Isotopes: Definition, Atomic Structure, and Mass Calculation
advertisement

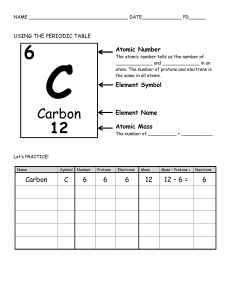
THE NATURE OF MATTER Chapter # 02 Topic :ISOTOPES Objective Define nucleon number Define and state isotope of same atoms with different nucleon number ATOMIC STRUCTURE Nucleus Electron Orbit Energy Levels ATOMIC STRUCTURE Atomic number the number of protons in an atom Atomic mass the number of protons and neutrons in an atom 2 4 He number of electrons = number of protons Interpreting Chemical Symbol Mass=P+N mass number (nucleon number) mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom. Number of neutrons in the oxygen atom is: 16 – 8 = 8. proton number (atomic number) P=E No. of protons= no. of electrons 16 O chemical symbol 8 atomic number (proton number) is the number of protons in an atom. Each oxygen atom has 8 protons. As the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons in an atom, each oxygen atom contains 8 electrons. 4 Definition of Isotopes Isotopes are atoms of the same element which contains the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. Isotopes mass number proton number 16 17 18 8 8 8 O O O Oxygen-16 n = 8 Oxygen-17 n = 17 – 8 = 9 Oxygen-18 n = 18 – 8 = 10 Isotopes Isotopes have the same chemical properties but slightly different physical properties Q. Do all isotopes of the same same mass? element have the Isotopes of Some Elements and Their Atomic Mass The atomic mass of an element • is listed below the symbol of each element on the periodic table. • Gives the mass of an “average” atom of each element compared to 12C. 10 The calculation for atomic mass requires the • percent(%) abundance of each isotope. • atomic mass of each isotope of that element. • sum of the weighted averages. mass of isotope(1)x (%) + mass of isotope(2) x (%) =Ar 100 100 Ar=(Average atomic mass) 11 24Mg = 23.99 amu x 78.70/100 = 18.88 amu 25Mg = 24.99 amu x 10.13/100 = 2.531 amu 26Mg = 25.98 amu x 11.17/100 = 2.902 amu Atomic mass (average mass) Mg = 24.31 amu 12