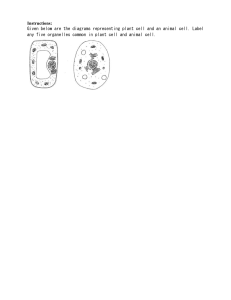
Biology Study Outline MSCCRS 2018 Name: ____________________________ This study outline is not designed to be an extensive study guide for the state test, only to bring the students attention to key topics in the curriculum. Use your notes and textbook to answer the questions. I. Cells as a System 1. List the characteristics of living things (you should have at least 6): a. b. c. d. e. f. 2. What is metabolism? What does it have to do with living things? 3. What does the Cell Theory say? 4. What are the contributions of the following scientists to developing the Cell Theory: a. Schwann b. Hooke c. Schleiden d. Virchow 5. List the levels of organization and give an example of each from the human body. 6. Is a virus living or nonliving? Support your answer. 7. Complete the chart about organic macromolecules Macromolecule Element and monomers Functions Examples Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids 8. Define the following terms as they relate to enzymes a. Enzyme b. Activation energy c. Specificity d. Denaturation e. pH or Temperature change 9. What is an organelle? 10. From the list of organelles, choose 5 that you are least familiar with and write their function: nucleus, cytoskeleton, smooth er, rough er, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, mitochondria, chloroplast, centrosomes, vacuoles. 11. What organelles are present in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes? 12. What organelles are only present in plant cells? What organelles are only present in animal cells? 13. What structure are present in a virus that are similar to those in a cell? 14. Why do viruses need a host cell to reproduce (hint: What organelles to they not have? What functions are required for life that they can’t do?) 15. What is the difference in active and passive transport? (Use the terms Concentration Gradient and ATP energy and draw a picture to support your answer). 16. What are examples of active transport? 17. What is osmosis? Describe what happens to a cell in a hypertonic, isotonic, and hypotonic solution. 18. When does DNA replication occur? Why must DNA be replicated? 19. Describe and Draw what happens during the following steps of mitosis. a. Prophase b. Metaphase c. Anaphase d. Telophase 20. What is cellular differentiation? How does it occur? Why does it occur? 21. Describe or draw the following forms of asexual reproduction: a. Budding b. Vegetative propagation c. Regeneration d. Binary fission 22. Why are offspring made through asexual reproduction genetically identical to the parent? II. Energy Transfer 23. Draw the ATP/ADP cycle with arrows showing when energy is stored and when energy is released. 24. What is the reaction for photosynthesis? 25. What are the two steps of photosynthesis? What happens to the energy during each step? 26. What step of photosynthesis makes glucose? 27. What is the reaction for aerobic cellular respiration? 28. What are the 3 steps of aerobic cellular respiration? What happens to the energy during each step? 29. What are the 2 steps of anaerobic cellular respiration? How many ATP are made? 30. What is made by plants and fungi during fermentation? __________________________ What is made by animals and bacteria during fermentation? ______________________ III. Reproduction and Heredity 31. What type of cells are made during meiosis? 32. Contrast the arrangement of chromosome during Metaphase of Mitosis and Metaphase I of Meiosis. Draw pictures as part of your explanation. 33. What process increases genetic variety during meiosis and when does it occur? What is the name for the pair of chromosomes involved in this process? 34. What is the difference between homologous chromosomes and sister chromatids? Draw a picture as part of your explanation. 35. What is nondisjunction? What are some disorders it can cause? What type of technology can be used to detect trisomies? 