Hypertension Medications Guide: ACE Inhibitors, Beta Blockers & More
advertisement

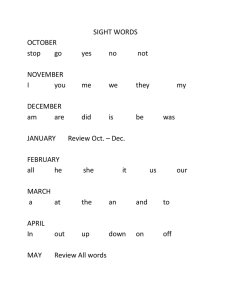
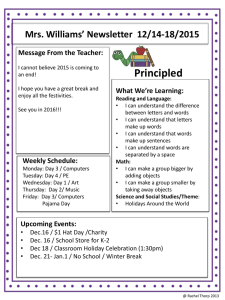
Medications for the treatment of hypertension Classification Examples Action (How does it lower BP?) Nursing Considerations Side Effects Low BP Dry, hacking Angiotensinconverting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor Captopril Enalapril Lisinopril Blocks the enzyme that ASA/NSAIDs reduce effect, diuretics cough, angioedema, converts A1 to A2 (powerful vasoconstrictor in endothelial potentiate effect, Don’t use with K+ sparing high K level DM or renal lining) meds, blocks breakdown of bradykinin dysfxn, NSAIDs, K supp, K+ sparing meds Alpha 1adrenergic blocker Prazosin Terazosin Doxazosin Produces peripheral vasodilation (so dec SVR & BP) Give at bedtime Syncope 30-90 min after 1st dose, in BPH, increases urine outflow Clinical Parameter: Hold Alpha & Beta adrenergic blocker Angiotensin II receptor (ARB) blocker Labetalol Carvedilol Losartan Valsartan Produces peripheral vasodilation, dec HR So dec CO, SVR, and BP Stops A2 action Produces vasodilation Inc sodium & water excretion if SBP < 90 mmHg or AP < 60 bpm, Don’t stop meds abruptly-chest pain, HF Onset few weeks to 1.5 months, can use if cough with ACE, with CKD, don’t use ACE Dizziness, muscle cramps/wkns, heartburn, orthostatic hypotension Dizziness, sexual dysfunction, lower limb edema, dry mouth and eyes, fatigue, same as blockers Low BP, dehydration with ARBs Betaadrenergic blocker Atenolol Metoprolol Propanolol Decreases renin excretion by kidneys: Dec HR Dec BP Dec force contr. So dec card wrkld & CO Clinical Parameter: Hold if SBP < 90 mmHg or AP < 60 bpm, may block early signs of hypoglycemia (tremors, palpitations, tachycardia)-caution in DM Low BP & HR, bronchospasm in COPD, dizziness, fatigue, HA. weakness, cold hands/feet, swelling hands/feet Medications for the treatment of hypertension Diltiazem & verapamil- Calciumchannel blocker Diltiazem Verapamil Amlodipine Nifedipine Blocks Ca across cell membrane causing vasodilation, dec HR, slows AV electrical conduction Amlodipine & Nifedipinecause vascular smooth muscle relaxation, so dec SVR & BP Clinical Parameter: Hold if SBP < 90 mmHg or AP < 60 bpm, Grapefruit juice may inc toxicity in some meds Amlodipine- stronger peripheral vasodilator HA, dizziness, fatigue, lightheadednes s, palpitations, flushing, edema lower limbs, GERD, inc appetite Clinical Parameter: Hold if SBP < 90 mmHg or Centrallyacting sympatholytic Clonidine methyldopa Blocks sympathetic activity within the brain, causes vasodilation, dec SVR & BP AP < 60 bpm, give at bedtime to reduce Orthostatic daytime sedation, don’t stop meds abruptly- hypotension, dry mucus rebound HTN, tachycardia, HA, membranes, bradycardia, tremors, anxiety, sweating, impotence ETOH/sedatives inc sedation Thiazide diuretic Loop diuretic K+ sparing diuretic Hydrochlorothiazide Chlorothiazide Potentiates Digoxin b/c Orthostatic hypotension, Blocks reuptake of sodium chloride in the distal tubules, potassium excreted, K level ____, low K, dizziness, so inc excretion of Na, Cl, & K, dec ECF, dec SVR Consider low Na diet to reduce depleting K, inc lightheadednes s, blurred potassium in diet vision, HA, weakness Furosemide Torsemide Bumetanide Blocks reuptake of sodium chloride in the loop of Henle, so inc excretion of Na, Cl, & K Stronger than thiazides, shorter duration of action, K level ____ Orthostatic hypotension, low K, low Na, & other electrolytes, HA, dizziness, thirst, muscle cramps Amiloride Triamterene Lowers Na & K exchange in distal and collecting tubules, lessens excretion of K, H, Ca, & Mg K level ____, Don’t use in RF, Caution with ACE and ARB pts, Avoid K foods/supplements Orthostatic hypotension, high K, dry mouth, HA, Medications for the treatment of hypertension dizziness, muscles cramps, weakness Aldosterone Receptor Blocker (also K+ sparing) Spironolactone Blocks aldosterone from retaining Na and excreting K in distal and collecting tubules Don’t mx with other K+ sparing meds or supplements, Caution with ACE and ARB pts Orthostatic hypotension, high K, sexual dysfunction, dizziness, HA Hydralazine & SodiumHydralazine Vasodilator (IV meds) SodiumNitroprusside Nitroglycerin Nitroprusside-lowers SVR & BP with direct arterial vasodilation Nitro-relaxes arterial/venous smooth muscle, reducing preload & SVR, low dose venous dilation, high dosearterial dilation Generally for treating hypertensive crisis, Obtain BP & HR, but no parameters HA, dizziness, bradycardia, syncope, orthostatic hypotension General principles of administration of anti-hypertensives 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Many side effects diminish with time. Side effects are a major reason for noncompliance. Fatigue is a common complaint with initiation of therapy. Many medications cause sexual problems—erectile dysfunction, decreased libido. Encourage patient to discuss with physician; a different medication may work as well. Teach to monitor blood pressure. Patients don’t need to be obsessed with monitoring. Daily monitoring may be a good idea as therapy is initiated, then it can usually be reduced. Some physician’s want twice daily records before changing the medication. However, a single reading is not as important as a series of readings over time. Rest quietly in a comfortable chair 5-10 minutes before taking blood pressure. HTN is asymptomatic; do not stop taking medication abruptly; or without consulting physician; abrupt discontinuation may cause severe rebound hypertension. Involves lifestyle changes: weight management, sodium reduction, smoking cessation and exercise. Therapy controls HTN; it will not cure it. Patient should plan regular and convenient times to take med and BP. If med affects potassium, patient should know foods high in potassium; this includes salt substitutes. Do not take extra doses if blood pressure is high; consult physician. Avoid hot baths, excessive alcohol and strenuous exercise within 3 hours of taking vasodilators. Give instructions for managing orthostatic hypotension, if indicated. High risk over-the-counter meds: high sodium antacids, appetite suppressants, cold and sinus medications. Patients should read warning labels. Medications for the treatment of hypertension 13. 14. The main reasons for non compliance are unpleasant side effects, high cost of meds, return of BP to normal, lack of motivation, lack of insurance, and lack of trusting relationship with health care provider. Combination tablets and long acting tablets may help with compliance by reducing the number of medications that have to be taken.