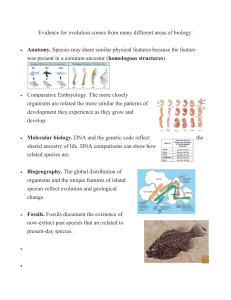
Evidence of Evolution Activity Name: ________________________ GOAL: To work through various lines of evidence of evolution. You will use various models in order to answer a series of questions about those models. Station 1 1 Use this image for the FOSSIL layers questions Station 1 Questions: • What is Pangaea? a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras • How is Pangaea different from present day? • What do you notice about where each of the fossils were found in the map below? Pangaea broke into two new continents Laurasia and Gondwanaland. Laurasia was made of the present day continents of North America (Greenland), Europe, and Asia. Gondwanaland was made of the present day continents of Antarctica, Australia, South America. provides evidence of Earth's past landscapes • How would the study of where fossils were found help give evidence for evolution? scientists can learn how much (or how little) organisms have changed as life developed on Earth • Which layers are oldest and have the oldest fossils? Which layers have more recent fossils? I and B are the oldest • R m and H and the newest How could observing the different fossils in the stratum layers help give evidence for evolution? they show that life on earth was once different from life found on earth today. • SUMMARIZE What is the type of evidence that is presented at this station? Fossil Records and Biogeography Station 2 (page 1 of 2 of station 2 information) STATION 2 (page 1 of 2 questions) • Describe how the limbs of the organisms are similar and how they are different? The structures given in the picture above are homologous to each other. • Explain why they are so similar in structure and yet can be used differently by the organism? How did this happen? Homologous structures are structures that are similar in related organisms because they were inherited from a common ancestor. • What does this help explain about how related or not these species are to each other? Biological diversity is being lost as species go extinct, and it is only by understanding species that we can shape the social, political, and financial forces that affect conservation efforts. STATION 2 (page 2 of 2 of station information) The vermiform appendix had digestive functions in the ancestral human species, probably helping the cellulose in grass breakdown in the intestine, as they were herbivours. The Appendix has become vestigial in human beings because they have become very small in size and don’t contribute in cellulose fermentation. However, several appendix problems occur in people and the removal of this part in the body will do no harm and is relatively common. • STATION 2 (page 2 of 2 questions) Which type of structures (homologous, analogous, vestigial) are shared between related organisms? Which are not? homologous structures • Explain how these structures are evidence of evolution? These are structures shared by related organisms that were inherited from a common ancestor • What is a vestigial structure? • Explain how a vestigial organ is evidence of evolution? Vestigial structures are various cells, tissues, and organs in a body which no longer serve a function. they suggest that an organism changed from using the structure to not using the structure, or using it for a different purpose • SUMMARIZE What is the type of evidence that is presented at this station? Comparing anatomical structures Station 3 STATION 3 QUESTIONS • What trends do you notice about all organisms at each stage of development? they look similar to not looking similar • Which ones do you think are more closely related? • What do you notice about trends in development between organisms that are closely related to each other versus organisms that are less closely related? They have similar structures 2 IMAGE ABOVE: TOP ROW is the YOUNGEST form of the embryo, BOTTOM ROW is the OLDEST form of the embryo. Follow each creature (8 shown) from top to bottom. • SUMMARIZE What is the type of evidence that is presented at this station? embryology Station 4 STATION 4 QUESTIONS: • Compare the small sequence of amino acids for the same protein in 5 different animals. What do you notice? They are pretty similar • Look at the segment of DNA for chimps and humans that give instructions for making the amino acid chain above. What do you notice? There's only three differences • (Think Ahead: What are changes in DNA called?) mutation • How many differences in amino acids do you see between a human and a chimpanzee? How does that compare to different organisms? 0. all the other organisms have at least one • What can be concluded about these differences versus how closely related organisms are? They have different functions • What evidence exists that humans and great apes shared a common ancestor? fossils, proteins and genetic studies • SUMMARIZE What is the type of evidence that is presented at this station? DNA comparison Station 5 STATION 5 QUESTIONS • Define descent with modification (find the definition on the internet if you do not already know it). the passing on of traits from parent organisms to their offspring • Hyracotherium lived in a dense forest area dominated by a rich undergrowth of ferns. Discuss why the small body size might be an advantage in this type of environment. They were smaller so they could move easier • A change in vegetation from dense forest to grasslands occurred due to climate changes and this selected for changes in the shape of the horse’s leg and body size. Explain how these changes in vegetation could lead to the evolution of the horse. A change in vegetation from dense forest to grasslands occurred due to climate changes and this selected for changes in the shape of the horse's leg • The teeth of the browsers*see info at top of page (such as Mesohippus) were covered with a thick layer of enamel (hard outer-coating of teeth). The teeth of the modern-day horses, by comparison, have less enamel and appear to be much wider and flatter. Explain these changes seen in horse teeth over time. The teeth of the browsers, such as Mesohippus, were covered with a thick layer of enamel • All of these variations have come about in the last 4,000 to 6,000 years as humans domesticated horses for work, travel, and show. Explain how all of these variations can happen in such a relatively short period of time when previous changes took millions of years? Horse behaviour appears little changed by domestication, as evidenced by the reproductive success of feral horse populations around the world • SUMMARIZE What is the type of evidence that is presented at this station? Variation and adaptation Station 6 (page 1 of 2) You have to NOW read the information on the next page and USE both to answer the Questions for station 6 are on the second page of station 6 STATION 6 (page 2 of 2) STATION 6 QUESTIONS (need to use BOTH pages of station 6 images to answer) • Science is a communal effort. Which scientists laid the foundation for Darwin’s theory of natural selection? What ideas did they contribute that were crucial for Darwin to build on? Darwin's ideas about evolution and Mendel's research in genetics are combined into what we now call the idea of blending inheritance • What do we know now about DNA and genetics that further disproves LaMarck’s theory? The other way that Lamarck's theory has been proven wrong is the study of genetics. Darwin knew that traits are passed on • Are human subject to natural selection? Does our human population have all 4 required factors? Natural selection is still influencing the evolution of a wide variety of human traits, from when people start having children to their body mass index • SUMMARIZE What is the type of evidence that is presented at this station Scientific Theory