PMDC / DC Winding on rotor PMSM PM on rotor AC Induction motor Copper/Aluminium bar Squirrel cage Wound/slip ring Stator Coil winding's PM on stator Coil winding's Coil winding's Controller Controller is required No controller is required Controller is required Various control operations Torque Suitable for low speed high torque applications High speed range compare to DC Suitable for low torque application Higher torque compared to BLDC Higher speed range & Eff. Comparatively Low from PMSM Speed Lower speed range due to mechanical imitation of brushes Life 10k-20k hours 2k-5k hours 10k-20k hours 30k-40k Efficiency 90% 60-70% High eff. Up to 92-96% 1.Sinusoidal Drive with FOC. 2.Trapezoidal with Back EMF Sensing With sensor Sensor-less 85-96% Back EMF / Hall effect sensor Little to no maintenance Periodic maintenance require Very efficient heat dissipation Very Efficient Low electric noise generation Audible vibrating magnet and fan Higher manufacturing cost Suitable for controlled environment Very low manufacturing cost comparatively Suitable for controlled environment Low weight relatively Higher weight 3 & 4 wheels 4 Wheeler's and some of the heavy comercial Commutation method Rotor position detection Maintenance Heat Dissipation Noise Cost Operation environment Sinusoidal Drive with FOC. Trapezoidal with Back EMF Sensing Uses mechanical commentator to reverse polarity of the armature electromagnet With sensor Sensor-less Not Required Little to no maintenance Superior thermal characteristic result in better heat dissipation Low electric noise generation Higher manufacturing cost due to complexity Suitable for controlled environment Periodic maintenance require, can replace brushes for extended life if necessary Winding's on rotors results in low hear dissipation Audible noise of brushes during rotation Low manufacturing cost Weight - Easily able to operate in extreme environment due to lack of electronics - Applications 2 & 3 Wheeler's 2 wheeler