MONOSACCHARIDEPOLYSACCHARIDESTRUCTURES2TeacherandStudentCopy
advertisement

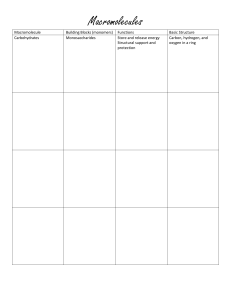
MONOSACCHARIDES, DISACCHARIDE, & POLYSACCHARIDES Monomers to Polymers – Putting it all together! Name:_______________________________________ Period:__________ Date:_______________________ Directions: Based on the structures provided, provide answers to each of the questions. SC.9.12.L.18.1: Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of biological macromolecules. MONOSACCHARIDE 1. What is the example of the monosaccharide, to the left? ___________________ 2. “Mono-” means__________________ 3. How many sugar molecules are in a monosaccharide?_____________________ 4. Is this structure a monomer? _____ Explain______________________________ _____________________________ DISACCHARIDE 1. What is the example of the disaccharide, on the left? ______________________ 2. “Di-” means__________________ 3. How many monosaccharides are in sucrose? ___________ 4. What are the monosaccharides in sucrose? _____________________ & _____________________ POLYSACCHARIDE 1. What is the example of the polysaccharide, on the left? _____________________________ 2. “Poly-” means_____________________ 3. How many monosaccharides are shown in the starch polysaccharide? _______ 4. What is the monosaccharide in the polysaccharide, starch? __________________ 5. Is the structure, to the left, a polymer? ______ Explain ________________________________ ______________________________________ Putting it all together: _________ 1. What is the relationship between monomers and polymers? ____________________________________________________ Provide an example from the material studied. ______________________________________________________________ 2. How do monomers relate to monosaccharides and polymers to polysaccharides? ___________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Monosaccharides, disaccharides & polysaccharides represent which group of macromolecules? _______________________ 4. What is the primary function of carbohydrates? ______________________________________________________________ © Plants! Emerge 2018 MONOSACCHARIDES, DISACCHARIDE, & POLYSACCHARIDES KEY Monomers to Polymers – Putting it all together! Name:_______________________________________ Period:__________ Date:_______________________ Directions: Based on the structures provided, provide answers to each of the questions. SC.9.12.L.18.1: Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of biological macromolecules. MONOSACCHARIDE 1. What is the example of the monosaccharide, to the left? GLUCOSE 2. “Mono-” means ONE OR SINGLE 3. How many sugar molecules are in a monosaccharide? ONE 4. Is this structure a monomer? YES Explain GLUCOSE IS ONLY ONE SIGNLE UNIT OR A ONE COMPOUND DISACCHARIDE 1. What is the example of the disaccharide, on the left? SUCROSE 2. “Di-” means TWO 3. How many monosaccharides are in sucrose? 2 4. What are the monosaccharides in sucrose? GLUCOSE & FRUCTOSE 1. What is the example of the polysaccharide, on POLYSACCHARIDE the left? STARCH 2. “Poly-” means MANY 3. How many monosaccharides are shown in the starch polysaccharide? 5 4. What is the monosaccharide in the polysaccharide, starch? GLUCOSE 5. Is the structure, to the left, a polymer? YES Explain POLYMERS ARE MADE OF MANY MONOMERS, AS IS STARCH Putting it all together: 1. What is the relationship between monomers and polymers? MONOMERS MAKE UP POLYMERS. Provide an example from the material studied. MANY GLUCOSE MONOMERS MAKE UP A POLYMER OF STARCH. 2. How do monomers relate to monosaccharides and polymers to polysaccharides? MONOMERS AND POLYMERS ARE GENERAL TERMS. MONOSACCHARIDES AND POLYSACCHARIDES ARE SPECIFIC MONOMERS AND POLYMERS, RESPECTIVELY, TO CARBOHYDRATES. MONOMER: MONOSACCHARIDE; POLYMER: POLYSACCHARIDE. 3. Monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides represent which group of macromolecules? CARBOHYDRATES 4. What is the primary function of carbohydrates? TO PROVIDE SHORT-TERM ENERGY STORAGE © Plants! Emerge 2018