36. Describe Mendel’s Laws: a. Law of Dominance b. Law of Segregation c. Law of Independent Assortment 37. If a long haired (recessive), heterozygous grey rabbit is crossed with a heterozygous short haired, white rabbit… a. What are the genotypes of the parents? ___________ x ___________ b. Work punnett squares for both fur color and fur length: c. What is the chance their offspring will be white with long hair? (show your work!) 38. What phenotype does a heterozygous individual have in true dominance? ____________________ 39. What phenotype does a heterozygous individual have in incomplete dominance? _______________ 40. What phenotype does a heterozygous individual have in codominance? ______________________ 41. What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes for human blood type? (list them all) ● ● ● ● ● ● 42. What are the 2 rules for reading a pedigree? ● ● 43. Describe the relationship between DNA, gene, and chromosome. 44. How does DNA control traits? 45. Transcribe and translate the following segment of DNA: a. T A G A C C T T G C C A T A C C G A C A A C C A G T T T mRNA: A.A’s: 46. Tell the purpose of the following types of RNA. When applicable, do they contain codons or anticodons? a. Mrna b. Trna c. Rrna 47. What is a mutation? a. Substitution b. Insertion c. Deletion d. Which type is more severe? e. Which type causes a frameshift? f. Can there be a mutation that does not have an effect? _______ Explain. 48. What are transgenic organisms? What are some applications of making transgenic organisms? 49. What is a stem cell? Why do they have so much promise in research and disease treatment? 50. What is gel electrophoresis used for? IV. Adaptations and Evolution 51. What is chemical evolution? 52. Since there was no oxygen in early Earth’s atmosphere and the first organisms were simple, what mustthe first type of cell have been? 53. Describe the steps leading from that ^ first cell to the diversity of life. Use terms like aerobic, anaerobic, heterotrophic, autotrophic, organelles, eukaryote, and prokaryote. 54. Describe how natural selection or survival of the fittest leads to evolution. 55. What is the link between adaptation and evolution. 56. Where are the following found in a fossil record? (Top or Bottom) a. Oldest ________ b. Youngest ________ c. Most complex ________ d. Most simple ________ 57. Describe how to find the following in a phylogenetic tree: a. Common Ancestor b. Closely related species c. Species that evolved first d. Species that have a certain train in common e. Species that have the most DNA similarities f. Order of evolution 58. How do homologous structures and comparative embryology indicate a common ancestry? 59. In order for speciation to occur, what must happen? (Use terms isolation and selective pressure). 60. How do drug resistant antibiotic evolve? V. Interdependence of Organisms and Their Environments 61. Define the following: a. Individual b. Population c. Community d. Ecosystem 62. What do the arrows represent in food chains and webs? (Pay attention to which way the arrows go DRAW AN EXAMPLE) 63. What is the importance of decomposers in an ecosystem? What are some examples? 64. What is the role of bacteria in the nitrogen cycle? 65. What processes release carbon into the atmosphere? 66. What is transpiration? 67. What is combustion? 68. What effect does carbon dioxide have on temperature? Why? 69. What happens to the amount of energy and biomass at each trophic level? Why? 70. Define using + and – or 0 a. Mutualism b. Commensalism c. Parasitism d. Competition 71. What is mimicry? Why do organisms mimic each other? 72. What is carrying capacity? Draw a graph to illustrate. 73. What is a limiting factor? List examples of density dependent and density independent limiting factors. 74. What is the difference between primary and secondary succession? When might each occur? 75. What is a pioneer species?2 76. What are some ways humans are negatively impacting the environment as the population grows? What are some ways we can correct or prevent that damage? 77. What is biomimicry? Mark Mitosis (MI), Meiosis(ME) or Both(BO) for the items in the chart: Somatic Cells DNA Copies Once Gametes _____ & _____ Haploid Diploid Homologues Identical 1 Division Variety Sexual Reproduction Growth Centromere Independent(IN) or Dependent(DE) Variable: _____ Treatment_____ Results_____ Manipulated variable_____ What you do _____ Responding variable_____ Cause_____ Effect_____ What you watch Why is it important to only change one variable at a time in an experiment? Define: 1. Optimal 2. Refute 3. Represent 4. Constant 5. Clarify 6. Refine 7. Evaluate 8. Support 9. Verify 10. Construct n 2 divisions 2n Tetrad Sister Chromatids Crossing Over