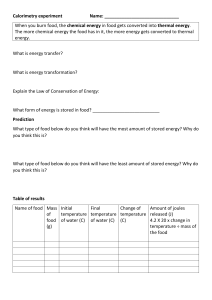
WHAT IS ENERGY Adam is a boy who has lots of energy Ishak is a boy who has less energy ENERGY IS THE ABILITY TO DO WORK Who do you think needs more energy? A few questions to think about …….. • Why do we feel weak when we do not eat food? • Does everything around us need energy to work? • How does the appliances and vehicles get their energy? • Where does the wind, sun, waves, earth, etc get their energy from? • Is there a need to measure energy? • What is overeating? Why is it harmful for humans? • Is energy stored or transferred? • Can energy be conserved? About energy • Energy is the ability to do work. • We measure energy in kilojoules (KJ). • One kilojoule (KJ) = 1000 joules. • Energy content of a food is measured in calories, 1 calorie = 4 joules • The energy requirement depends on the work that needs to be done. • Fuel is the substance that provides energy. • Coal, petrol, wood, LPG are all fuels that are used for energy. What is an ideal fuel? • • • • • • • • • • • More energy—Maximum energy, more work done Cost effective Combustible. Sustainable Ecofriendly Renewable Easily available Convertible Long lasting Organic Safe to store and use Types of energy • Energy due to position or shape– Potential energy • Energy that is due to movementKinetic energy. • Energy that is stored in food/fuel Chemical energy • Energy stored in objects that are stretched- elastic energy • Energy stored in the nucleus—Nuclear energy. • Energy in objects when it is above ground—Gravitational. • • • • Movement of electricity-Electrical Movement of particles – Heat energy Movement of objects –Mechanical Movement that causes push and pull of magnets—Magnetic energy • Movement of sound waves – Sound energy • Movement of electromagnetic radiationlight energy Types of energy Some common energy changes we come across • Energy from the food we eat. • Energy from the sun • Plants performing photosynthesis to convert light to chemical energy • Energy from the fuels like wood, petrol, coal, kerosene, biofuel • Energy from wind. • Energy from flowing water • Energy from tides What are fossil fuels? Trees, plants and other organic matter were buried under the ground millions of years ago due to earthquakes. These matter under a lot of heat and pressure got converted to coal. Various aquatic animals and sea creatures got buried under the ocean bed millions of years ago. These matter under a lot of heat and pressure converted to petroleum and gas. Together, coal, petroleum and natural gas are called fossil fuels. Wind energy, solar and hydroelectric power • The wind turns the blades of giant wind mills. This is used by the turbines to generate electricity. • Water stored in dams are allowed to fall on the blades of giant turbines which turns them. This energy is used to generate electricity and is called hydroelectric power. • The heat energy from the sun is converted to chemical energy in solar cells and is used later as electric power. • Water runs through the solar panels and is heated up using sun’s heat. NUCLEAR FISSION and NUCLEAR FUSION • When an atom is split into two it releases a lot of energy. This is called as nuclear fission. • When two atoms combines together it releases a lot of energy. This is called as nuclear fusion. Laws of energy and Energy transfer diagram • Energy can neither be created nor be destroyed. • Energy can be transferred from one form to another. • IF energy is converted from one form to another it is energy transformation. In a radio, the chemical energy is converted to sound energy • The changes energy undergoes when it is converted from one form to another is energy transfer. In a radio, the chemical energy is converted to electrical energy which flows through the circuit, ultimately converting to sound energy. • The transfer of energy can be represented by a energy transfer diagram Useful energy and wasted energy • Not all energy is converted to useful energy. Some of them are converted into forms of energy that are not useful in the context. • For example, when electricity is used to light a bulb, some of the electrical energy is converted to heat energy. • How little the energy is converted to forms that are not useful to us determines the efficiency of the object. • For example CFL is more efficient than the traditional light bulbs. SANKEY DIAGRAM • We draw a Sankey diagram to represent how the energy has been utilized, how much it is converted to useful energy and how much into wasted energy. • The thickness of the arrow shows the amount of energy transferred. • The useful energy is shown in an arrow that points to the right. • The wasted energy is represented by an arrow that points downwards. CALCULATING ENERGY EFFICIENCY To calculate the efficiency of the engine or the machine we use the following formula. Eg: If a light bulb uses 80 joules of energy, out of which 20 joules are converted into light, the efficiency of the bulb is 20 80 x 100 = 25% Relationship between Mass, Velocity and Energy • If two objects are moving with the same velocity, the heavier object will have greater energy. Eg: IF a Car and an Bus are moving at the same speed/velocity, the bus will have greater energy because it is heavier and needs to spend more energy to pull itself. • If two objects have the same mass, then the object that has greater energy will move faster. Let us discuss a few case scenarios 1. A stone is thrown up into the air, stops after a few seconds and then falls back. 2. A feather is dropped down from the top of a building. 3. A lift goes up from the ground floor till the top of the building. 4. You are in a roller coaster and reach the top of the ride. 5. You are shooting an catapult. You place a stone on the band and pull it. Take aim and release the elastic band. What happens in each of the cases? Is the energy converted from one form to another? What are the energy types involved in this?